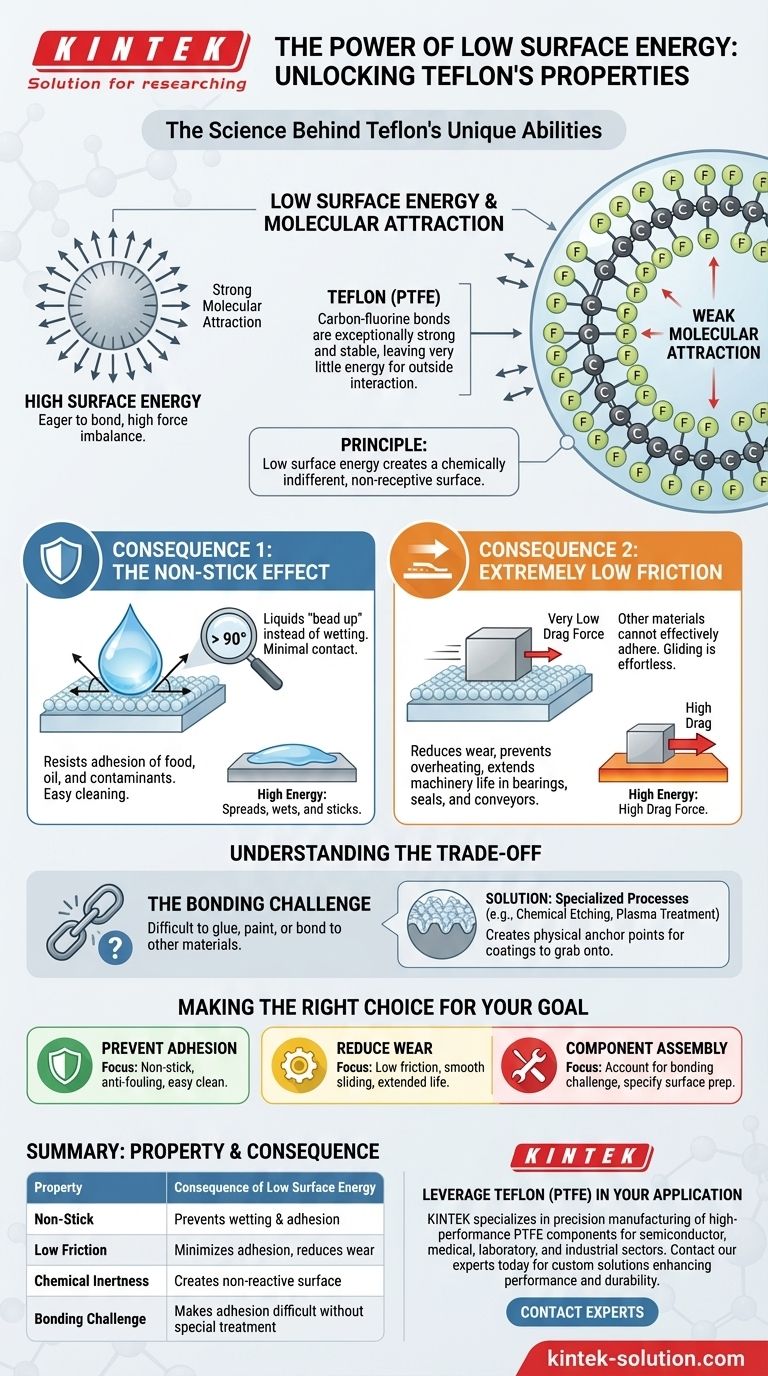
At its core, Teflon's low surface energy is the direct physical cause of its famous non-stick and low-friction properties. This characteristic means the material has extremely weak molecular attraction at its surface, making it difficult for other substances to find anything to "grab onto," which prevents them from adhering.
The central principle to understand is this: Low surface energy creates a chemically indifferent and non-receptive surface. Instead of sticking, other materials—from water and oil to solid objects—are effectively repelled, forced to bead up or slide off with minimal resistance.
