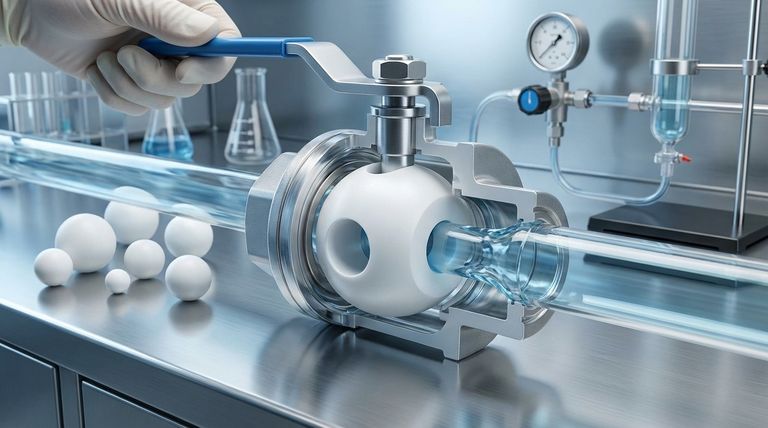
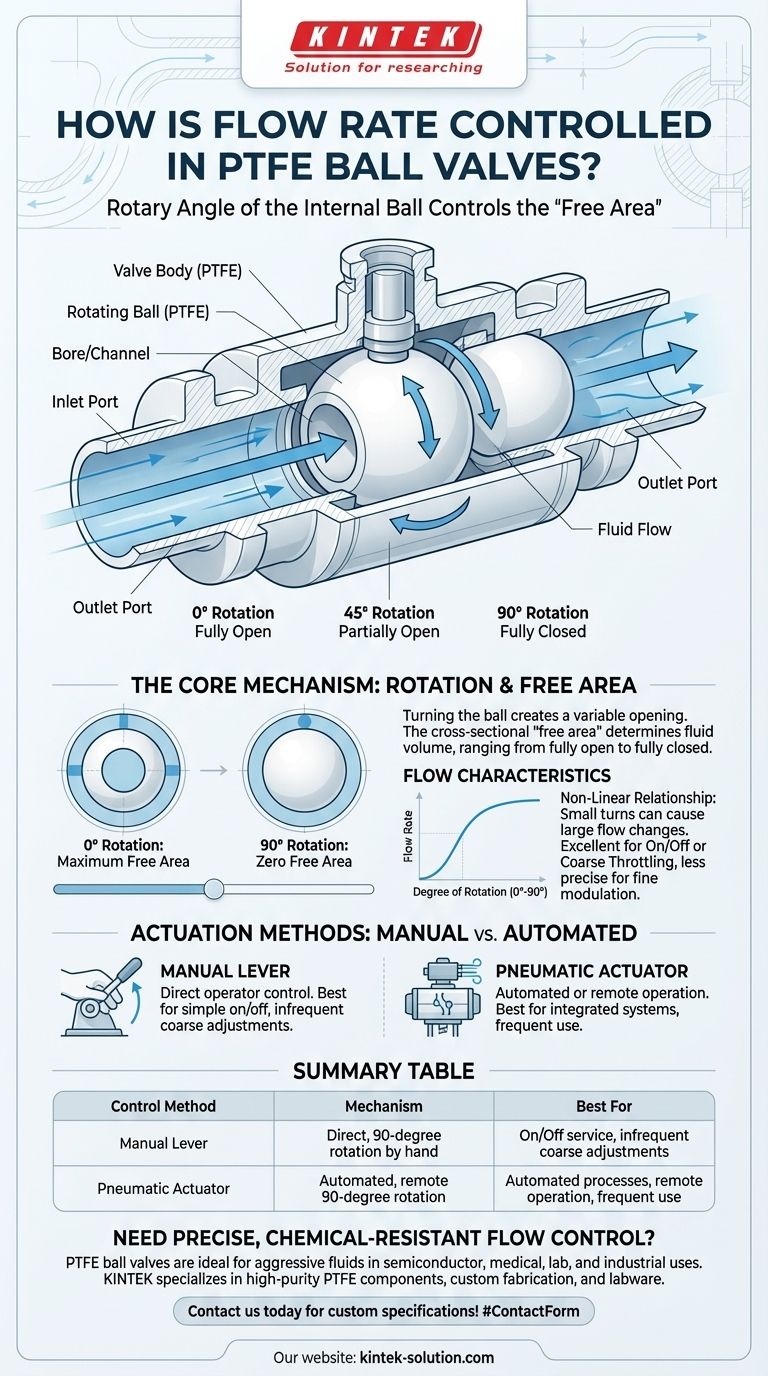
In short, flow rate in a PTFE ball valve is controlled by the rotary angle of the internal ball. A channel, or bore, is drilled through the center of this ball, and turning it changes how much this channel aligns with the valve's inlet and outlet ports, directly regulating the volume of fluid that can pass through.
