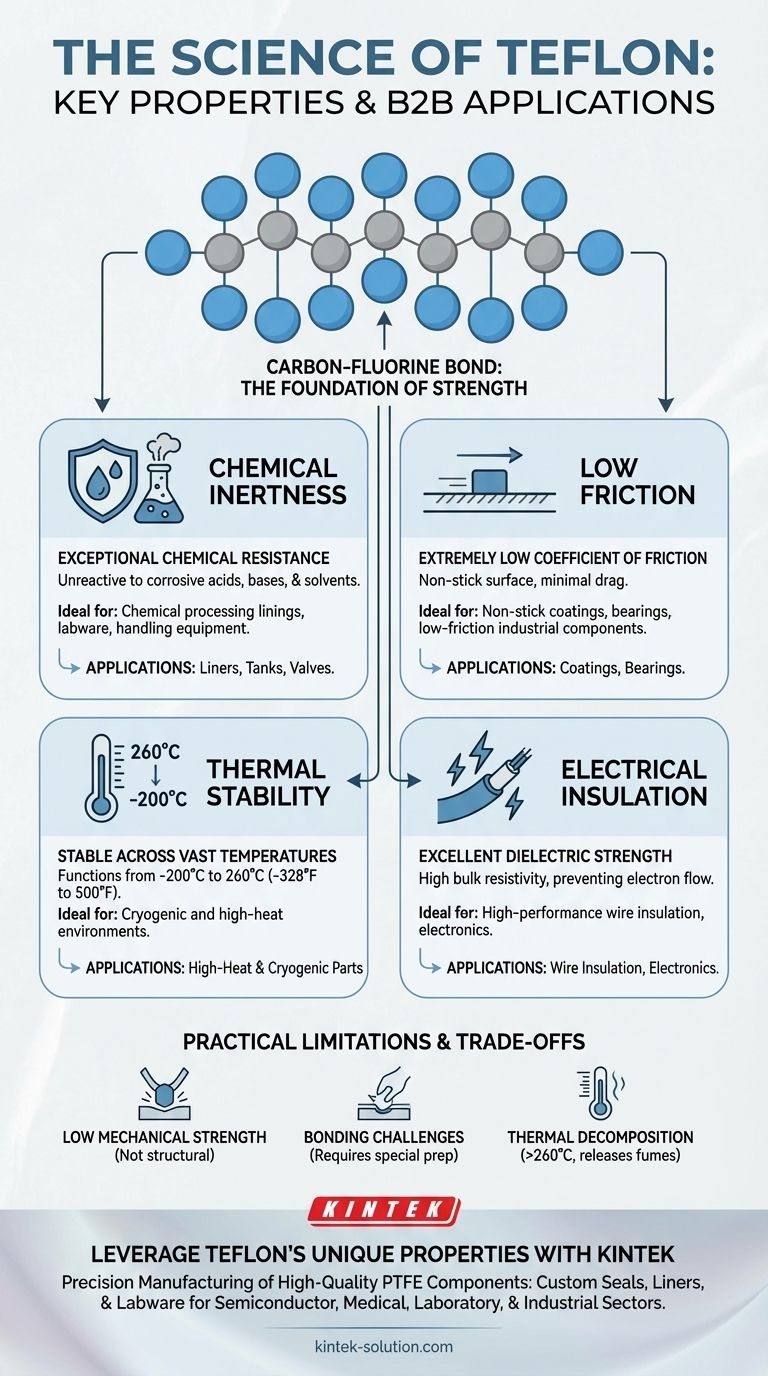
At its core, Teflon's wide utility comes from a powerful combination of four key properties. It is exceptionally non-reactive (chemically inert), has an extremely low coefficient of friction (making it non-stick), remains stable across a wide range of temperatures, and is an excellent electrical insulator. These traits all originate from the unique and incredibly strong chemical bond between its carbon and fluorine atoms.
The central takeaway is that nearly all of Teflon's remarkable and diverse properties can be traced back to a single source: the immense strength and stability of the carbon-fluorine bond, which creates a uniquely non-reactive and "slippery" molecular surface.

The Foundation: Understanding the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), the chemical name for Teflon, is a polymer—a long chain of repeating molecules. In this case, the chain is a backbone of carbon atoms, each completely surrounded and shielded by fluorine atoms.
An Exceptionally Strong Bond
The bond between carbon and fluorine is one of the strongest known single bonds in organic chemistry. This immense strength is the primary reason for Teflon's stability and durability.
