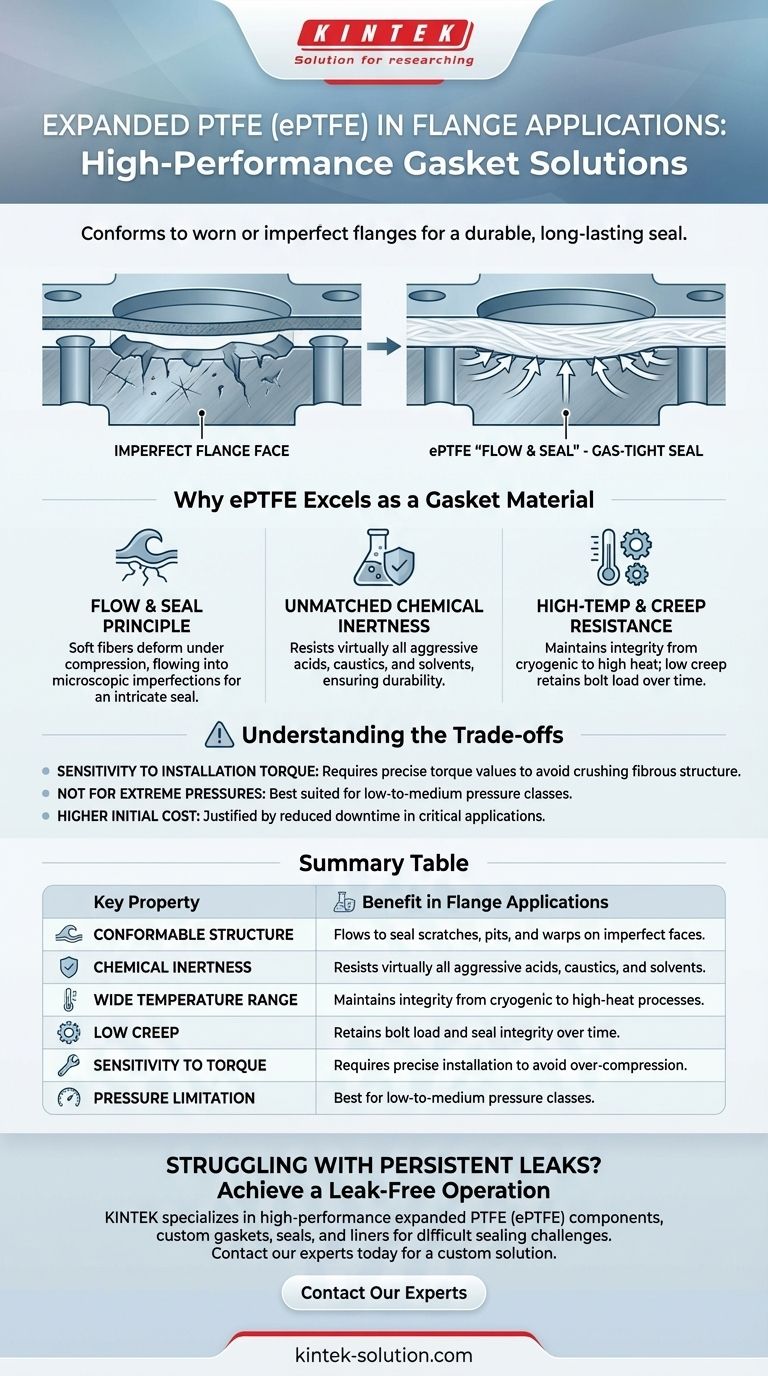
In flange applications, expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is overwhelmingly used as a high-performance gasket material. Its unique properties make it exceptionally effective at creating a durable, long-lasting seal, particularly on flanges that are worn, damaged, or otherwise imperfect. Unlike rigid gaskets that require perfectly flat surfaces, ePTFE conforms to surface irregularities to prevent leaks.
The core value of expanded PTFE in flange sealing comes from its unique structure. It is a soft, fibrous material that "flows" under compression to fill every scratch, pit, and warp in a flange face, creating a highly reliable seal where other materials would fail.

Why ePTFE Excels as a Gasket Material
The effectiveness of ePTFE is not based on a single property, but on the combination of its physical structure and inherent chemical resilience. This makes it a premier problem-solver for difficult sealing challenges.
