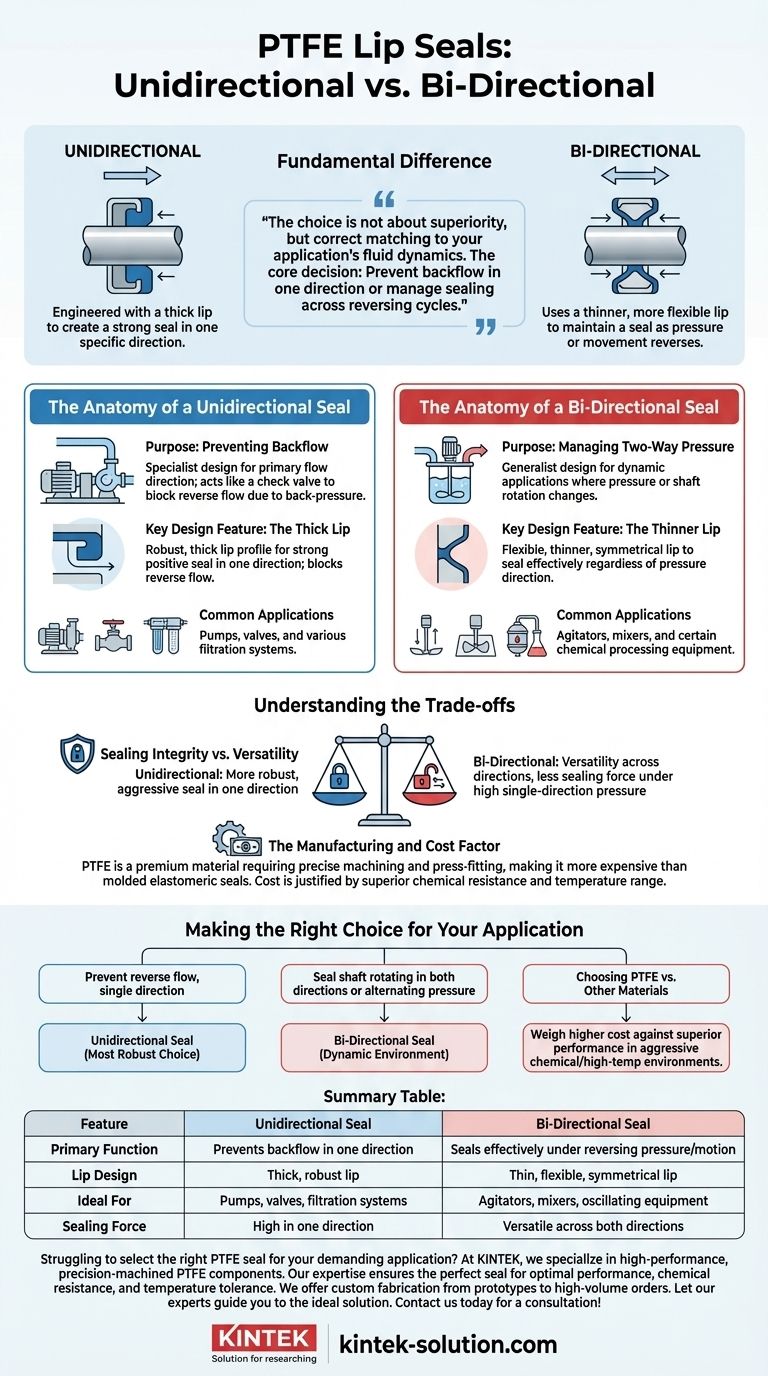
The fundamental difference between bi-directional and unidirectional PTFE lip seals lies in their design and intended function. A unidirectional seal is engineered with a thick lip to create a strong seal in one specific direction, while a bi-directional seal uses a thinner, more flexible lip to maintain a seal as pressure or movement reverses.
Your choice between these two seal types is not about which is superior, but which is correctly matched to the fluid dynamics of your application. The core decision hinges on whether you need to prevent backflow in a single direction or manage sealing across reversing cycles.

