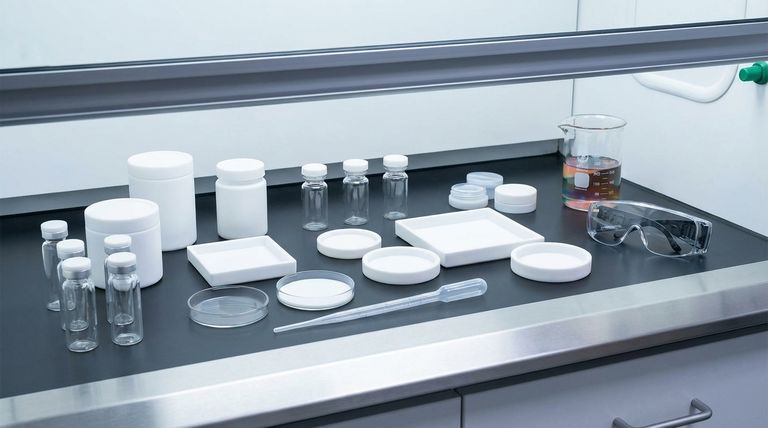
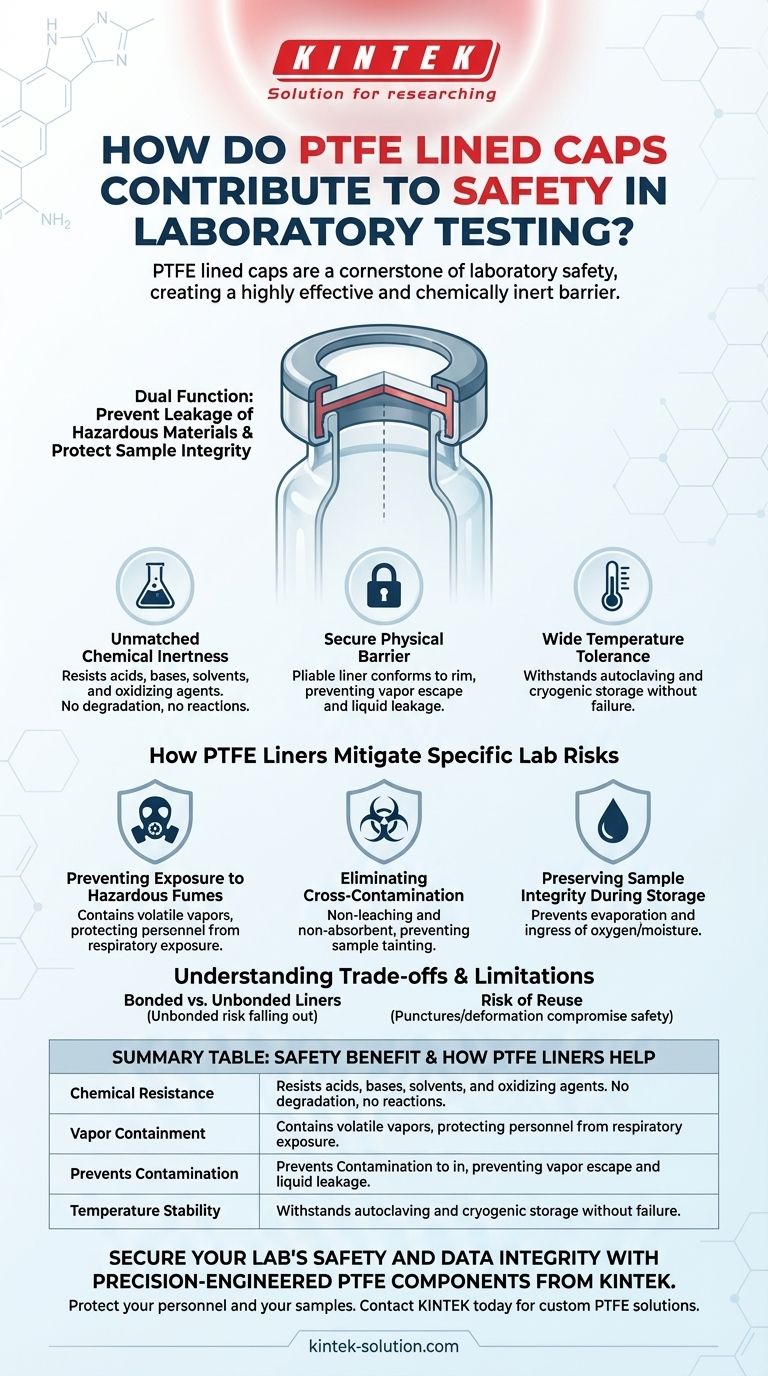
PTFE lined caps are a cornerstone of laboratory safety because they create a highly effective and chemically inert barrier. This dual function is critical for preventing the leakage of hazardous materials, protecting personnel from exposure, and ensuring the integrity of the sample itself.
