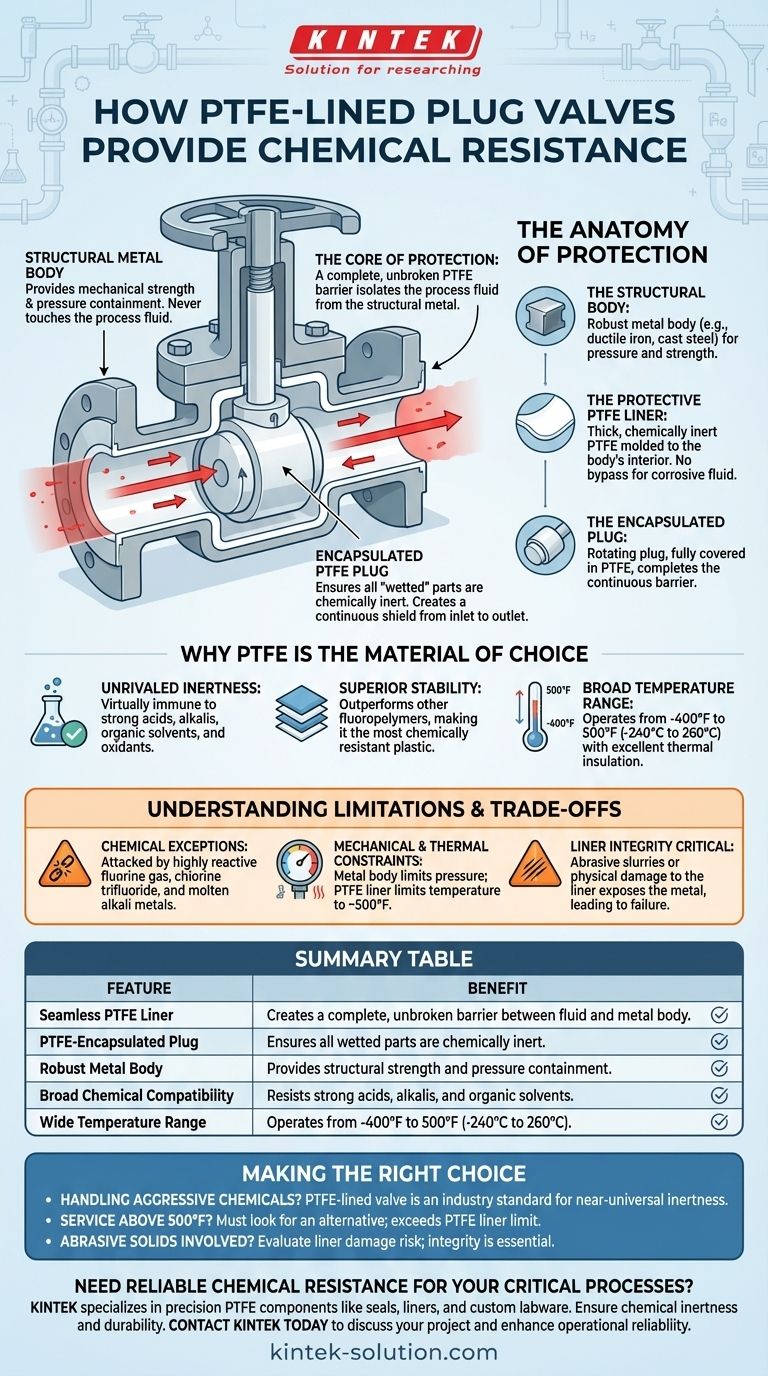
At its core, the construction of a PTFE-lined plug valve provides chemical resistance by creating a complete, unbroken barrier of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) between the process fluid and the valve's structural metal components. This design leverages the exceptional chemical inertness of PTFE to protect the cast iron or steel body, ensuring that only the highly resistant liner ever comes into contact with the corrosive media.
The fundamental challenge in handling corrosive fluids isn't just finding a resistant material, but creating a mechanically sound valve from it. PTFE-lined plug valves solve this by combining the structural strength of metal with the near-universal chemical immunity of a PTFE liner, effectively getting the best of both worlds.
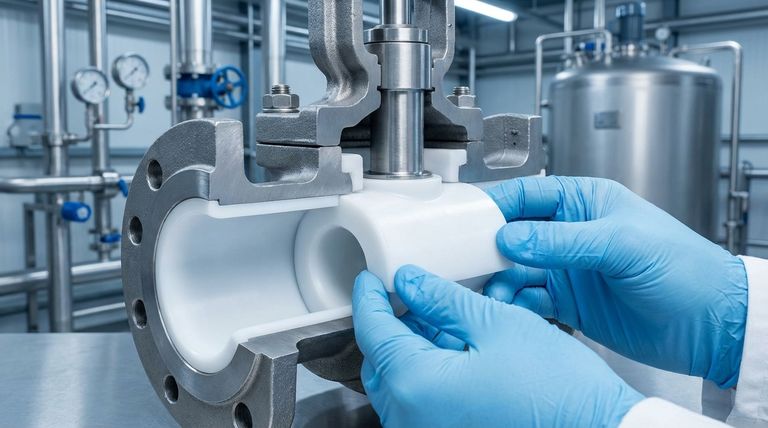

The Anatomy of Protection
Understanding how the valve is built reveals why it is so effective. The design ensures that at no point can the corrosive fluid bypass the protective lining and attack the valve's core structure.