The Anatomy of a Unidirectional Seal
A unidirectional seal is a specialist, designed for applications with a primary flow direction where preventing any form of reverse flow is critical.
Purpose: Preventing Backflow
These seals act like a check valve. They are deployed in systems where media is intended to flow one way, but conditions like back-pressure could cause it to reverse.
Key Design Feature: The Thick Lip
The defining feature is a thick, robust lip profile. This design creates a strong, positive seal against pressure from one side. A narrow channel is often incorporated, allowing media to flow in the intended direction while effectively blocking it from returning.
Common Applications
You will typically find unidirectional seals in equipment like pumps, valves, and various filtration systems, where maintaining the direction of flow is essential for the system's function and integrity.
The Anatomy of a Bi-Directional Seal
A bi-directional seal is a generalist, designed for dynamic applications where the direction of pressure or shaft rotation changes.
Purpose: Managing Two-Way Pressure
These seals are built for equipment where the sealing challenge is constant but not directionally consistent. Think of a shaft that rotates both clockwise and counter-clockwise or a chamber where pressure alternates.
Key Design Feature: The Thinner Lip
To seal effectively in both directions, these seals feature a thinner and often more symmetrical lip. This flexibility allows the lip to engage and seal properly regardless of which direction the pressure is applied from.
Common Applications
Their design makes them ideal for machinery with reversing or oscillating motion, such as agitators, mixers, and certain types of chemical processing equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right PTFE seal involves more than just directionality; it requires understanding the inherent compromises in their design and manufacturing.
Sealing Integrity vs. Versatility
A unidirectional seal's thick lip generally provides a more robust and aggressive seal, but only in its designed direction. The thinner lip of a bi-directional seal offers versatility but may not provide the same level of sealing force under extremely high, single-direction pressure.
The Manufacturing and Cost Factor
It is critical to remember that PTFE is a premium material. Unlike common elastomeric seals that can be molded, PTFE components must be precisely machined and then press-fitted.
This machining process, combined with the higher cost of the raw material itself, results in a more expensive final product. This cost is justified by PTFE's superior chemical resistance and temperature range, but it is a significant factor in a project's budget.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by a clear analysis of your system's operational demands.
- If your primary focus is preventing reverse flow in a system with a clear, single direction: A unidirectional seal is the correct and most robust choice.
- If your primary focus is sealing a shaft that rotates in both directions or handling alternating pressure: A bi-directional seal is explicitly designed for this dynamic environment.
- If you are choosing between PTFE and other materials: You must weigh the higher cost of machined PTFE against its superior performance in aggressive chemical or high-temperature environments.
Ultimately, matching the seal's fundamental design to the specific requirements of your application ensures optimal performance and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Unidirectional Seal | Bi-Directional Seal |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Prevents backflow in one direction | Seals effectively under reversing pressure/motion |
| Lip Design | Thick, robust lip | Thin, flexible, symmetrical lip |
| Ideal For | Pumps, valves, filtration systems | Agitators, mixers, oscillating equipment |
| Sealing Force | High in one direction | Versatile across both directions |
Struggling to select the right PTFE seal for your demanding application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance, precision-machined PTFE components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures you get the perfect seal—whether unidirectional or bi-directional—for optimal performance, chemical resistance, and temperature tolerance.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Let our experts guide you to the ideal solution. Contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are PTFE O-rings? High-Performance Seals for Extreme Conditions
- What is the purpose of a PTFE liner in rod end bearings? Achieve Maintenance-Free, Low-Friction Performance
- What are the key properties of Teflon (PTFE) used in custom parts? | Achieve Peak Performance
- Why are PTFE gaskets popular in various industries? Unmatched Chemical Resistance & Reliability
- What types of media are suitable for PTFE Bellow Mechanical Seals? Sealing the Most Aggressive Chemicals
- What advantages do PTFE valve seat rings offer? Achieve Superior Sealing in Demanding Environments
- What are the typical working conditions for POT-PTFE bearings? Key Parameters for High-Load Structural Applications
- What are the key properties of virgin Teflon balls? Leverage Superior Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















