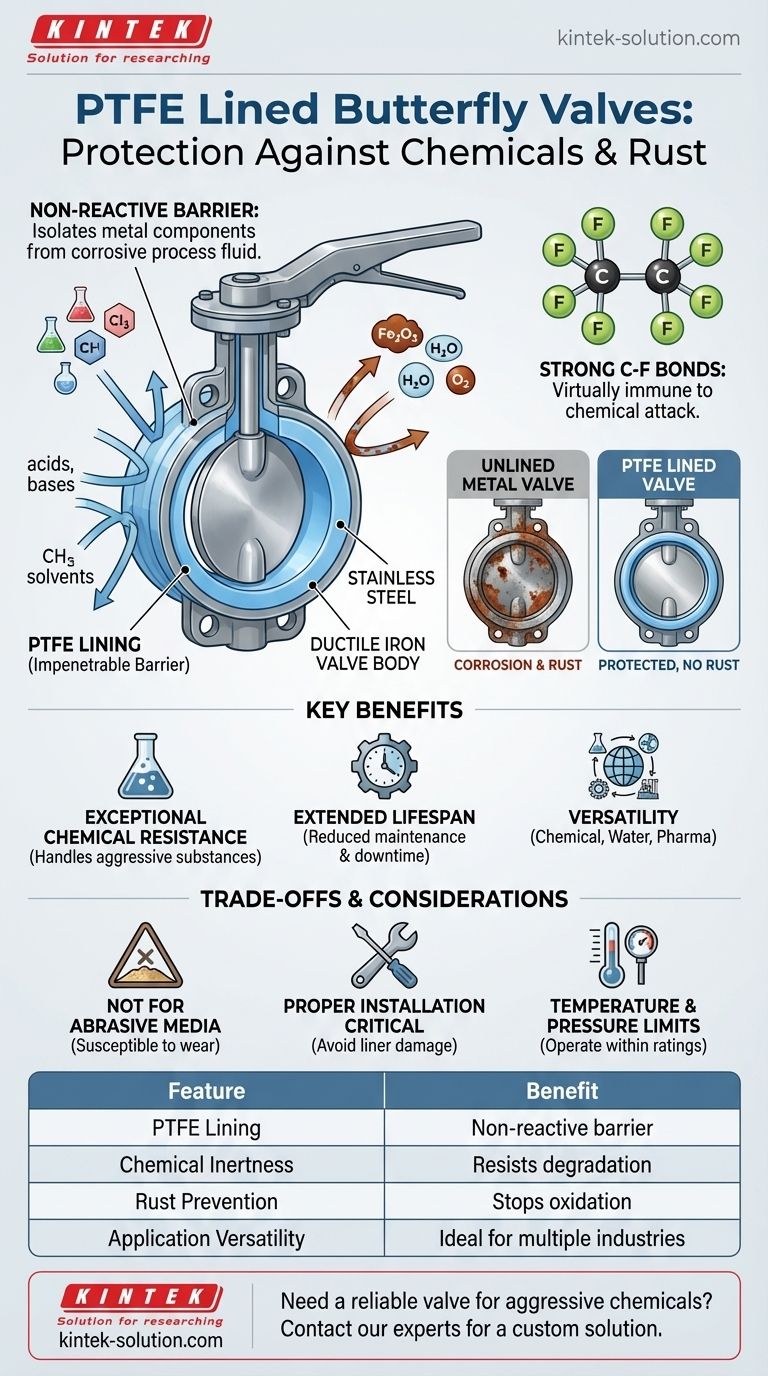
At its core, a Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) lined butterfly valve provides protection by creating a complete, non-reactive barrier between the valve's internal metal components and the process fluid. This chemically inert lining acts as an impenetrable shield, preventing corrosive media from ever making contact with the underlying metal, thereby stopping both chemical degradation and rust before they can begin.
The fundamental value of a PTFE lining lies in its chemical structure. The exceptionally strong carbon-fluorine bonds make PTFE virtually immune to chemical attack, allowing the valve to operate reliably in aggressive environments where unlined metal valves would quickly fail.

The Core Principle: Chemical Inertness
A valve's longevity in a harsh environment depends entirely on its ability to resist the process media. PTFE lining achieves this through a simple but powerful principle: total material separation.
The Power of Carbon-Fluorine Bonds
PTFE is a fluoropolymer, and its defining feature is the strength of its carbon-fluorine bonds. These are among the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry.