The true value of a PTFE lined cap lies in its ability to be an invisible, non-reactive guardian. By creating an exceptionally secure and chemically inert seal, it simultaneously protects the lab environment from the sample and the sample from contamination.

The Science Behind the Seal: Why PTFE Excels
To understand the safety benefits, you must first understand the material itself. PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a fluoropolymer with a unique combination of properties that make it ideal for demanding laboratory applications.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is famous for being one of the most non-reactive materials known. It resists attack from a vast range of aggressive chemicals, including strong acids, bases, solvents, and oxidizing agents.
This inertness is a primary safety feature. It ensures the cap liner will not degrade, dissolve, or react when in contact with the container's contents, which could otherwise compromise the seal and lead to a dangerous leak.
A Secure Physical Barrier
The PTFE liner is a pliable material that conforms to the rim of the vial or bottle, creating a tight, reliable seal.
This physical barrier prevents the escape of volatile vapors, which can be toxic or flammable, safeguarding the air quality in the lab. It also stops liquid from leaking due to agitation, transportation, or accidental tipping.
Wide Temperature Tolerance
PTFE maintains its integrity across a broad temperature range. It can withstand the high temperatures of autoclaving for sterilization as well as cryogenic storage conditions.
This stability prevents the liner from becoming brittle at low temperatures or melting at high ones, either of which would cause seal failure and a potential safety breach.
How PTFE Liners Mitigate Specific Lab Risks
The properties of PTFE directly translate into the mitigation of common and serious laboratory hazards. An effective cap is your first line of defense.
Preventing Exposure to Hazardous Fumes
Many laboratory reagents are volatile, releasing fumes that can be harmful if inhaled. A cap with a PTFE liner effectively contains these vapors, protecting laboratory personnel from respiratory exposure to toxic or corrosive substances.
Eliminating Cross-Contamination
Because PTFE is so non-reactive, it does not leach chemicals into the sample or absorb chemicals from the sample.
This prevents cross-contamination between different samples stored with reused caps and ensures that analytical results are accurate. Inaccurate results, especially in a diagnostic or safety context, are a risk in themselves.
Preserving Sample Integrity During Storage and Analysis
A compromised sample is a wasted sample at best and a dangerous one at worst. Evaporation can concentrate a chemical, potentially making it more hazardous.
A PTFE liner prevents this evaporation and protects the sample from oxygen or moisture ingress, ensuring the material inside the vial is exactly what you expect it to be.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, no solution is perfect for every scenario. Acknowledging the trade-offs is key to proper implementation.
Bonded vs. Unbonded Liners
Liners can be bonded (glued) into the cap or simply press-fit. Unbonded liners can sometimes fall out, creating a nuisance and a potential contamination risk if the liner drops onto a non-sterile surface.
Cost Considerations
PTFE lined caps are typically more expensive than those with simpler liners made of pulp, foil, or foam. For highly sensitive, volatile, or corrosive materials, the added cost is a necessary investment in safety and data quality. For benign applications like storing water, a cheaper option may suffice.
The Risk of Reuse
While PTFE is durable, repeated use can compromise safety. Puncturing the liner with a syringe for autosampler analysis creates a hole that compromises the seal. Repeated tightening and loosening can also deform the liner over time. For critical applications, single-use is the safest protocol.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct cap is a critical risk-assessment step. Your decision should be guided by the nature of the chemicals you are handling and your experimental goals.
- If your primary focus is storing aggressive acids, bases, or volatile organic solvents: A PTFE lined cap is the only appropriate choice to ensure liner integrity and prevent dangerous leaks.
- If your primary focus is trace-level analysis or sample purity: The non-leaching, inert nature of PTFE is essential to avoid contaminating your sample and compromising results.
- If your primary focus is general, non-hazardous storage on a tight budget: A simpler, less expensive liner may be adequate, but you must confirm it is compatible with the stored material.
Ultimately, choosing the right equipment is a fundamental part of responsible laboratory practice.
Summary Table:
| Safety Benefit | How PTFE Liners Help |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to acids, bases, solvents; prevents liner degradation and leaks. |
| Vapor Containment | Seals in volatile, toxic, or flammable fumes, protecting lab air quality. |
| Prevents Contamination | Non-leaching and non-absorbent; maintains sample purity and accuracy. |
| Temperature Stability | Withstands autoclaving and cryogenic conditions without seal failure. |
Secure your lab's safety and data integrity with precision-engineered PTFE components from KINTEK.
Whether you are handling aggressive chemicals in the semiconductor industry, managing sensitive samples in medical or laboratory settings, or require reliable seals for industrial applications, KINTEK delivers. We specialize in manufacturing high-quality PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—with a focus on precision and chemical inertness. From custom prototypes to high-volume orders, we ensure your caps provide the ultimate barrier protection.
Protect your personnel and your samples. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and receive a quote for custom PTFE solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance



