The Science Behind Surface Energy
To grasp why Teflon (PTFE) is so unique, we must first understand what surface energy is and why Teflon has so little of it.
What is Surface Energy?
Surface energy is the excess energy that exists at the surface of a material compared to the bulk. Molecules inside a material are pulled equally in all directions by neighboring molecules.
At the surface, however, molecules have fewer neighbors, creating an imbalance of forces. This imbalance results in an inward pull, creating tension and making the surface molecules more "eager" to bond with whatever comes into contact with them.
Why Teflon is Different
Teflon's chemical structure is the key. It consists of a carbon backbone completely shielded by a dense layer of fluorine atoms.
The carbon-fluorine bond is exceptionally strong and stable. This stability means the fluorine atoms have very little leftover energy to interact with or attract other molecules, resulting in one of the lowest surface energies of any known solid.
The Direct Consequences of Low Surface Energy
This single chemical property—low surface energy—gives rise to Teflon's most valuable and well-known characteristics.
The Non-Stick Effect
The most famous result is Teflon's non-stick nature. Because the surface has such weak forces of attraction, liquids like water and oil cannot "wet" it.
Instead of spreading out, they are forced to minimize their contact with the surface by beading up into droplets. This resistance to being wetted is what prevents food from sticking and makes the material highly resistant to staining and fouling.
Extremely Low Friction
Friction is directly related to the forces of adhesion between two surfaces. Since other materials cannot effectively adhere to Teflon's surface, the force required to slide an object across it is incredibly low.
This low coefficient of friction is why Teflon is used in demanding mechanical applications like bearings, seals, and conveyor belts, where it reduces wear, prevents overheating, and extends the life of machinery.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, Teflon's low surface energy creates one significant challenge that is crucial to understand in any application.
The Bonding Challenge
The very property that makes Teflon non-stick also makes it extremely difficult to bond to other materials. You cannot easily glue or paint a Teflon surface.
Getting a non-stick coating to stick to a frying pan, for example, requires specialized industrial processes like chemical etching or plasma treatment. These methods roughen the surface on a microscopic level to create physical anchor points for the coating to grab onto, bypassing the need for chemical adhesion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this principle allows you to select and use materials more effectively based on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is preventing adhesion: The low surface energy directly translates to a non-stick, anti-fouling surface that is easy to clean.
- If your primary focus is reducing mechanical wear: The low surface energy ensures a minimal coefficient of friction, allowing parts to slide smoothly with little resistance.
- If your primary focus is component assembly: You must account for the bonding challenge and specify appropriate surface preparation techniques to achieve a durable bond.
Ultimately, Teflon's low surface energy is the foundational property from which all its remarkable capabilities are derived.
Summary Table:
| Property | Consequence of Low Surface Energy |
|---|---|
| Non-Stick | Prevents wetting and adhesion of liquids and solids. |
| Low Friction | Minimizes adhesion between surfaces, reducing wear. |
| Chemical Inertness | Creates a non-reactive, stable surface. |
| Bonding Challenge | Makes adhesion to other materials difficult without special treatment. |
Leverage the unique properties of Teflon (PTFE) in your application.
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures you get components that maximize non-stick and low-friction benefits while overcoming bonding challenges through advanced fabrication techniques, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our custom PTFE solutions can enhance your product's performance and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE considered a versatile material? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Properties
- What are PTFE micro powders and how are they manufactured? Enhance Your Materials with Fluoroadditives
- What is PTFE commonly known as and when was it developed? The 'Plastics King' for Extreme Performance
- What are some physical properties of PTFE? Master Its Unique Properties for Extreme Applications
- How does Teflon demonstrate superior chemical resistance? Unlocking Its Molecular Fortress
- What is the temperature resistance range of PTFE? Mastering Extreme Heat and Cold for Demanding Applications
- What industrial applications utilize expanded PTFE? Sealing, Filtration & Insulation Solutions
- Why is Teflon used in high-performance applications? Unmatched Low Friction & Chemical Resistance



