This molecular stability is what makes PTFE chemically inert. It does not react with nearly all acids, bases, strong oxidants, or organic solvents, making it a perfect material for a protective shield.
Creating an Impenetrable Barrier
In a PTFE-lined butterfly valve, the liner is molded to cover all "wetted" parts—the interior of the valve body and the surface of the disc.
This means the corrosive fluid only ever touches the PTFE. The structural metal parts, such as the ductile iron body or stainless steel disc, are completely isolated from the hostile media.
How It Prevents Rust
Rust is simply the oxidation of iron or its alloys. This chemical reaction requires the metal to be exposed to an oxidant, often found in water or acidic solutions.
By physically preventing this contact, the PTFE lining effectively stops the oxidation process. The metal components are shielded, so rust cannot form, ensuring the valve's structural integrity is maintained.
Key Benefits in Demanding Applications
The robust nature of the PTFE lining translates directly into significant operational advantages, especially in industries where media compatibility is a primary concern.
Exceptional Chemical Resistance
The chemical inertness of PTFE is comprehensive. It allows these valves to handle some of the most aggressive substances used in industry, including aqua regia, strong acids, and powerful alkalis without degrading.
Extended Lifespan and Reliability
Because the lining protects the valve from its primary failure mechanism—corrosion—the valve lasts significantly longer. This results in reduced maintenance needs, less downtime, and lower replacement costs over the system's life.
Versatility Across Industries
The combination of durability and high resistance makes these valves suitable for a wide range of applications. They are commonly specified in chemical processing, water treatment, pharmaceuticals, and other industries that handle corrosive or high-purity media.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While PTFE-lined valves are a powerful solution, they are not universally applicable. Understanding their limitations is key to proper selection and avoiding failure.
Not Ideal for Abrasive Media
PTFE is a relatively soft material. While it excels with corrosive liquids and gases, it can be quickly damaged by fluids containing abrasive solids, such as sand, sludge, or other particulates. These particles can wear away or tear the lining, leading to a catastrophic failure.
Proper Installation is Critical
The integrity of the valve depends entirely on the integrity of the liner. Any damage to the lining during installation, such as a scratch or a tear, creates a leak path for corrosive media to attack the underlying metal. Careful handling and proper flange alignment are essential.
Temperature and Pressure Limits
PTFE has a high temperature tolerance, but it is not limitless. Exceeding the manufacturer's specified temperature and pressure ratings can cause the liner to deform, lose its seal, or fail. It is crucial to operate the valve within its designated design limits.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Selecting the correct valve requires matching its material properties to the specific demands of your process fluid and operating conditions.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive chemicals: A PTFE-lined valve is an ideal and cost-effective choice due to its near-universal chemical inertness.
- If your system contains abrasive solids or slurries: You should specify a valve with a hard-wearing metal or ceramic seat, as a soft PTFE liner will be susceptible to mechanical damage.
- If your goal is long-term, low-maintenance reliability: The protective nature of the PTFE lining provides a durable solution that minimizes downtime and reduces total cost of ownership in compatible applications.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE-lined valve is an investment in chemical compatibility and long-term operational stability.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| PTFE Lining | Creates a non-reactive barrier, isolating metal parts from corrosive fluids. |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all acids, bases, and solvents, preventing degradation. |
| Rust Prevention | Stops oxidation by blocking contact between metal and oxidants. |
| Application Versatility | Ideal for chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and water treatment. |
Need a reliable valve for aggressive chemicals? KINTEK specializes in precision-manufactured PTFE components, including custom-lined butterfly valves, seals, and labware. We protect your systems from corrosion in the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and get a custom solution that ensures long-term performance and reduces your total cost of ownership.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the limitations of PTFE in terms of fabrication? Navigating Manufacturing Challenges
- Why are PTFE bushes preferred in harsh chemical environments? Ensure Unmatched Reliability and Low Friction
- How does the non-absorbent nature of PTFE Teflon washers affect their performance? Ensure Long-Term Sealing Reliability
- What are the overall benefits of PTFE spring energized seals for oil and gas operations? Achieve Unmatched Reliability in HPHT Environments
- What are the recommended cutting parameters for machining PTFE? Achieve Precision with the Right Speed, Feed, and Depth of Cut
- What are the features of split-film PTFE gland packing? A High-Pressure Sealing Solution
- What is PV value and why is it important for PTFE seals? Prevent Premature Seal Failure
- What industries commonly use PTFE gasket materials? Ensure Sealing Integrity in Demanding Environments



















