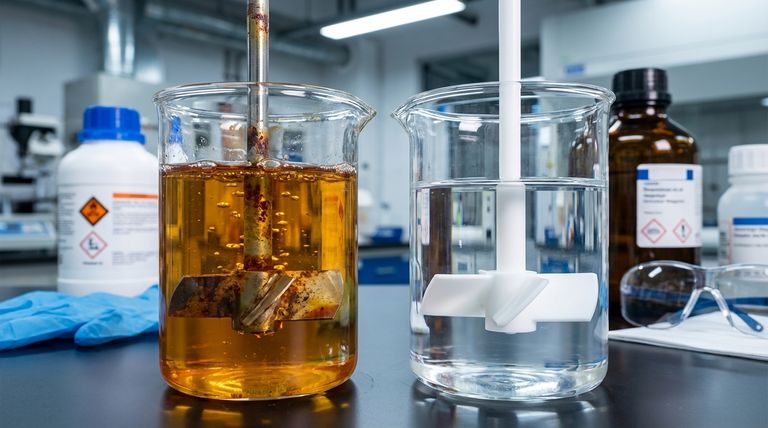
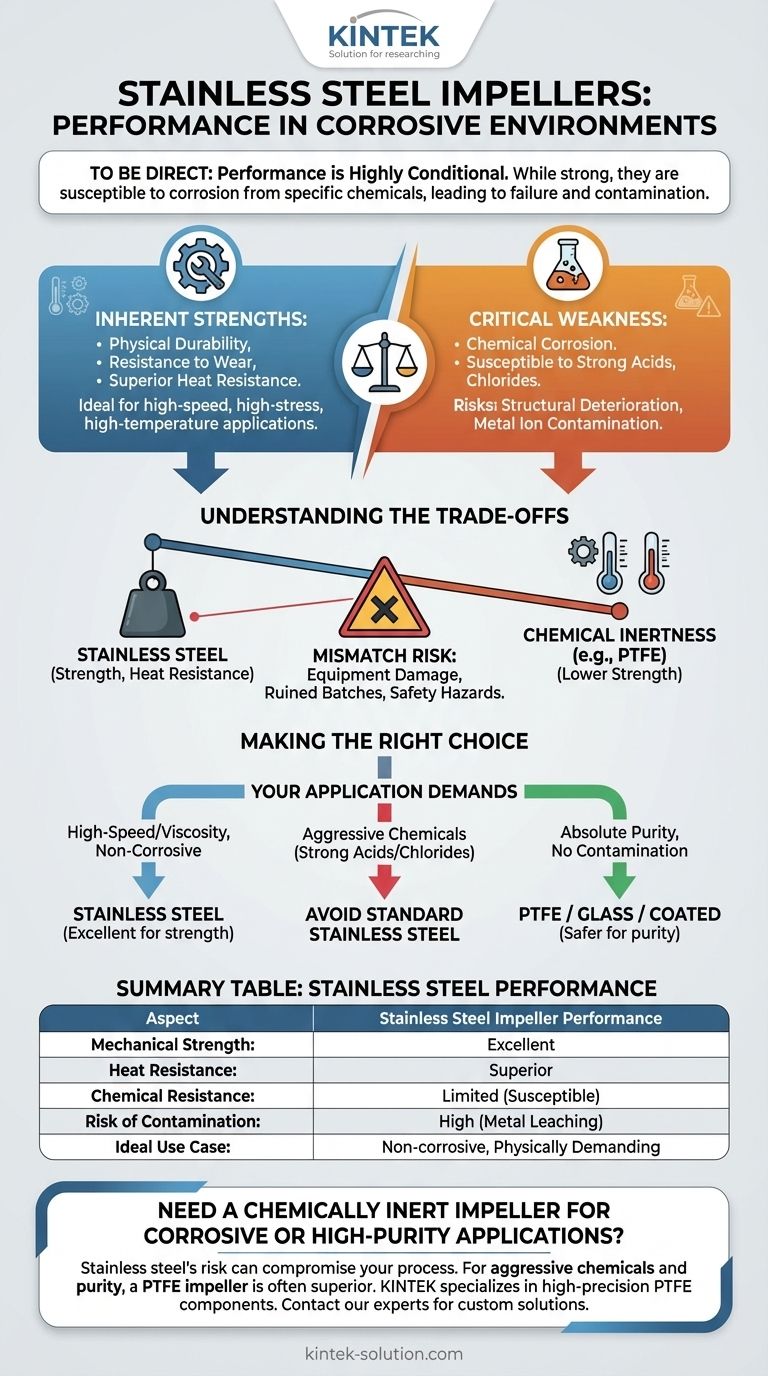
To be direct, the performance of stainless steel impellers in corrosive environments is highly conditional. While known for their physical strength and durability, they are susceptible to corrosion from specific chemicals and strong acids, which can lead to equipment failure and contamination of the mixture.