A Protective Fluorine Shield
The fluorine atoms are larger than the carbon atoms they are bonded to. They effectively form a tight, continuous sheath around the carbon backbone, protecting it from almost any external chemical interaction.
Teflon's Defining Properties Explained
This unique molecular structure gives rise to the material's most famous characteristics. Each property makes Teflon the ideal choice for a specific set of demanding applications.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
Because the carbon backbone is so well-protected by the stable fluorine sheath, very few chemicals can react with it. Teflon is resistant to nearly all corrosive acids, bases, and solvents.
This property makes it indispensable for lining pipes, tanks, and vessels that handle highly corrosive materials in chemical processing and laboratory settings.
Exceptionally Low Friction
The fluorine sheath creates a very smooth, low-energy surface at the molecular level. Other substances have little to nothing to "grab onto," resulting in an extremely low coefficient of friction.
This is the principle behind non-stick cookware. It also makes Teflon a superior material for low-friction coatings, bearings, and other industrial applications where smooth movement is critical.
High Thermal Stability
The strength of the carbon-fluorine bond means it takes a great deal of energy to break the molecule apart. Consequently, Teflon remains stable across a vast temperature range.
It can function effectively in conditions from -200°C (-328°F) up to 260°C (500°F), making it suitable for both cryogenic and high-heat applications.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
The same strong bonds that hold the molecule together also hold its electrons very tightly. This prevents electrons from moving freely, making Teflon an outstanding electrical insulator, or dielectric.
Its high dielectric strength and bulk resistivity are why it's commonly used for insulating high-performance wires and cables, particularly in aerospace and computing.
Understanding the Practical Limitations
No material is perfect, and understanding Teflon's trade-offs is crucial for its proper application. Its greatest strengths are also the source of its weaknesses.
Relatively Low Mechanical Strength
While durable, Teflon is a relatively soft and flexible material. Compared to metals or other engineering plastics, it has low tensile strength and can be susceptible to "creep"—deforming slowly under a sustained load. It is not suitable for structural applications.
Bonding and Machining Challenges
The very non-stick properties that make Teflon so useful also make it notoriously difficult to glue or bond to other materials. Special surface preparation techniques are required to achieve adhesion.
Thermal Decomposition Concerns
While highly heat-resistant, if heated well above its service temperature of 260°C (500°F), Teflon will begin to decompose. This process can release fumes that are toxic, which is a critical safety consideration in high-temperature designs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting Teflon is about matching its unique profile to the problem at hand.
- If your primary focus is creating a non-stick or low-friction surface: Teflon's anti-adhesion and uniquely low coefficient of friction are its most valuable assets.
- If your primary focus is handling corrosive materials: Its extreme chemical inertness makes it one of the most reliable choices for lining pipes, valves, and containers.
- If your primary focus is insulating electrical components: Its high dielectric strength provides superior performance for high-frequency cables and critical electronics.
- If your primary focus is operating in extreme temperatures: Its wide and stable working temperature range makes it a dependable choice for both high-heat and cryogenic environments.
Ultimately, Teflon's versatility is a direct result of its simple yet profoundly stable molecular architecture.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosive acids, bases, and solvents. | Lining for pipes, tanks, and labware. |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Creates non-stick, low-friction surfaces. | Non-stick coatings, bearings. |
| High Thermal Stability | Stable from -200°C to 260°C. | Cryogenic and high-heat environments. |
| Excellent Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength and bulk resistivity. | Insulating wires and cables for electronics. |
Leverage Teflon's unique properties for your specialized application. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-quality PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures a solution that meets your exact requirements for performance and durability. Contact our team today to discuss your project and discover the KINTEK difference.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What makes PTFE plastic uniquely versatile across industries? The 4 Key Properties Explained
- What makes PTFE suitable for chemical and pharmaceutical industries? Ensuring Purity and Performance in Critical Applications
- What makes PTFE a valuable material in industrial applications? Its Unique Properties Solve Critical Challenges
- What is Teflon and what are its key properties? A Guide to its Extreme Chemical and Temperature Resistance
- How does PTFE's coefficient of friction compare to other plastics? Unmatched Low-Friction Performance
- What are the cost differences between Nylon and PTFE? A Guide to Smart Material Selection
- What are the key characteristics of PTFE material? Unlock Its Performance in Extreme Environments
- What is PTFE and what is it commonly known as? The Ultimate Guide to Teflon & Its Uses



















