Beyond the common additives, a diverse range of specialized fillers are used to enhance Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). These include minerals like calcium fluoride (CaF2) and alumina (Al2O3), high-performance polymers such as Ekonol and Ryton, and other materials like wollastonite and molybdenum disulphide, each chosen to impart specific mechanical, thermal, or electrical properties.
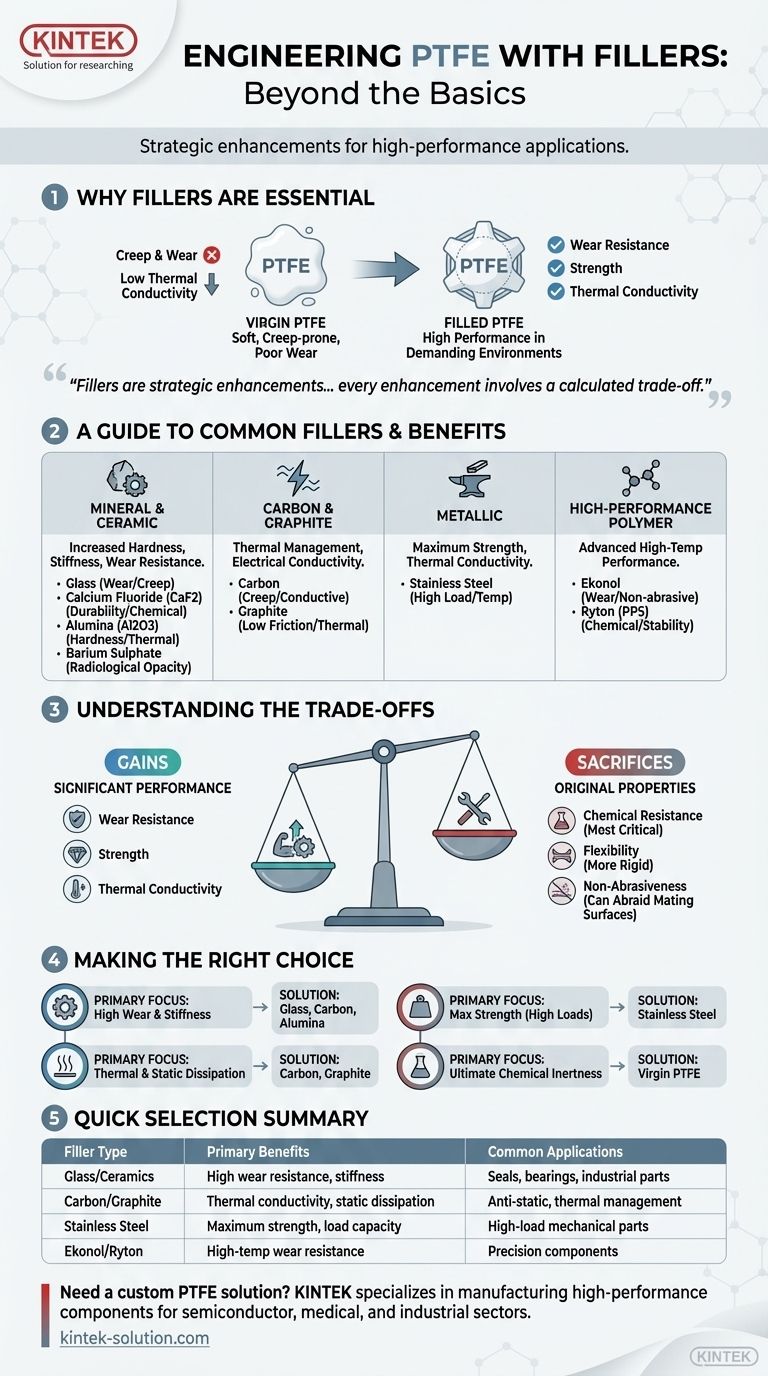
Fillers are not simply additives; they are strategic enhancements that transform PTFE from a soft, general-purpose material into a high-performance polymer engineered for specific, demanding applications. The key is to understand that every enhancement involves a calculated trade-off.

