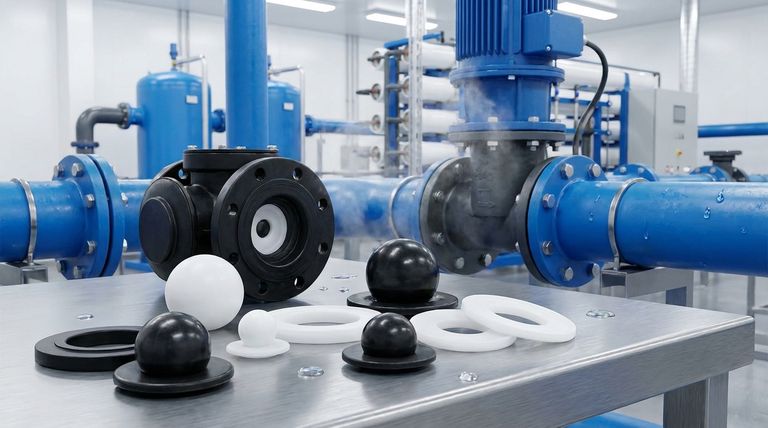
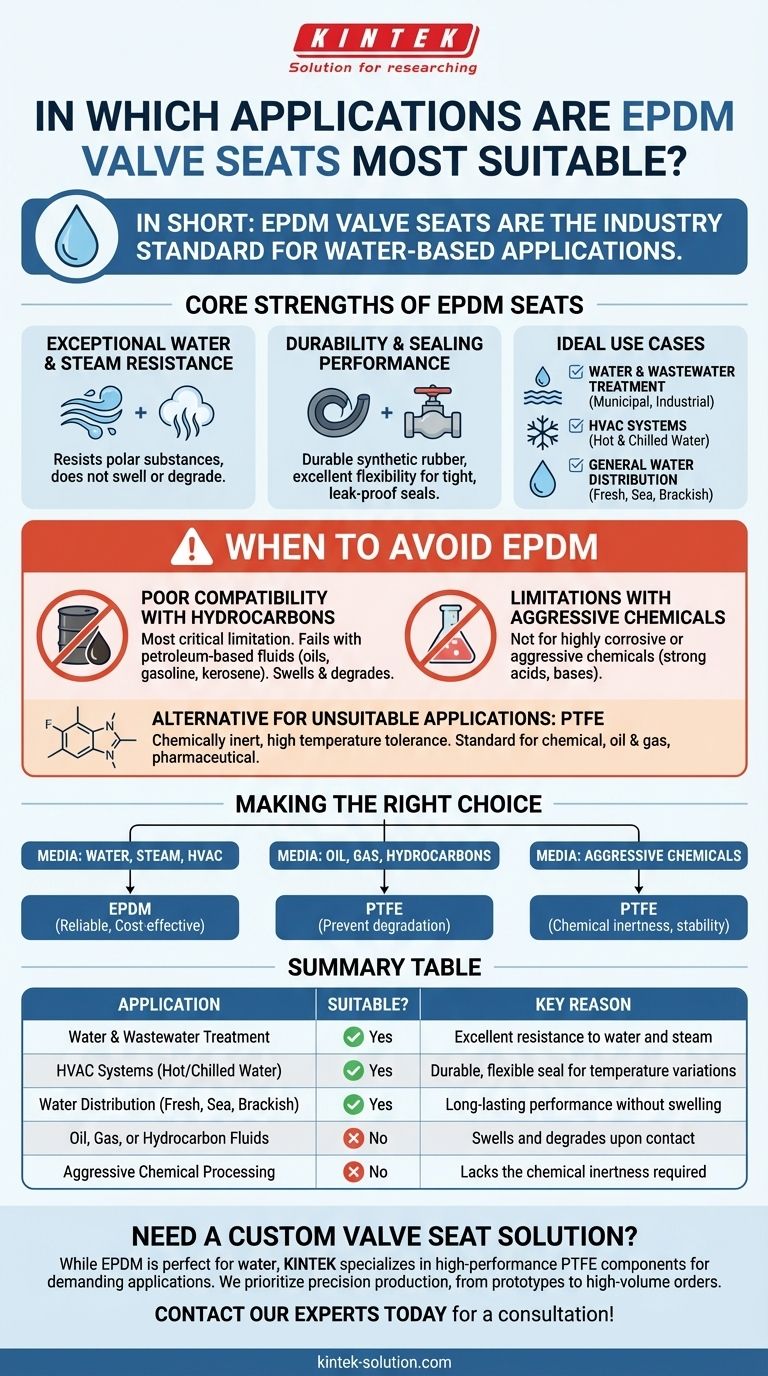
In short, EPDM valve seats are the industry standard for water-based applications. Their chemical structure makes them exceptionally resistant to water, steam, and polar solvents, making them the default choice for systems like municipal water treatment, distribution, and commercial HVAC.
