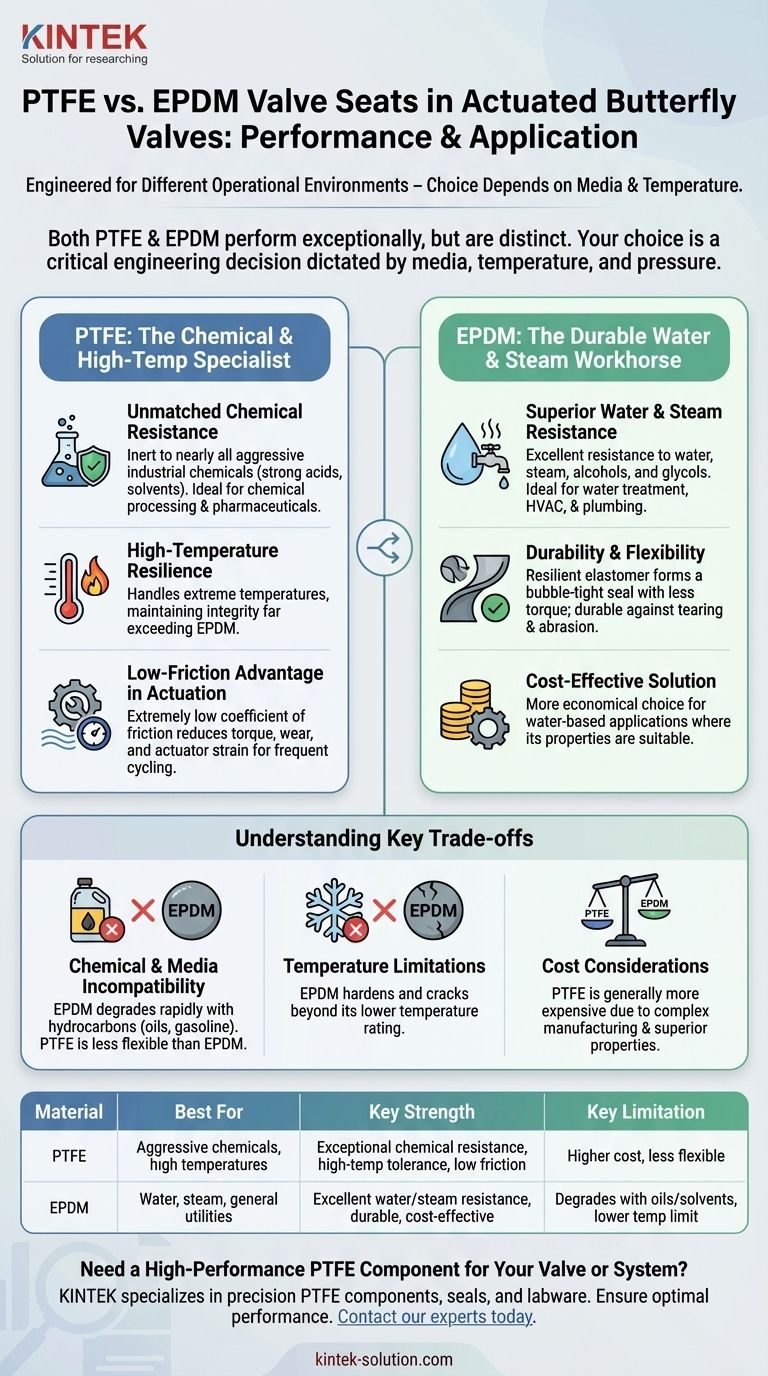
Both PTFE and EPDM perform exceptionally well in actuated butterfly valves, but they are engineered for fundamentally different operational environments. Your choice depends entirely on the chemical media and temperature of your system. PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is the definitive choice for aggressive chemicals and high-temperature applications, while EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) is the durable, cost-effective standard for water, steam, and general utility services.
The decision between PTFE and EPDM is not about which material is "better" in a general sense. It is a critical engineering choice dictated by your system's specific media, temperature, and pressure to ensure optimal performance, safety, and valve longevity.

The Profile of PTFE: The Chemical and High-Temp Specialist
PTFE seats are specified when the operational demands are severe. Their unique molecular structure makes them inert to nearly all industrial chemicals and capable of handling extreme temperatures.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is renowned for its exceptional chemical inertness. It can handle a vast range of aggressive media, including strong acids, solvents, and corrosive chemicals, without degrading.