The core principle is simple mechanical obstruction. By rotating the ball, you are creating a variable opening—from fully open to fully closed—which provides a straightforward, albeit non-linear, method for managing flow.

The Core Mechanism: The Rotating Ball
Understanding how a simple rotation translates into precise control requires looking at the valve's internal geometry and the methods used to operate it.
How Rotation Creates Control
At the heart of the valve is a spherical ball with a hole drilled straight through it. When the valve is fully open, this hole is perfectly aligned with the flow path, offering minimal resistance.
As the ball is rotated (typically through a 90-degree turn), the solid part of the ball begins to obstruct the flow path, reducing the available area for the fluid to pass.
The "Free Area" Concept
The term "free area" refers to the cross-sectional area of the opening that the fluid sees. This area is directly determined by the rotational angle of the ball.
A 0-degree rotation means the channel is aligned and the free area is at its maximum. A 90-degree rotation means the solid side of the ball is facing the flow, and the free area is zero, completely stopping the flow.
Actuation: Manual vs. Automated
The method of rotating the ball determines how the valve is used in a system.
The references point to two primary methods: a manual lever for direct operator control, or a pneumatic actuator for automated or remote operation. The choice depends entirely on the application's requirements for speed, frequency, and system integration.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, using a standard ball valve for flow control involves important considerations that impact system performance.
Strength: Simplicity and Reliability
The primary advantage of this mechanism is its simplicity. With few moving parts, ball valves are robust, reliable, and provide a positive shut-off, meaning they seal very effectively when fully closed.
Limitation: Non-Linear Flow Characteristics
The relationship between the degree of rotation and the flow rate is not linear. A small turn from the fully closed or fully open position can cause a very large change in flow.
This makes standard ball valves excellent for on/off service or coarse throttling, but less suitable for applications requiring fine, precise modulation of the flow rate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct control method is critical for achieving your desired system performance.
- If your primary focus is simple on/off control or infrequent, coarse adjustments: A manually operated lever is the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is integrating the valve into an automated process or require remote operation: A pneumatic actuator provides the necessary interface for system control.
Ultimately, understanding the ball valve's rotational control mechanism allows you to leverage its simplicity for the right task.
Summary Table:
| Control Method | Mechanism | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Lever | Direct, 90-degree rotation by hand | On/Off service, infrequent coarse adjustments |
| Pneumatic Actuator | Automated, remote 90-degree rotation | Automated processes, remote operation, frequent use |
Need precise, chemical-resistant flow control for your critical process?
The simple, robust design of PTFE ball valves makes them ideal for handling aggressive fluids in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-purity PTFE components, including custom ball valves, seals, liners, and labware.
We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to meet your exact specifications.
Contact us today to discuss your application requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are some common variations and grades of PTFE used in seals? Optimize Performance with the Right Material
- What makes PTFE bellows suitable for dynamic flexing applications? Endure Millions of Cycles in Harsh Environments
- What type of coolants are recommended for machining PTFE? Control Heat for Precision Results
- How can Teflon PTFE sheets be used in heat press applications? Protect Your Designs and Equipment
- How do fillers enhance the properties of modified PTFE gaskets? Improve Strength, Wear, and Creep Resistance
- How does PTFE compare to other non-stick materials? The Ultimate Guide to Chemical & Friction Performance
- What is PTFE and what are its common applications? Discover the Versatile High-Performance Polymer
- How can deformation be minimized during Teflon machining? Master Precision with Sharp Tools and Coolant



