The core issue is that "stainless" does not mean "invulnerable." Choosing an impeller requires balancing the superior mechanical strength and heat resistance of stainless steel against the significant risk of chemical corrosion and product contamination in aggressive environments.

The Inherent Strengths of Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is often a default choice for laboratory and industrial equipment for several valid reasons. Its properties make it ideal for applications where physical stress is the primary concern.
Exceptional Physical Durability
Stainless steel impellers are robust. They easily withstand the high rotational speeds and mechanical stresses common in demanding mixing applications without deforming or breaking.
Resistance to Wear and Tear
This material is highly resistant to physical abrasion and wear, which ensures a long service life under normal operating conditions.
Superior Heat Resistance
Compared to polymer alternatives like PTFE, stainless steel has a much higher melting point and excellent heat resistance, making it suitable for high-temperature processes.
The Critical Weakness: Chemical Corrosion
The primary limitation of stainless steel emerges when chemical compatibility, not physical strength, is the main challenge. Its corrosion resistance is not universal.
Susceptibility to Specific Chemicals
Despite its name, stainless steel can be aggressively corroded by certain substances. Strong acids, chlorides, and other specific chemical agents can break down its protective passive layer.
The Risk of Physical Deterioration
When corrosion occurs, the impeller itself begins to deteriorate. This can lead to a loss of structural integrity, imbalanced rotation, and eventual equipment failure.
The Problem of Contamination
Perhaps the most critical risk in sensitive applications is contamination. As the impeller corrodes, metal ions can leach into the mixture, compromising the purity and integrity of the final product or experimental result.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting an impeller material is rarely about finding a single "best" option; it's about understanding the compromises between mechanical properties and chemical inertness.
Strength vs. Chemical Inertness
The fundamental trade-off is clear. Stainless steel provides superior mechanical strength and temperature resistance, while materials like PTFE offer far greater chemical inertness at the cost of lower physical durability and heat tolerance.
The Cost of a Mismatch
Using a stainless steel impeller in an incompatible chemical environment is a significant risk. The consequences include not only damage to the equipment but also ruined batches, inaccurate data, and potential safety hazards.
Always Verify Compatibility
Before using a stainless steel impeller, it is crucial to consult a chemical compatibility chart. You must verify that the specific grade of steel is resistant to all chemicals in your mixture at the intended operating temperatures and concentrations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the specific demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is high-speed or high-viscosity mixing in a non-corrosive medium: Stainless steel is an excellent choice for its strength and durability.
- If your primary focus is mixing chemically aggressive solutions, especially strong acids or chlorides: You should avoid standard stainless steel to prevent corrosion and sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is ensuring the absolute purity of the final mixture: A more inert material like glass or PTFE-coated steel is a safer choice to eliminate the risk of metal leaching.
Ultimately, matching the impeller material to the specific chemical environment is the only way to ensure reliable and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Stainless Steel Impeller Performance |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent for high-speed, high-viscosity mixing |
| Heat Resistance | Superior; suitable for high-temperature processes |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited; susceptible to strong acids, chlorides |
| Risk of Contamination | High; metal ions can leach into mixture |
| Ideal Use Case | Non-corrosive, physically demanding applications |
Need a chemically inert impeller for corrosive or high-purity applications?
Stainless steel's risk of corrosion and contamination can compromise your process. For mixing aggressive chemicals like strong acids or ensuring product purity, a PTFE impeller is often the superior choice.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom impellers, seals, and labware. We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, offering custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Ensure process reliability and product integrity. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and receive a solution tailored to your chemical and mechanical requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- Why are PTFE vials considered environmentally friendly? Reduce Lab Waste with Durable Reusables
- What industrial applications does PTFE have? Unlock Performance in Extreme Environments
- What are the primary applications of PTFE? Unlocking High-Performance Solutions
- What are the common characteristics of Teflon? Unlocking Extreme Chemical and Thermal Resistance
- Why is chemical compatibility important when choosing a PTFE-coated septum? Avoid Sample Contamination and Data Loss



