The "Flow and Seal" Principle
Expanded PTFE has a porous, mesh-like structure of fibers and nodes. While this allows for integration with body tissue in medical applications, in an industrial flange, it gives the material its unique sealing capability.
When compressed by bolt load, these soft fibers deform and flow into the microscopic imperfections of the flange faces. This creates an intricate, gas-tight seal that is impossible to achieve with harder, more rigid gasket materials on anything less than a perfect surface.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most chemically non-reactive substances known. This property is fully retained in its expanded form.
This means an ePTFE gasket will not degrade when exposed to the vast majority of aggressive acids, caustics, and solvents used in industrial pipelines. This near-universal chemical compatibility simplifies gasket selection and reduces inventory needs.
High-Temperature and Creep Resistance
ePTFE maintains its integrity across a wide temperature range, making it suitable for both cryogenic and high-heat processes.
Critically, it exhibits very low "creep," which is the tendency of a gasket material to flow out from between the flanges over time and under load. Its high strength and low shrinkage ensure the bolt load is maintained, and the seal remains intact long after installation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While ePTFE is a superior sealing material, it is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Sensitivity to Installation Torque
Because ePTFE is designed to be soft and conformable, it is also sensitive to over-compression.
Applying excessive bolt torque can crush the fibrous structure and cause the gasket to extrude out of the flange joint. This destroys the seal and can lead to immediate failure. Following manufacturer-specific torque values is non-negotiable.
Not for Extreme Pressures
While strong, standard ePTFE gaskets are best suited for low-to-medium pressure classes. In extremely high-pressure applications, a composite gasket with a metal core or a solid metal gasket may be required to prevent blowout.
Higher Initial Cost
Expanded PTFE is a specialty material, and its initial purchase price is typically higher than standard compressed non-asbestos or rubber gaskets. However, this cost is often justified by its performance in preventing leaks in critical, corrosive, or hard-to-seal applications, which reduces downtime and maintenance costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Flange
To determine if ePTFE is the correct choice, evaluate the primary challenge you are trying to solve with the flange connection.
- If your primary focus is sealing old, warped, or damaged flanges: ePTFE is the ideal choice due to its exceptional ability to conform to surface imperfections.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive or high-purity chemicals: ePTFE is one of the safest and most reliable options because of its extreme chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is sealing fragile flanges (e.g., glass-lined, plastic): ePTFE is highly effective as it can achieve a tight seal with a much lower bolt load, preventing damage to the flange.
Ultimately, expanded PTFE should be seen as a powerful tool for solving your most persistent and difficult industrial sealing problems.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit in Flange Applications |
|---|---|
| Conformable Structure | Flows to seal scratches, pits, and warps on imperfect flange faces |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists virtually all aggressive acids, caustics, and solvents |
| Wide Temperature Range | Maintains integrity from cryogenic to high-heat processes |
| Low Creep | Retains bolt load and seal integrity over time |
| Sensitivity to Torque | Requires precise installation to avoid over-compression |
| Pressure Limitation | Best for low-to-medium pressure classes; not for extreme pressures |
Struggling with persistent leaks on worn, damaged, or hard-to-seal flanges?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance expanded PTFE (ePTFE) components, including custom gaskets, seals, and liners. Our ePTFE solutions are engineered to solve your most difficult sealing challenges by conforming to surface imperfections and resisting aggressive chemicals.
We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors with precision production, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us help you achieve a leak-free operation. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific flange sealing needs and receive a custom solution quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What scientific research supports the use of PTFE Liners in medical devices? Proven Benefits for Safety & Performance
- Why are PTFE expansion bellows considered a cost-effective long-term investment? Reduce Total Cost of Ownership
- How does the self-lubricating property of PTFE rotary shaft seals benefit industrial applications? Achieve Maintenance-Free, High-Performance Sealing
- What temperature range can PTFE encapsulated O-rings withstand? -60°C to 205°C, Depending on Core
- What are the key roles of PTFE rotary shaft seals in industrial applications? Ensure Reliability in Extreme Conditions
- What makes ePTFE gaskets effective against gas leakage? The Key to Superior Gas Sealing
- What are the limitations of PTFE when used as a mechanical component? Overcoming Softness & Instability
- How do PTFE balls perform against various chemicals? Unmatched Chemical Resistance for Harsh Environments



















