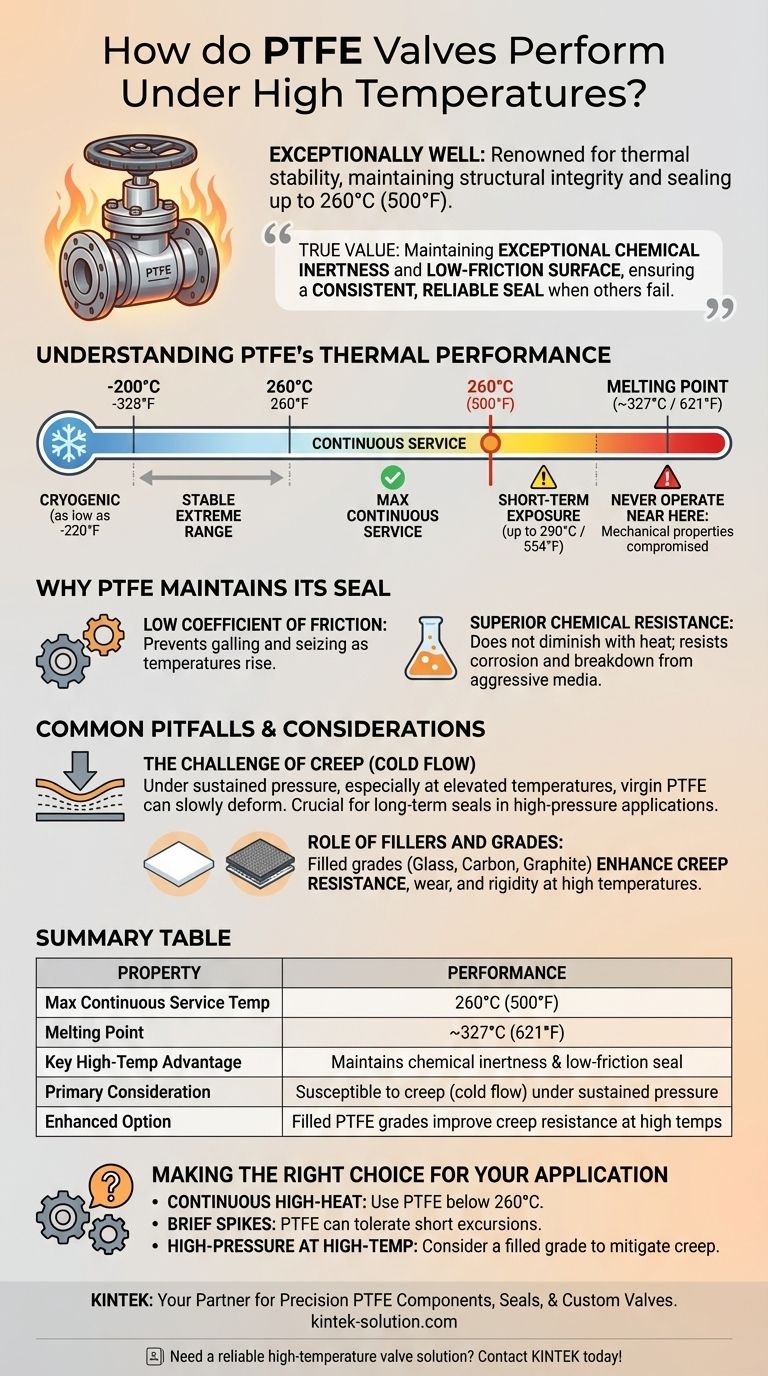
In short, PTFE valves perform exceptionally well under high temperatures. They are renowned for their thermal stability, reliably maintaining their structural integrity and sealing capabilities at continuous service temperatures up to 260°C (500°F). This makes PTFE a standard choice for demanding applications where both heat and chemical resistance are critical.
The true value of PTFE in high-temperature environments is not just its heat tolerance, but its ability to maintain its exceptional chemical inertness and low-friction surface, ensuring a consistent, reliable seal when other materials would degrade or fail.

Understanding PTFE's Thermal Performance
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) possesses a unique molecular structure that gives it remarkable stability across an extreme temperature range. This stability is the foundation of its performance in critical valve applications.
The Critical Temperature Thresholds
It is essential to distinguish between different temperature limits. For most engineering applications, the maximum continuous service temperature for PTFE is 260°C (500°F).
The material can often handle short-term exposure to higher temperatures, in some cases up to 290°C (554°F), without immediate degradation. However, its ultimate melting point is approximately 327°C (621°F). Operating near this temperature is never advised as mechanical properties will be severely compromised.
Why PTFE Maintains Its Seal
PTFE's effectiveness at high temperatures comes from its ability to retain its key physical properties. Its low coefficient of friction prevents the valve components from galling or seizing as temperatures rise.
Furthermore, its superior chemical resistance does not diminish with heat, ensuring it won't corrode or break down when exposed to aggressive media, a common cause of seal failure in other materials.
Stability Across an Extreme Range
While its high-heat performance is notable, PTFE is also exceptionally capable in cryogenic conditions. It maintains its properties in temperatures as low as -200°C (-328°F) and even lower.
This makes PTFE valves suitable for systems that experience dramatic temperature swings, from deep cold to high heat, without a loss of sealing performance.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While PTFE is a robust material, understanding its limitations is key to successful implementation. Its performance is not absolute and can be affected by specific operational conditions.
The Challenge of Creep (Cold Flow)
One of the primary trade-offs with PTFE is its susceptibility to creep, also known as cold flow. Under sustained pressure, especially at elevated temperatures, the material can slowly deform over time.
This can potentially compromise a long-term seal in high-pressure applications. Engineers must account for this behavior during the design phase.
The Role of Fillers and Grades
Not all PTFE is created equal. The performance characteristics described are for pure, or "virgin," PTFE.
Filled grades of PTFE, which include additives like glass, carbon, or graphite, are often used to enhance specific properties. These fillers can significantly improve creep resistance, wear, and rigidity at high temperatures, though sometimes at the expense of some chemical resistance.
Service Temperature vs. Melting Point
It is a critical error to conflate a material's maximum service temperature with its melting point. The service temperature is the highest temperature at which the material can reliably perform its mechanical function.
Pushing PTFE valves too close to the melting point will cause a rapid decline in their ability to hold a seal long before they actually liquefy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right valve material requires matching its properties to your specific operational goals.
- If your primary focus is continuous high-heat service: PTFE is an excellent choice, but be sure to operate consistently at or below the recommended 260°C (500°F) limit.
- If your system experiences brief temperature spikes: PTFE can likely tolerate short excursions above its continuous service limit, but this should not be a regular operational condition.
- If you need to maintain a high-pressure seal at high temperatures: Standard PTFE is a strong candidate, but consider a filled grade to mitigate the long-term risk of material creep.
Ultimately, PTFE's unique combination of thermal stability and chemical inertness makes it one of the most reliable choices for valve seals in extreme temperature environments.
Summary Table:
| Property | Performance |
|---|---|
| Max Continuous Service Temp | 260°C (500°F) |
| Melting Point | ~327°C (621°F) |
| Key High-Temp Advantage | Maintains chemical inertness & low-friction seal |
| Primary Consideration | Susceptible to creep (cold flow) under sustained pressure |
| Enhanced Option | Filled PTFE grades improve creep resistance at high temps |
Need a reliable high-temperature valve solution? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and custom valves, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get a component that delivers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance for your most demanding applications. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and let our solutions enhance your system's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications



















