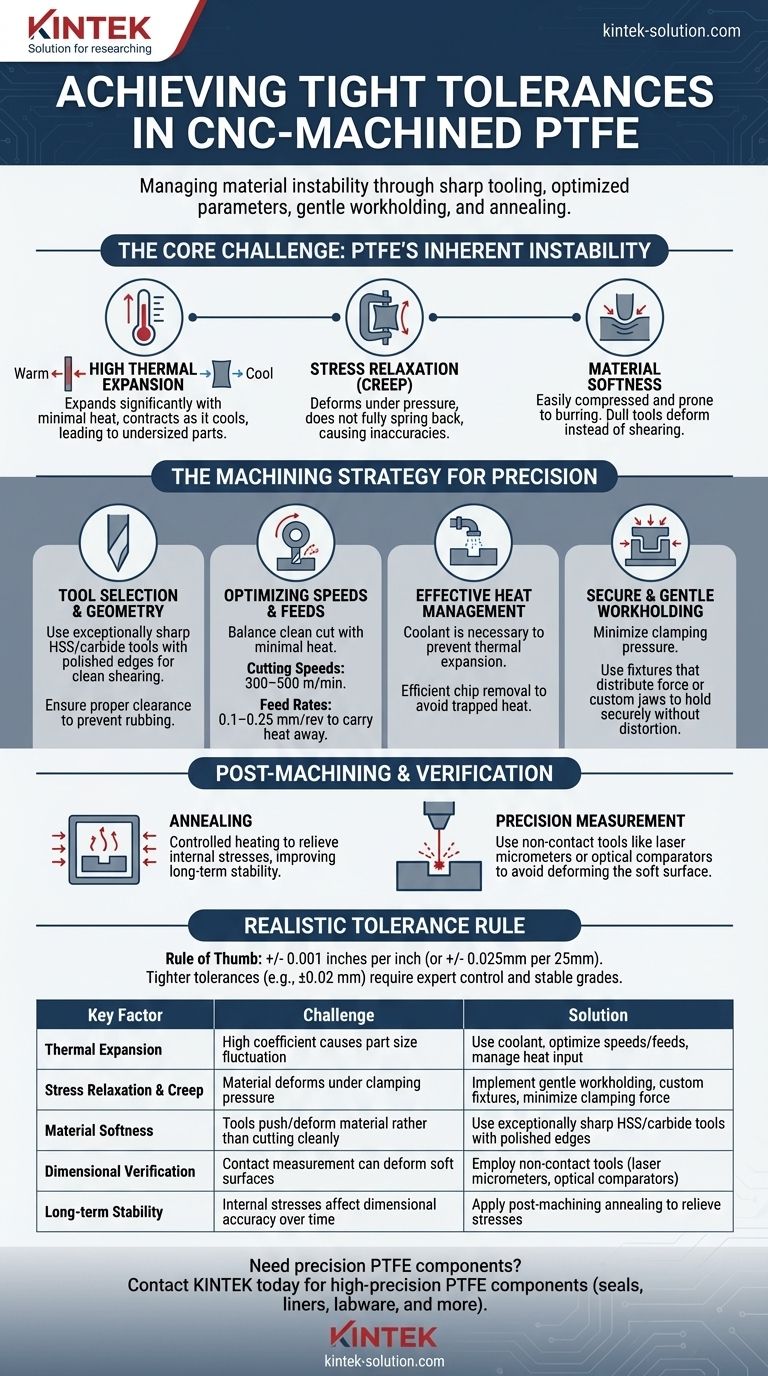
Achieving tight tolerances in CNC-machined PTFE is a process of managing the material's inherent instability. It requires a combination of extremely sharp tooling, optimized cutting parameters to minimize heat, gentle workholding, and post-machining stabilization techniques like annealing to relieve internal stresses.
The central challenge is not cutting PTFE, but controlling its high thermal expansion, softness, and tendency to creep under stress. Success depends more on managing these material properties than on the cutting operation itself.
