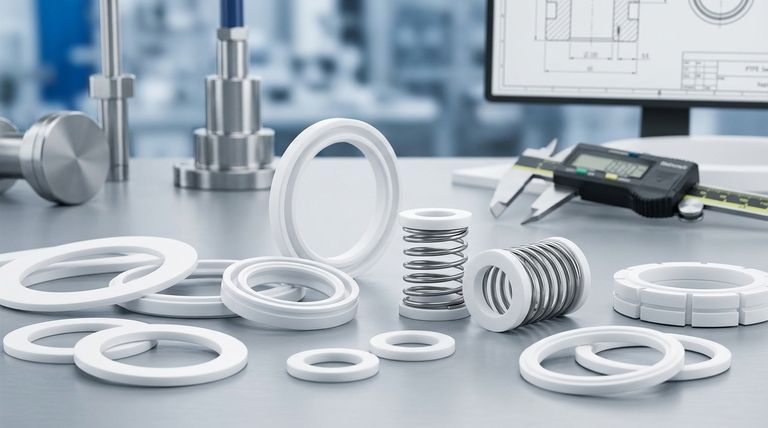
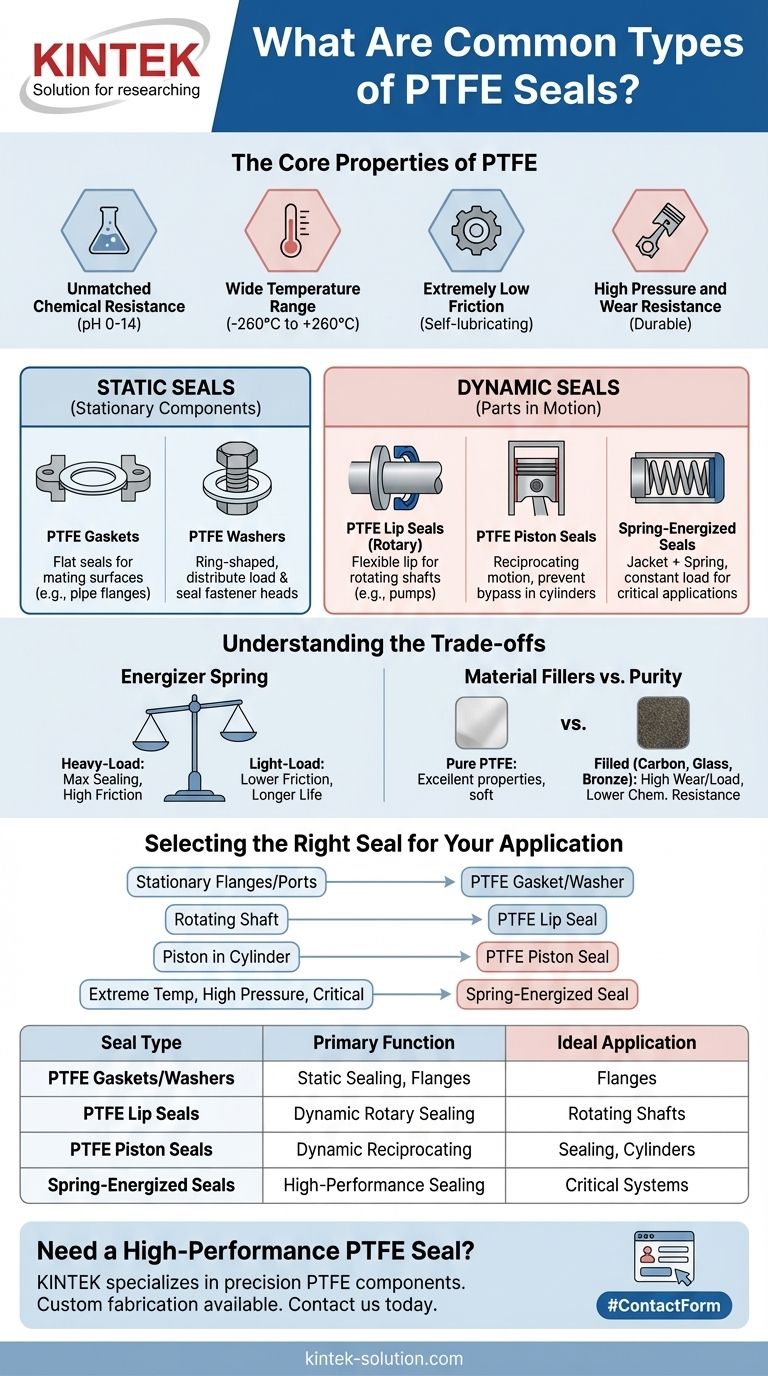
The most common types of PTFE seals are designed for either static or dynamic applications, and they include gaskets, washers, lip seals, piston seals, and spring-energized seals. While all share PTFE's core properties of high chemical and temperature resistance, their specific shape and construction determine their ideal use, from sealing stationary pipe flanges to containing pressure in high-speed rotating equipment.
The key is to understand that while Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides the raw material's exceptional characteristics, it is the seal's mechanical design—whether it's a flat gasket, a flexible lip seal, or a spring-energized ring—that dictates its function and suitability for a specific engineering challenge.

The Core Properties of PTFE
Before examining specific seal types, it's essential to understand why PTFE is such a sought-after material. Its unique molecular structure gives it a powerful combination of characteristics that make it ideal for demanding sealing applications.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert to most chemicals, including aggressive acids, solvents, and oils. It performs reliably in environments with a pH range from 0 to 14, making it a default choice for chemical processing and pharmaceutical industries.
