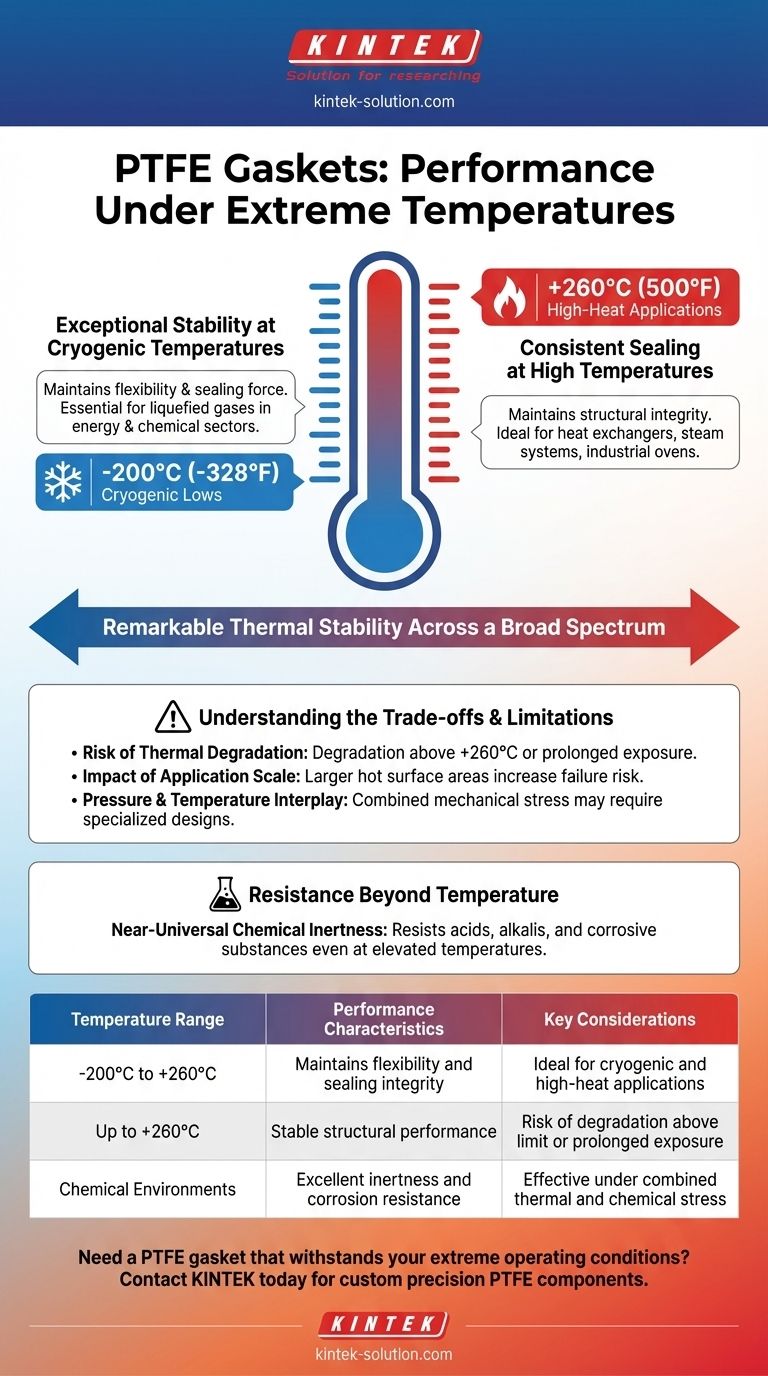
In short, PTFE gaskets exhibit remarkable thermal stability across a broad spectrum of temperatures. They are engineered to maintain their sealing integrity in conditions ranging from cryogenic lows of -200°C (-328°F) up to high-heat applications reaching +260°C (500°F), making them a versatile choice for many demanding industries.
While PTFE offers an impressive operational temperature range, its reliability at the upper limit is not absolute. True success hinges on understanding how factors like exposure duration and application scale can impact material integrity and prevent seal failure.

The Foundation of PTFE's Thermal Performance
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) possesses a unique molecular structure that gives it exceptional resistance to thermal stress. This stability is consistent across both extreme cold and high heat, which is rare among sealing materials.