Why Fillers are Essential for PTFE
Virgin PTFE, also known as Teflon, is prized for its extreme chemical inertness and low friction. However, it has significant mechanical limitations that fillers are designed to overcome.
Overcoming PTFE's Natural Weaknesses
Pure, unfilled PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is susceptible to creep, which is the tendency to deform permanently under a sustained load. It also has poor wear resistance and low thermal conductivity.
The Strategic Role of Enhancements
Fillers are microscopic particles mixed into the PTFE resin before it is processed. This composite structure dramatically improves key properties, such as wear resistance, strength, and thermal conductivity, making it suitable for challenging industrial environments.
A Guide to Common PTFE Fillers
Different fillers are selected to achieve specific performance goals. They can be broadly categorized by their material type and the primary benefits they provide.
Mineral and Ceramic Fillers
These fillers are primarily used to increase hardness, stiffness, and wear resistance.
- Glass: A common choice that significantly improves wear and creep resistance. It is often used in the form of microspheres or fibers.
- Calcium Fluoride (CaF2): Enhances durability and wear resistance, particularly in chemically aggressive environments.
- Alumina (Al2O3): A very hard ceramic that provides excellent wear resistance and improves thermal conductivity.
- Barium Sulphate: Increases hardness and density, often used in applications requiring radiological opacity.
Carbon and Graphite Fillers
These are excellent for thermal management and applications requiring electrical conductivity.
- Carbon: Improves creep resistance, hardness, and thermal conductivity. It can also make the PTFE electrically conductive, which is useful for anti-static applications.
- Graphite: A popular additive that lowers the coefficient of friction, enhances wear resistance, and improves thermal conductivity. It is often combined with carbon.
Metallic Fillers
Metal powders are used when maximum strength and thermal conductivity are required.
- Stainless Steel: Dramatically increases the strength, hardness, and wear resistance of PTFE. It is ideal for high-load, high-temperature service.
High-Performance Polymer Fillers
These advanced fillers are used for the most demanding applications.
- Ekonol: An aromatic polyester that improves wear resistance and performance at high temperatures without being abrasive to mating surfaces.
- Ryton (PPS): Provides excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability at elevated temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Adding fillers is an engineering compromise. While you gain significant performance in one area, you often sacrifice some of PTFE's unique original properties.
The Compromise on Chemical Resistance
This is the most critical trade-off. Virgin PTFE is nearly impervious to all chemicals. Most fillers reduce this exceptional chemical resistance, as the filler material itself may be susceptible to attack.
Impact on Flexibility
The addition of rigid filler particles inherently makes the PTFE composite harder and less flexible than its unfilled counterpart.
Abrasiveness to Mating Surfaces
Hard fillers, especially glass and other ceramics, can be abrasive to softer metal surfaces they come into contact with, such as aluminum or brass shafts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct filled PTFE compound requires aligning the material's properties with the primary demand of your application.
- If your primary focus is high wear resistance and stiffness: Choose a compound filled with glass, carbon, or alumina.
- If your primary focus is thermal conductivity and static dissipation: A carbon or graphite-filled PTFE is the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength under high loads: Stainless steel-filled PTFE offers superior mechanical durability.
- If your primary focus is ultimate chemical inertness and purity: Unfilled, virgin PTFE remains the only suitable option.
By understanding the distinct role of each filler, you can select an engineered material precisely suited to solve your specific challenge.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Primary Benefits | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Glass / Ceramics | High wear resistance, stiffness | Seals, bearings, industrial parts |
| Carbon / Graphite | Thermal conductivity, static dissipation | Anti-static components, thermal management |
| Stainless Steel | Maximum strength, load capacity | High-load mechanical parts |
| High-Performance Polymers (e.g., Ekonol) | Wear resistance at high temperatures | Precision components, non-abrasive surfaces |
Need a custom PTFE solution for your specific application? At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our precision production and custom fabrication expertise ensure your material meets exact performance demands. Contact us today to discuss how our engineered PTFE can solve your unique challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability



