This makes PTFE the default choice for applications in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and other industries where media compatibility is the primary concern.
High-Temperature Resilience
Alongside its chemical resistance, PTFE offers a high-temperature tolerance that far exceeds that of EPDM. This allows it to maintain its integrity and sealing capability in demanding, high-heat processes.
The Low-Friction Advantage in Actuation
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction. In an actuated valve (whether electric or pneumatic) that may cycle frequently, this property is a significant advantage.
This low-friction surface reduces the torque required to open and close the valve, minimizing wear on the seat and actuator, which contributes to a longer service life and greater system efficiency.
The Profile of EPDM: The Durable Water and Steam Workhorse
EPDM is a versatile and resilient elastomer that serves as the backbone for a huge number of industrial and commercial applications, particularly those involving water.
Superior Water and Steam Resistance
EPDM's primary strength is its excellent resistance to water, steam, alcohols, and glycols. It does not swell or degrade when exposed to these common media.
This makes it the ideal material for water treatment plants, HVAC systems, and general plumbing applications where a reliable, long-lasting seal against water is necessary.
Durability and Flexibility
EPDM is a flexible and resilient material. This elasticity allows it to form a reliable, bubble-tight seal with less torque than harder materials might require.
Its durability also gives it good resistance to tearing and abrasion, making it a robust choice for systems that don't involve harsh chemicals or high temperatures.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong material can lead to premature valve failure, leaks, and system downtime. The decision requires a clear-eyed view of each material's limitations.
Chemical and Media Incompatibility
This is the most critical trade-off. Using an EPDM seat in a system with hydrocarbons (oils, gasoline) or many solvents will cause it to swell and degrade rapidly, leading to seal failure.
Conversely, while PTFE is chemically robust, it is less flexible than EPDM, which can be a factor in certain low-pressure sealing applications.
Temperature Limitations
EPDM has a much lower maximum operating temperature than PTFE. Exposing an EPDM seat to temperatures beyond its rating will cause it to harden, crack, and lose its ability to seal effectively.
Cost Considerations
Generally, PTFE is a more expensive material than EPDM due to its complex manufacturing process and superior chemical and thermal properties. For water-based applications where EPDM is suitable, it is almost always the more economical choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your system's operational parameters must be the sole guide for your selection.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals or high temperatures: Choose PTFE. Its chemical inertness and thermal resilience are non-negotiable for ensuring safety and reliability in these environments.
- If your primary focus is water, steam, or general utilities: Choose EPDM. It provides excellent, durable performance for these applications at a more favorable cost.
- If your system involves frequent cycling via an actuator: Consider the benefits of PTFE's low friction, which can reduce wear and actuator strain, but only if it also meets your chemical and temperature requirements.
Ultimately, selecting the correct valve seat is a foundational step in designing a safe and reliable automated flow control system.
Summary Table:
| Material | Best For | Key Strength | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE | Aggressive chemicals, high temperatures | Exceptional chemical resistance, high-temp tolerance, low friction | Higher cost, less flexible than EPDM |
| EPDM | Water, steam, general utilities | Excellent water/steam resistance, durable, cost-effective | Degrades with oils/solvents, lower temp limit |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Component for Your Valve or System?
Selecting the right material is critical for safety and performance. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to meet your exact specifications.
Ensure optimal valve performance and longevity. Contact our experts today to discuss your PTFE component needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How does the application of PTFE gaskets improve equipment performance? Enhance Sealing Integrity & Reliability
- What are the standard temperature limits for PTFE Teflon O-rings? Master the -200°C to 250°C Range
- When might additional lubrication be needed for PTFE applications? Understand the exceptions to the rule.
- What are the main machining techniques used for PTFE? Achieve Precision with CNC Turning, Milling & More
- Why is the manufacturing cost of PTFE processing machines high? The Engineering Behind High-Performance Polymer Processing
- What additional construction applications exist for PTFE beyond slide bearings? Leverage PTFE for Thermal Breaks & Washers
- What is the Shore hardness and compression strength of PTFE? A Guide to Its Mechanical Limits
- What is the recommended method for bonding PTFE to its support? Achieve a Permanent, High-Strength Bond



















