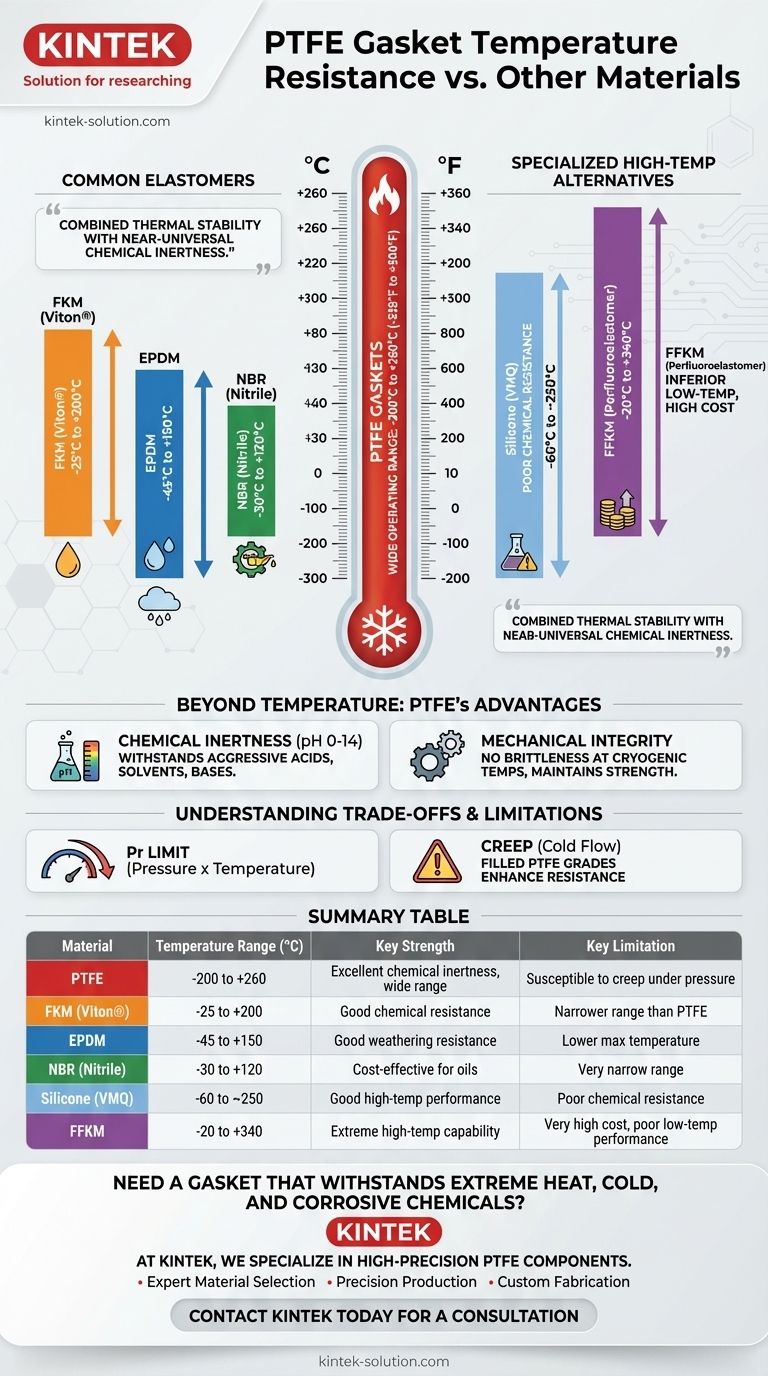
PTFE gaskets offer one of the widest operating temperature ranges of any common sealing material. They reliably perform in extreme conditions from as low as -200°C to a high of +260°C (-328°F to +500°F), making them a superior choice for applications involving both cryogenic cold and significant heat.
While PTFE's temperature range is exceptional, its true value lies in the combination of that thermal stability with near-universal chemical inertness—a pairing few other materials can match.

A Head-to-Head Temperature Comparison
To understand the unique position of PTFE, it's best to compare it directly against other common gasket and sealing materials.
The Exceptional Range of PTFE
The defining characteristic of a PTFE gasket is its ability to maintain its sealing properties and mechanical strength across a vast temperature spectrum.
This makes it suitable for everything from liquid nitrogen applications to high-temperature processing lines without degrading.
How Common Elastomers Compare
Most standard elastomers operate within a much narrower thermal window.
