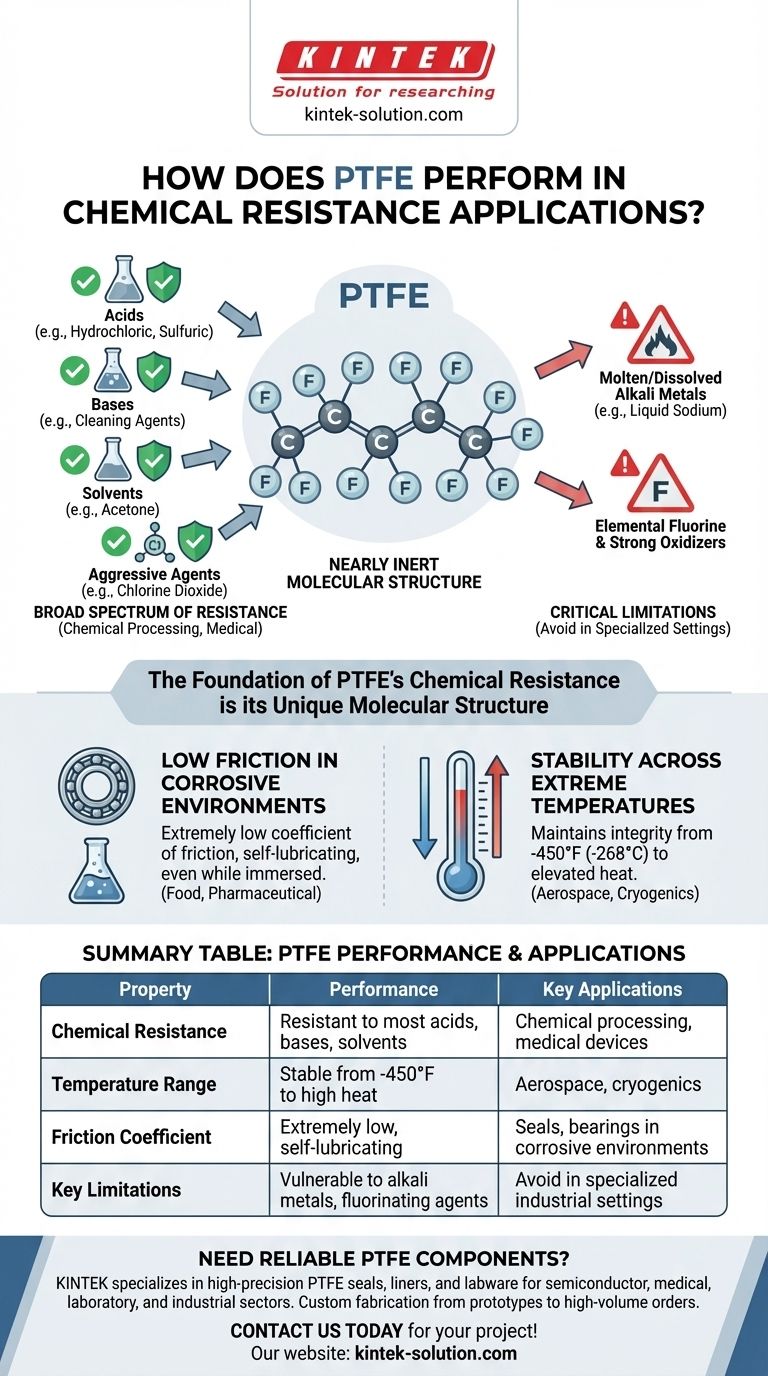
In terms of chemical performance, PTFE is one of the most resistant polymers available. It is nearly inert when exposed to the vast majority of industrial chemicals, including aggressive acids, bases, solvents, and cleaning agents. This exceptional stability is the primary reason for its widespread use in demanding environments where material degradation would lead to catastrophic failure.
The core takeaway is that PTFE's chemical resistance is its defining feature, making it a default choice for many harsh applications. However, its near-universal inertness has a few critical, well-defined exceptions that must be understood to prevent component failure.

The Foundation of PTFE's Chemical Resistance
The chemical resilience of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is not an incidental feature; it is a direct result of its unique molecular structure. This structure makes it a reliable material for components that must maintain their integrity under constant chemical stress.