Exceptional Stability at Cryogenic Temperatures
PTFE gaskets perform reliably in cryogenic systems where temperatures can plummet to -200°C (-328°F). Unlike many materials that become brittle and fail at such low temperatures, PTFE retains sufficient flexibility and sealing force.
This property makes it essential for applications involving liquefied gases and other super-cooled processes found in the energy and chemical sectors.
Consistent Sealing at High Temperatures
At the other end of the spectrum, PTFE gaskets maintain their structural integrity and sealing properties in continuous service up to +260°C (500°F).
This makes them ideal for high-temperature equipment such as heat exchangers, steam systems, and industrial ovens where consistent, reliable sealing under thermal load is critical.
Resistance Beyond Temperature
The operational environment for a gasket is rarely limited to just one variable. PTFE's thermal stability is complemented by its near-universal chemical inertness.
It resists degradation from acids, alkalis, and other corrosive substances, even at elevated temperatures. This dual resistance makes it a robust solution for complex and harsh industrial environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is without its operational boundaries. While PTFE's temperature range is wide, pushing it to its upper limit requires careful consideration to avoid failure.
The Risk of Thermal Degradation
The most significant limitation is the potential for thermal breakdown. If exposed to temperatures above its +260°C rating or for prolonged periods near this limit, PTFE can begin to degrade.
This degradation can cause the material to soften, creep, or even burn, leading to a complete loss of the seal.
The Impact of Application Scale
Caution is especially warranted in applications involving large, hot surface areas. A larger gasket has more potential for uneven heating and sustained thermal load across its surface.
This increases the risk of finding a weak point where degradation can begin, ultimately compromising the entire seal.
Pressure and Temperature Interplay
In applications with both high pressure and high temperature, the mechanical stress on the gasket is amplified. While certain designs like PTFE envelope gaskets are engineered to handle these combined forces, standard PTFE may not be sufficient.
It is critical to evaluate the combined system demands, not just temperature in isolation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To leverage PTFE's benefits effectively, align its properties with your specific operational goal.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic or low-temperature sealing: PTFE is an exceptionally reliable choice, maintaining its integrity down to -200°C without becoming brittle.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature operations up to 260°C: PTFE is highly effective, but you must carefully evaluate the duration of exposure and the total surface area to mitigate the risk of thermal degradation.
- If your primary focus is sealing in harsh chemical environments: PTFE's chemical inertness, combined with its wide temperature range, makes it a superior material for handling corrosive substances under thermal stress.
Understanding these operational boundaries is the key to leveraging PTFE's thermal capabilities for long-term, reliable sealing.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Performance Characteristics | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| -200°C to +260°C | Maintains flexibility and sealing integrity | Ideal for cryogenic and high-heat applications |
| Up to +260°C | Stable structural performance | Risk of degradation above limit or prolonged exposure |
| Chemical Environments | Excellent inertness and corrosion resistance | Effective under combined thermal and chemical stress |
Need a PTFE gasket that withstands your extreme operating conditions?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, gaskets, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require custom prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures your gaskets deliver reliable performance under thermal stress, chemical exposure, and pressure.
Contact us today to discuss your application requirements and receive a tailored solution that guarantees sealing integrity and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How is Teflon coating applied in the construction industry? Enhancing Safety and Durability in Building Components
- What are dynamic applications and why are PTFE O-Rings suitable for them? Unlock Low-Friction, Chemical-Resistant Sealing
- What is the role of PTFE sheets in sublimation printing? Achieve Flawless, Professional Results
- What are the key differences between NBR and PTFE seat materials in butterfly valves? Choose the Right Material for Your System
- What properties make Teflon sheets useful for industrial applications? Solve Friction, Heat, and Chemical Challenges
- Which industries commonly use Teflon bushes? Solve Critical Engineering Challenges in Harsh Environments
- What types of flange connections benefit from PTFE envelope gaskets? Seal Fragile Flanges & Harsh Chemicals
- What are the benefits of using PTFE lined check valves in water pump systems? Boost Reliability & Cut Costs



