The suitability of a valve seat is not determined by the application name, but by the chemical compatibility of the seat material with the media flowing through it. EPDM excels with water and steam but fails with oils and hydrocarbon-based fluids.

The Core Strengths of EPDM Seats
Understanding the properties of Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber is key to knowing where it performs best. Its molecular makeup gives it a distinct set of advantages in specific environments.
Exceptional Water and Steam Resistance
EPDM's primary strength is its outstanding resistance to polar substances like water. Unlike other elastomers, it does not swell, soften, or degrade when exposed to water, wastewater, or steam, ensuring a long-lasting and reliable seal.
Durability and Sealing Performance
As a durable synthetic rubber, EPDM provides excellent flexibility. This allows it to create a tight, leak-proof seal within the valve, even with minor imperfections in the valve body or disc. This resilience contributes to its long service life in demanding systems.
Ideal Use Cases
Based on these properties, EPDM seats are the preferred choice in several key industries.
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: From municipal plants to industrial water purification, EPDM handles the various stages of water processing without issue.
- HVAC Systems: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems rely on the circulation of hot and chilled water, a perfect environment for EPDM.
- General Water Distribution: Any system designed for the transport of fresh water, sea water, or brackish water is a suitable application.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When to Avoid EPDM
No single material is a universal solution. The same properties that make EPDM ideal for water applications make it entirely unsuitable for others. Knowing its limitations is critical to preventing costly valve failure.
Poor Compatibility with Hydrocarbons
This is the most critical limitation of EPDM. It has poor resistance to petroleum-based fluids, including oils, gasoline, kerosene, and most hydrocarbon solvents. Contact with these substances will cause the EPDM seat to swell, soften, and quickly disintegrate, leading to catastrophic valve failure.
Limitations with Aggressive Chemicals
While EPDM handles many diluted chemicals well, it is not designed for highly corrosive or aggressive chemical processing. For applications involving strong acids, bases, or specialized solvents, a more inert material is required.
The Role of PTFE as an Alternative
For applications where EPDM is unsuitable, materials like PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) are often used. PTFE is nearly chemically inert and has a much higher temperature tolerance, making it the standard choice for the chemical processing, oil and gas, and pharmaceutical industries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seat material is a simple matter of matching the material to the media.
- If your primary focus is water, steam, or HVAC: EPDM is the most reliable and cost-effective choice for ensuring a durable, leak-proof seal.
- If your primary focus is oil, gas, or hydrocarbon solvents: You must specify a different material, such as PTFE, to avoid rapid material degradation and system failure.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical processing: PTFE is the superior choice due to its chemical inertness and stability across a wide temperature range.
Ultimately, choosing the right valve seat material is the most critical factor in ensuring the valve's long-term performance and safety.
Summary Table:
| Application | Suitable? | Key Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Water & Wastewater Treatment | ✅ Yes | Excellent resistance to water and steam |
| HVAC Systems (Hot/Chilled Water) | ✅ Yes | Durable, flexible seal for temperature variations |
| Water Distribution (Fresh, Sea, Brackish) | ✅ Yes | Long-lasting performance without swelling |
| Oil, Gas, or Hydrocarbon Fluids | ❌ No | Swells and degrades upon contact |
| Aggressive Chemical Processing | ❌ No | Lacks the chemical inertness required |
Need a Custom Valve Seat Solution?
While EPDM is perfect for water, many demanding applications require the superior chemical resistance and temperature stability of PTFE.
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including custom valve seats, seals, and liners—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We prioritize precision production, offering custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to ensure your system's reliability and safety.
Let us help you select the perfect material for your specific media and operating conditions. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE and Nitrile Diaphragm Pump Components for Demanding Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key properties of PTFE that benefit bellows and diaphragms? Achieve Unmatched Reliability in Harsh Environments
- What are the key features of PTFE diaphragms? Maximize Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the main technical features that influence the performance of PTFE diaphragms? Optimize for Durability & Chemical Resistance
- What are the common applications of PTFE diaphragms in the Chinese market? Key Uses in Chemical, Pharma & Semiconductor
- How does the low coefficient of friction of PTFE balls benefit their use in valves and pumps? Enhance Efficiency and Reliability



