A Nearly Inert Molecular Structure
PTFE consists of a long chain of carbon atoms completely shielded by a layer of fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine bond is exceptionally strong and stable, making it extremely difficult for other chemicals to react with and break down the polymer chain.
Broad Spectrum of Resistance
This molecular stability translates into an impressively broad resistance profile. PTFE reliably withstands exposure to substances like hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, acetone, and sodium peroxide. It also resists aggressive cleaning and disinfecting agents, such as chlorine dioxide, without degrading.
Proven Performance in Critical Industries
This resilience is proven in the field. In chemical processing, PTFE is used for pipelines and seals that handle aggressive media. In the medical field, its ability to resist acids, bases, and enzymes makes it a trusted material for device liners that undergo frequent and harsh sterilization.
Understanding the Critical Limitations
No material is perfect, and PTFE's chemical resistance has specific, well-known boundaries. Acknowledging these limitations is crucial for safe and effective material selection. Ignoring them can lead to complete and rapid failure.
The Exceptions: Alkali Metals and Fluorinating Agents
PTFE is vulnerable to attack from a very specific list of substances. It is not resistant to molten or dissolved alkali metals, such as liquid sodium. It will also be attacked by elemental fluorine and other extremely potent oxidizers.
Why These Exceptions Matter
While these chemicals are not common in most applications, they are used in certain specialized industrial and laboratory settings. In their presence, the strong carbon-fluorine bonds are broken, causing the PTFE to degrade rapidly. This is not a slow process of corrosion but a fundamental chemical breakdown of the material itself.
How Chemical Resistance Complements Other Properties
PTFE's value is amplified by how its chemical inertness works in tandem with its other unique physical properties. This combination allows it to solve complex engineering challenges that other materials cannot.
Low Friction in Corrosive Environments
Many mechanical parts require lubrication, but in industries like food processing or pharmaceuticals, traditional oils and greases can be a source of contamination or may be dissolved by solvents. PTFE's extremely low coefficient of friction allows it to function as a bearing or seal without any external lubrication, even while immersed in corrosive chemicals.
Stability Across Extreme Temperatures
PTFE maintains its structural and chemical integrity from cryogenic temperatures (-450°F / -268°C) to elevated heat. This means it can be used for sealing super-cooled media like liquid hydrogen or in high-temperature aerospace components, all while resisting any potential chemical attack.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE should be a deliberate decision based on its well-understood performance profile.
- If your primary focus is general chemical processing (acids, bases, solvents): PTFE is an industry-standard choice, offering exceptional reliability and long service life.
- If your primary focus is medical, food, or pharmaceutical applications: PTFE's inertness is critical for preventing contamination and withstanding aggressive sterilization protocols.
- If your environment involves reactive alkali metals or strong fluorinating agents: You must avoid PTFE and seek a specialized alternative, as it will fail under these specific conditions.
Ultimately, understanding both PTFE's unparalleled chemical resistance and its precise limitations is the key to engineering with confidence.
Summary Table:
| Property | Performance | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to most acids, bases, solvents | Chemical processing, medical devices |
| Temperature Range | Stable from -450°F to high heat | Aerospace, cryogenics |
| Friction Coefficient | Extremely low, self-lubricating | Seals, bearings in corrosive environments |
| Key Limitations | Vulnerable to alkali metals, fluorinating agents | Avoid in specialized industrial settings |
Need reliable PTFE components for your demanding applications? At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE seals, liners, and labware tailored for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure your components withstand harsh chemicals and extreme conditions. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and benefit from our expertise in material performance and precision production!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the physical properties of PTFE O-rings? A Guide to Their Unique Strengths and Limitations
- What are the key advantages of using PTFE envelope gaskets? Superior Sealing for Aggressive Chemical & High-Pressure Applications
- What are the primary applications of PTFE bars in the chemical industry? Solve Your Toughest Corrosion Problems
- What are critical installation practices for PTFE O-rings? Avoid Leaks and Ensure a Perfect Seal
- What efficiency benefits do PTFE lip seals provide in aerospace applications? Reduce Fuel Costs & Boost Reliability
- What is a PTFE lined dual plate check valve? A Guide to Corrosion-Resistant Backflow Prevention
- How can bonded PTFE be machined after curing? A Guide to Sharp Tools & Thermal Control
- What makes Teflon suitable for electrical applications? Unmatched Insulation for Extreme Conditions



