The Structural Body
The outer body of the valve is typically made from robust and economical materials like ductile iron or cast steel. Its sole purpose is to provide mechanical strength and pressure containment for the system. This metal body never touches the process fluid.
The Protective PTFE Liner
The key to the valve's performance is the thick PTFE liner molded to the interior of the body. PTFE is a fluoropolymer plastic renowned for being almost completely chemically inert. This liner forms a seamless, non-reactive shield.
The Encapsulated Plug
The rotating plug, which controls the flow, is also completely encapsulated in PTFE. This ensures that all "wetted" parts—any surface that touches the fluid—are made of or covered by this inert material, creating a continuous and unbroken barrier from the inlet to the outlet.
Why PTFE is the Material of Choice
The selection of PTFE is not arbitrary. Its unique molecular properties make it one of the most resilient materials available for industrial use, far superior to many other plastics and even exotic metals in certain applications.
Unrivaled Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually immune to chemical attack. It can handle the most aggressive media, including strong acids like aqua regia, strong alkalis, all organic solvents, and powerful oxidants without degrading.
Superior to Other Polymers
Its chemical stability is so profound that it outperforms many other fluoropolymers. It is highly insoluble in almost any solvent or chemical, making it the most chemically resistant plastic known.
Broad Temperature Range
In addition to its chemical resilience, PTFE provides excellent thermal insulation and maintains its integrity across a vast operating temperature range, from -400°F to 500°F (-240°C to 260°C).
Understanding the Limitations and Trade-offs
While exceptionally robust, no material is without its limits. Acknowledging these trade-offs is crucial for correct application and system safety.
The Few Chemical Exceptions
PTFE's near-universal resistance has a few, very specific exceptions. It can be attacked by highly reactive substances like fluorine gas, chlorine trifluoride, and molten alkali metals. For nearly all other industrial chemicals, it remains inert.
Mechanical and Thermal Constraints
PTFE is a polymer, not a metal. Its primary weakness is mechanical, not chemical. The valve's pressure and structural ratings are determined by the metal body, while its temperature ceiling is dictated by the PTFE liner's limit of around 500°F (260°C).
The Criticality of Liner Integrity
The entire protective system depends on the liner remaining intact. Abrasive slurries or physical damage that could scratch, gouge, or breach the liner would expose the metal body to the corrosive fluid, leading to rapid valve failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a PTFE-lined plug valve should be a deliberate decision based on the specific demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is handling highly aggressive and diverse chemicals: A PTFE-lined valve is an industry standard and one of the safest, most reliable choices available due to its near-universal inertness.
- If your primary focus is service above 500°F (260°C): You must look for an alternative, as this temperature exceeds the operational limit of the PTFE liner.
- If your primary focus is handling abrasive solids: You must evaluate whether the particles could damage the liner, as its integrity is essential for chemical protection.
By understanding that this valve's strength comes from isolating its components, you can confidently apply it where its unique chemical resilience is needed most.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Seamless PTFE Liner | Creates a complete, unbroken barrier between fluid and metal body. |
| PTFE-Encapsulated Plug | Ensures all wetted parts are chemically inert. |
| Robust Metal Body | Provides structural strength and pressure containment. |
| Broad Chemical Compatibility | Resists strong acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. |
| Wide Temperature Range | Operates from -400°F to 500°F (-240°C to 260°C). |
Need reliable chemical resistance for your critical processes?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components, including seals, liners, and custom labware. Our expertise ensures that your equipment, like PTFE-lined valves, delivers the chemical inertness and durability required in demanding semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, prioritizing precision to meet your exact specifications.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and discover how our PTFE solutions can protect your systems and enhance your operational reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- How can the hardness of PTFE be increased? Reinforce with Fillers for Demanding Applications
- How does PTFE's non-stick property benefit industrial applications? Boost Efficiency & Reduce Downtime
- What are the operating parameters of PTFE bellow seals? Optimize Chemical & Purity Performance
- What are the limitations of PTFE in terms of fabrication? Navigating Manufacturing Challenges
- What are the limitations when machining Teflon/PTFE? Overcome Dimensional Instability & Creep
- How does the PTFE oil seal's design handle shaft eccentricity? Achieve Reliable Sealing Under Dynamic Conditions
- How do FEP and PTFE encapsulated O-rings contribute to equipment longevity? Prevent Costly Downtime with Superior Seals
- What are the key dielectric properties of PTFE that make it suitable for wires and cables? Ensuring Signal Integrity in Extreme Conditions



















