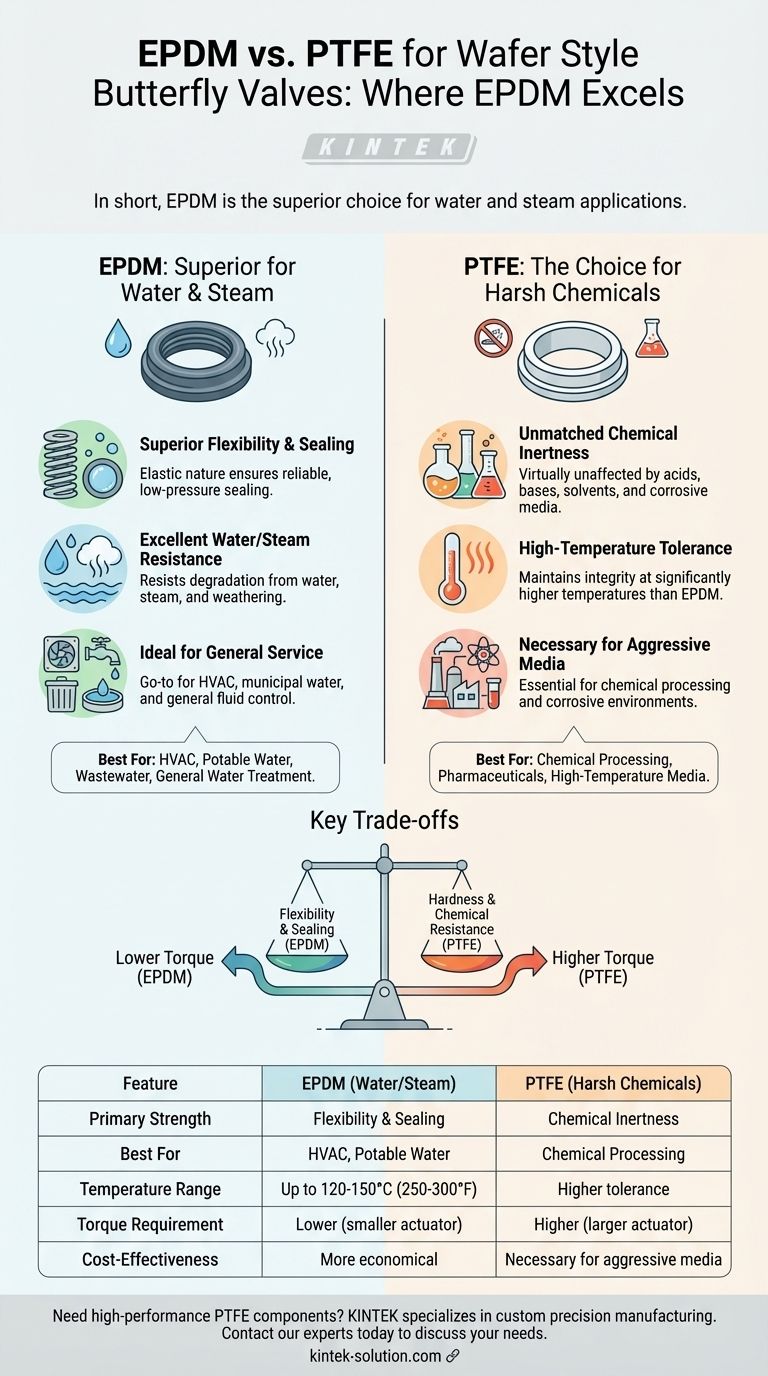
In short, EPDM is the superior choice for wafer style butterfly valves in applications primarily involving water or steam. This includes systems like HVAC, potable water distribution, and general water treatment, where EPDM's excellent flexibility and resistance to water-based degradation provide a durable, tight seal without the need for extreme chemical resistance.
The decision between EPDM and PTFE is a fundamental trade-off. You are choosing between EPDM's superior flexibility and sealing capability in water-based media versus PTFE's unmatched chemical inertness and high-temperature tolerance required for harsh industrial processes.

The Core Strengths of EPDM
Superior Flexibility and Sealing
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) is a synthetic rubber known for its elasticity. This flexibility allows the valve seat to create a bubble-tight seal with less torque required to close the valve.
This characteristic makes it highly reliable in systems where consistent, low-pressure sealing is critical.