Wide Temperature Range
PTFE seals maintain their integrity and performance across an exceptionally broad temperature spectrum, typically from cryogenic lows of -260°C (-436°F) up to highs of 260°C (500°F).
Extremely Low Friction
Often called the "King of Plastics," PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This self-lubricating property reduces wear, minimizes heat generation in dynamic applications, and extends the service life of the seal and mating components.
High Pressure and Wear Resistance
PTFE can be engineered to maintain its sealing properties under high pressure. Its durability also makes it highly resistant to wear, especially in reciprocating (back-and-forth) applications, which reduces system downtime and maintenance costs.
Classifying PTFE Seals by Function
PTFE seals can be broadly categorized into two groups: static seals, which are used between non-moving parts, and dynamic seals, which are designed for parts in motion relative to each other.
Static Seals: Sealing Stationary Components
These are the simplest forms of PTFE seals, designed to prevent leakage between two fixed surfaces.
- PTFE Gaskets: These are flat seals, often cut from a sheet, used to create a seal between two mating surfaces, such as pipe flanges or machinery housings. Their primary job is to fill microscopic gaps and prevent fluid or gas from escaping.
- PTFE Washers: These are ring-shaped seals used to distribute the load of a threaded fastener, like a bolt or screw. They also create a tight seal between the fastener head and the surface, preventing leaks in through-holes.
Dynamic Seals: For Parts in Motion
Dynamic seals are more complex, as they must maintain a seal while accommodating movement, friction, and wear.
- PTFE Lip Seals (Rotary Seals): These are designed for rotating shafts. They feature a flexible "lip" that maintains light contact with the shaft, preventing leakage while minimizing friction and wear. They are common in automotive, aerospace, and industrial equipment.
- PTFE Piston Seals: Specifically designed for reciprocating or back-and-forth motion, these seals are critical components in hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders. They prevent fluid from bypassing the piston, ensuring the system operates efficiently and powerfully.
- Spring-Energized Seals: This advanced design consists of a PTFE jacket and an internal metallic spring. The spring provides a constant, uniform load against the sealing surfaces, which compensates for material wear, temperature fluctuations, and minor misalignments, ensuring a reliable seal in the most critical applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a PTFE seal is not just about the material; it's about matching the design to the operational demands and understanding the inherent compromises.
The Role of the Energizer Spring
In spring-energized seals, the spring's design is critical.
- Heavy-Load Springs: Provide maximum sealing force. They are ideal for high-pressure gas applications where leakage is not an option, but this comes at the cost of higher friction and potentially faster wear.
- Light-Load Springs: Generate less force, resulting in lower friction and a longer service life. These are better suited for applications where minimal friction is the primary goal and slight seepage is acceptable.
Material Fillers vs. Purity
While pure PTFE has excellent properties, it can be soft and prone to deformation under high loads.
Manufacturers often add "fillers" like carbon, glass fiber, or bronze to the PTFE matrix. These fillers can dramatically increase wear resistance, load-bearing capacity, and thermal conductivity. However, they can also alter the seal's chemical resistance and increase friction compared to pure PTFE.
Design Complexity vs. Application
A simple gasket is sufficient and cost-effective for a stationary flange. However, using that same gasket on a rotating shaft would lead to immediate failure. The mechanical complexity of the seal must match the complexity of the application.
Selecting the Right Seal for Your Application
Your choice should be dictated entirely by the specific demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is sealing stationary flanges or ports: A simple PTFE gasket or washer is the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is sealing a rotating shaft in a pump or motor: A PTFE lip seal is specifically engineered for this dynamic rotary motion.
- If your primary focus is sealing a piston in a hydraulic cylinder: A PTFE piston seal is designed for high-pressure, reciprocating motion.
- If your primary focus is performance under extreme temperatures, high pressure, or in a critical system where seal failure is not an option: A spring-energized PTFE seal provides the most robust and reliable performance.
Ultimately, selecting the correct seal is a matter of precisely matching the component's design to the mechanical and environmental challenges it will face.
Summary Table:
| Seal Type | Primary Function | Ideal Application |
|---|---|---|
| PTFE Gaskets/Washers | Static Sealing | Pipe flanges, machinery housings, fastener sealing |
| PTFE Lip Seals | Dynamic Rotary Sealing | Rotating shafts in pumps, motors, and industrial equipment |
| PTFE Piston Seals | Dynamic Reciprocating Sealing | Hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders |
| Spring-Energized Seals | High-Performance Sealing | Extreme temperatures, high pressure, critical systems |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Seal?
Selecting the right PTFE seal is critical for your system's reliability, chemical resistance, and temperature performance. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring a perfect fit and superior performance for your specific application.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and let our experts provide a solution tailored to your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- How does the flexibility of PTFE expansion bellows benefit industrial piping systems? Absorb Stress, Prevent Failure
- What should be considered when bonding PTFE sheets? A Guide to Achieving a Reliable, Permanent Bond
- What are the key properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) sheets? Unlock Superior Performance in Demanding Applications
- What pressure can ePTFE gaskets withstand? Understanding Their True Capabilities
- What factors should be considered when choosing the thickness of a PTFE gasket? Optimize Your Seal for Flange Condition & Pressure
- Which industries commonly use PTFE Expansion Bellows? Solve Your Critical Chemical and Purity Challenges
- Where are PTFE energized seals used in oil and gas operations? Essential Sealing Solutions for Harsh Environments
- Why are Filled PTFE gaskets used in high-pressure settings? Enhanced Strength for Demanding Seals



