- FKM (Viton®): A capable material, but its range is limited to approximately -25°C to +200°C.
- EPDM: Offers better low-temperature performance (-45°C) but has a much lower maximum temperature of +150°C.
- NBR (Nitrile): A common, cost-effective choice for oils, but with a very narrow range of -30°C to +120°C.
Specialized High-Temperature Alternatives
Only a few specialized materials challenge PTFE at the high end, and each comes with a significant trade-off.
- Silicone (VMQ): Matches PTFE's high-temperature performance (up to ~250°C) but possesses very poor chemical resistance, making it unsuitable for most industrial processes.
- FFKM (Perfluoroelastomer): This material can exceed PTFE's upper limit, with some grades reaching 340°C. However, it offers inferior low-temperature performance and comes at a substantially higher cost.
Why Temperature Isn't the Only Factor
A material's temperature rating is only part of the story. The operational environment dictates whether that rating is actually achievable. PTFE's other properties are what make its thermal range so effective in practice.
The Critical Role of Chemical Inertness
PTFE is almost completely chemically inert, with a pH range of 0-14.
It can withstand the most aggressive acids, solvents, and bases without degrading. This means it can handle high temperatures in the presence of corrosive media where a material like Silicone would instantly fail.
Maintaining Mechanical Integrity
Across its wide thermal range, PTFE maintains excellent mechanical strength. It doesn't become brittle at cryogenic temperatures or excessively soft at its upper limit, ensuring a reliable and consistent seal.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. To use PTFE effectively, you must be aware of its operational constraints.
The Pressure and Temperature (Pr) Limit
A gasket can rarely withstand its maximum rated temperature and maximum rated pressure simultaneously.
Engineers consider the Pr value (Pressure x Temperature), which represents the combined load on the material. As the operating temperature increases, the maximum allowable pressure the PTFE gasket can handle will decrease.
Susceptibility to Creep
Pure, or "virgin," PTFE can be susceptible to creep (also known as cold flow). This is a tendency for the material to deform permanently under a constant load, which can compromise the seal over time, especially in high-pressure applications.
To counter this, filled PTFE grades (mixed with materials like glass, carbon, or graphite) are often used to enhance creep resistance and mechanical strength.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires looking beyond a single data point and considering the complete operational environment.
- If your primary focus is the widest possible temperature range: PTFE is the default choice, excelling in both cryogenic and high-heat scenarios where chemicals are present.
- If your primary focus is extreme high heat (above 260°C): Investigate FFKM, but be prepared for higher costs and poor low-temperature performance.
- If your primary focus is a non-corrosive, high-temperature seal: Silicone can be a viable alternative, but PTFE is superior if any aggressive media are involved.
- If your primary focus is a general-purpose seal with moderate demands: Less expensive materials like FKM or EPDM are often sufficient if your temperature and chemical needs fall within their limits.
By evaluating temperature alongside pressure and chemical exposure, you can select the gasket material that delivers true operational reliability.
Summary Table:
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Key Strength | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE | -200 to +260 | Excellent chemical inertness, wide range | Susceptible to creep under pressure |
| FKM (Viton®) | -25 to +200 | Good chemical resistance | Narrower range than PTFE |
| EPDM | -45 to +150 | Good weathering resistance | Lower max temperature |
| NBR (Nitrile) | -30 to +120 | Cost-effective for oils | Very narrow range |
| Silicone (VMQ) | -60 to ~250 | Good high-temp performance | Poor chemical resistance |
| FFKM | -20 to +340 | Extreme high-temp capability | Very high cost, poor low-temp performance |
Need a Gasket That Withstands Extreme Heat, Cold, and Corrosive Chemicals?
PTFE’s unique combination of a wide temperature range (-200°C to +260°C) and near-universal chemical resistance makes it the ideal choice for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including seals, gaskets, liners, and custom labware. We understand that every application has unique pressure, temperature, and chemical requirements.
We provide:
- Expert Material Selection: Guidance to ensure your PTFE gasket is optimized for your specific operating conditions, including filled grades for enhanced creep resistance.
- Precision Production: High-quality fabrication that guarantees a reliable, long-lasting seal.
- Custom Fabrication: From initial prototypes to high-volume production runs, we deliver components tailored to your exact specifications.
Let us help you achieve a leak-free, reliable seal for your most challenging environments.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation to discuss your project needs and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- Why is PTFE considered a significant discovery? A Material That Revolutionized Industry
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications



