Excellent Water and Steam Resistance
EPDM's molecular structure is inherently resistant to degradation from water, steam, and weathering. It does not swell, harden, or crack when exposed to these common media over long periods.
This ensures a long service life and reliable performance in water-centric applications.
Ideal for General Service Applications
Due to its properties, EPDM is the go-to material for a vast range of general and commercial fluid control.
Common examples include heating and cooling loops (HVAC), municipal water systems, and industrial wastewater processing where aggressive chemicals are not present.
When to Choose PTFE Instead
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is famous for its near-universal chemical resistance. It is virtually unaffected by acids, bases, solvents, and other aggressive chemicals that would rapidly degrade an EPDM seat.
This makes PTFE essential for chemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and any application involving corrosive media.
High-Temperature Tolerance
PTFE maintains its integrity at significantly higher temperatures than EPDM. This allows it to be used in processes involving hot chemicals, gases, or high-temperature fluids where EPDM would fail.
If the operational temperature exceeds the limits of EPDM (typically around 120-150°C or 250-300°F), PTFE becomes the necessary choice.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Flexibility vs. Hardness Dilemma
The primary trade-off is between EPDM's flexibility and PTFE's hardness. While EPDM's softness creates a better seal with less effort, PTFE's rigidity can sometimes lead to sealing challenges, especially in low-pressure applications.
The hardness of PTFE also means it is more susceptible to damage from slurries or abrasive particles, whereas EPDM's rubbery nature can better absorb such impacts.
Actuation and Torque Requirements
Because PTFE is a much stiffer material, butterfly valves with PTFE seats require significantly more torque to open and close.
This often necessitates a larger, more powerful—and more expensive—actuator compared to an identical valve with an EPDM seat. This is a critical factor in system design and cost analysis.
Cost and Application Specificity
EPDM is generally a more cost-effective material. Choosing PTFE when its chemical or temperature resistance is not strictly required leads to unnecessary expense, both in the valve itself and in the required actuation.
The goal is to match the material to the specific operational demands, not to over-engineer the solution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the correct material is the one that meets the demands of your specific system without incurring unnecessary costs.
- If your primary focus is HVAC, potable water, or wastewater: EPDM is the more effective and economical choice due to its superior sealing in water-based systems.
- If your primary focus is chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, or high-temperature media: PTFE is the only viable option because of its essential chemical and thermal resistance.
- If your primary focus is operational cost and reliability in a non-aggressive environment: EPDM's lower torque requirement leads to smaller actuators and reduced long-term energy costs.
Choosing the right valve seat is about precisely matching the material's capabilities to the challenges of its environment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | EPDM (Ideal for Water/Steam) | PTFE (Ideal for Harsh Chemicals) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Strength | Superior flexibility & sealing in water | Unmatched chemical inertness |
| Best For | HVAC, potable water, wastewater | Chemical processing, pharmaceuticals |
| Temperature Range | Up to 120-150°C (250-300°F) | Higher temperature tolerance |
| Torque Requirement | Lower (smaller, cheaper actuator) | Higher (larger, more expensive actuator) |
| Cost-Effectiveness | More economical for water-based media | Necessary for aggressive media |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your demanding applications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE seals, liners, and labware. If your wafer butterfly valves require the chemical and thermal resistance of PTFE for semiconductor, medical, or industrial processes, we can fabricate the exact components you need—from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance the reliability and longevity of your critical systems.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Machined Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Laboratory ITO FTO Conductive Glass Cleaning Flower Basket
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE and Nitrile Diaphragm Pump Components for Demanding Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Adjustable Height Flower Basket
- Custom PTFE Microwave Digestion Vessels for Demanding Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE's friction coefficient compare to other materials? The Benchmark for Low-Friction Performance
- How do PTFE envelope gaskets perform in terms of leakage prevention? Superior Sealing for Demanding Applications
- What are the properties of bronze-filled (40%) PTFE balls? A Guide to Enhanced Strength & Wear
- What are the key advantages of PTFE lined butterfly valves? Superior Chemical Resistance & Cost Savings
- What is the temperature range for PTFE oil seals and conventional oil seals? A Guide to Extreme vs. Standard Performance
- What factors should be considered when choosing between PTFE and graphite braided packing? Select the Right Seal for Your Application
- Which type of seal is best suited for high-speed applications? PTFE Seals for Speeds Up to 35 m/s
- Which acid is not resistant to Teflon encapsulated O-rings? Avoid HF for Seal Integrity








