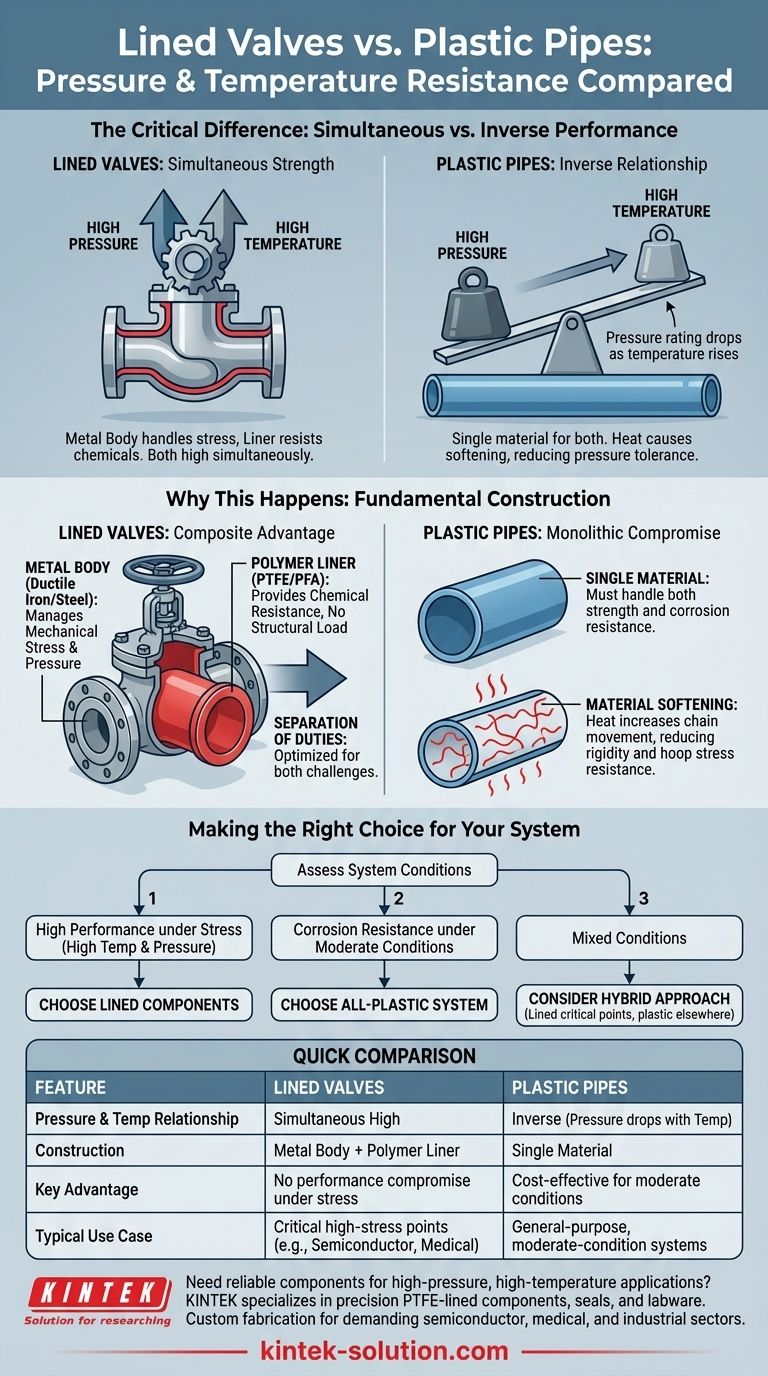
The critical difference is that lined valves can withstand high pressure and high temperature simultaneously, whereas plastic pipes cannot. The performance of plastic piping is defined by an inverse relationship between these two factors; as temperature rises, its ability to contain pressure decreases significantly.
The core reason for this performance gap lies in their fundamental construction. A lined valve combines a structural metal body with a chemically resistant polymer liner, separating the duties of mechanical strength and corrosion resistance. A plastic pipe uses a single material to handle both, creating an inherent compromise.

The Structural Advantage of Lined Valves
A lined valve is a composite component designed to optimize for two different challenges at once: mechanical stress and chemical attack. This separation of duties is the key to its superior performance in demanding applications.
The Role of the Metal Body
The outer casing of a lined valve is typically made of robust metal like ductile iron or steel. This metal body is solely responsible for managing the mechanical stresses of the system.
It contains the internal pressure and resists the physical strain caused by high temperatures and thermal expansion. The metal provides the structural integrity that plastic alone cannot.
The Role of the Polymer Liner
Inside the metal body is a thick, seamless liner made from a chemically inert fluoropolymer, such as Teflon (PTFE/PFA). This polymer liner never has to bear the system's pressure or thermal stress.
Its only job is to provide a barrier against corrosive or high-purity media. Because it is not a structural component, its chemical resistance is not compromised by mechanical load.
The Inherent Limitation of Plastic Piping
Plastic piping systems are monolithic, meaning the same material must perform every function. This creates a performance trade-off that is especially apparent under thermal load.
The Inverse Relationship: Pressure vs. Temperature
All-plastic pipes have a pressure rating that is highly dependent on temperature. A pipe that can safely handle 150 PSI at room temperature might only be rated for 30 PSI at a higher temperature.
This inverse relationship is a fundamental characteristic of thermoplastic materials.
Why This Happens: Material Softening
As temperature increases, polymer chains gain energy and move more freely, causing the material to soften and lose its rigidity and tensile strength.
This softening effect dramatically reduces the pipe's ability to resist the hoop stress generated by internal pressure, making it susceptible to bursting or catastrophic failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these components is not just about maximum performance. It involves balancing capability, complexity, and cost for the specific application.
System Integrity and Point of Failure
Valves and fittings are often the most complex points in a piping system and are subject to higher stress. Using a robust lined valve ensures these critical points are not the weak links.
However, a lined valve in a plastic piping system only moves the potential point of failure to the adjacent plastic pipe if the system's limits are exceeded.
Cost and Complexity
Lined valves are inherently more complex and expensive to manufacture than simple plastic pipes due to their multi-material construction.
For applications with moderate temperatures or pressures, an all-plastic system is a far more cost-effective solution.
Installation and Weight
Plastic piping is significantly lighter and often easier to install than metal-bodied components. This can reduce labor costs and the need for heavy-duty support structures.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Your decision should be dictated by the operating conditions your system will face.
- If your primary focus is high performance under stress: Choose lined components for any part of your system that will experience high temperatures and high pressures simultaneously.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance under moderate conditions: An all-plastic piping system is often the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your system has mixed conditions: Consider a hybrid approach, using lined valves and components at critical high-stress points within a larger plastic piping system.
Ultimately, understanding how each component derives its strength allows you to design a system that is both safe and economically sound.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Lined Valves | Plastic Pipes |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure & Temperature Relationship | Can withstand high pressure and high temperature simultaneously | Inverse relationship: pressure rating drops as temperature rises |
| Construction | Metal body for strength + polymer liner for chemical resistance | Single material handles both strength and corrosion resistance |
| Key Advantage | Separation of duties: no performance compromise under stress | Cost-effective for moderate conditions |
| Typical Use Case | Critical high-stress points in demanding applications (e.g., semiconductor, medical) | General-purpose, moderate-condition systems |
Need reliable components for high-pressure, high-temperature applications? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE-lined components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. Our custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure your system's integrity under the most demanding conditions. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and let us provide a solution that guarantees safety and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry



