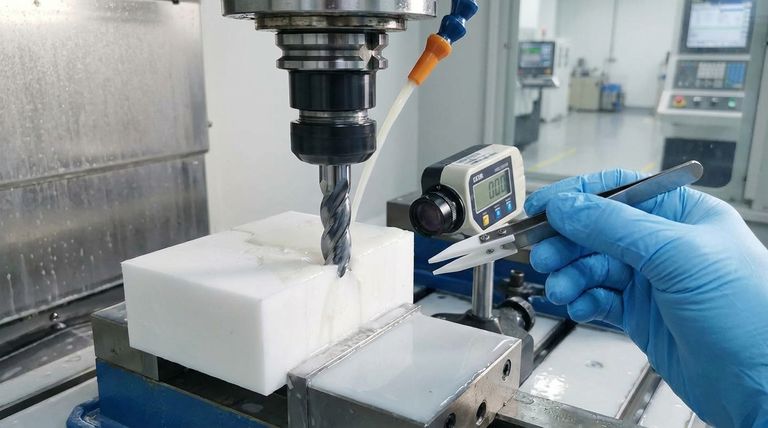

The Core Challenge: PTFE's Inherent Instability
To machine PTFE with precision, you must first understand the properties that make it difficult to control. The material itself is easy to cut, but its physical behavior during and after machining is what complicates achieving tight tolerances.
High Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a very high coefficient of thermal expansion. Even minimal heat generated during cutting will cause the material to expand significantly. As it cools back to ambient temperature, it will contract, meaning a part measured as correct while warm will be undersized once it has stabilized.
Stress Relaxation and Creep
PTFE is prone to stress relaxation, or "creep." If you clamp the material too tightly in a vise or chuck, it will deform under the pressure. Unlike metal, it will not fully spring back to its original shape after the pressure is released, leading to dimensional inaccuracies.
Material Softness
The softness of PTFE means it is easily compressed and prone to burring. Cutting tools that are not exceptionally sharp will tend to push and deform the material rather than shearing it cleanly. This results in a poor surface finish and makes holding precise dimensions nearly impossible.
The Machining Strategy for Precision
A successful strategy for machining PTFE focuses on mitigating the instabilities described above at every stage of the process.
Tool Selection and Geometry
Use exceptionally sharp tools. High-Speed Steel (HSS) or carbide tools are effective, but their condition is critical. They must have a sharp, polished cutting edge to ensure a clean shearing action. Providing proper tool clearance is also essential to prevent the tool from rubbing against the workpiece, which generates heat.
Optimizing Speeds and Feeds
The goal is to balance a clean cut with minimal heat input.
- Cutting Speeds: Moderate to high speeds, typically in the range of 300–500 m/min, are effective.
- Feed Rates: High feed rates of 0.1–0.25 mm/rev help produce a thicker chip that carries heat away from the part.
Effective Heat Management
Controlling temperature is the single most important factor. For heat-intensive operations, the application of a coolant is necessary to prevent thermal expansion from ruining dimensional accuracy. Efficient chip removal is also crucial, as lingering swarf can trap heat against the workpiece.
Secure and Gentle Workholding
To counteract stress relaxation, clamping pressure must be minimized. Use fixtures that distribute clamping force over a wide area or employ custom jaws that conform to the part's shape. The goal is to hold the part securely without compressing or distorting it.
Post-Machining and Verification
The work is not finished once the cutting stops. Post-machining steps are often required to ensure the final part meets specification.
The Role of Annealing
For the tightest tolerances, post-machining annealing is often necessary. This process involves heating the part in a controlled manner to relieve the internal stresses induced during machining. This significantly improves the long-term dimensional stability of the component.
Precision Measurement
Because PTFE is soft, standard contact-based measurement tools can deform the surface and provide inaccurate readings. Non-contact measurement tools, such as laser micrometers or optical comparators, are strongly recommended to ensure true dimensional verification.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While tight tolerances are achievable, it's critical to approach PTFE with realistic expectations and a solid understanding of its limitations.
The Realistic Tolerance Rule
A practical rule of thumb for standard PTFE is a tolerance of +/- 0.001 inches per inch of dimension (or +/- 0.025mm per 25mm). Achieving tolerances tighter than this, such as ±0.02 mm, is possible but requires expert process control and often the use of more stable, reinforced PTFE grades.
Designing for the Material
The most successful PTFE parts are designed with the material's properties in mind, not against them. Avoid unnecessarily complex features or sharp internal corners that can concentrate stress. Whenever possible, design with the most generous tolerances your application can allow.
Safety Considerations
PTFE dust can be hazardous if inhaled. Always wear a mask or machine the material under coolant to suppress dust and ensure a safe working environment.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your approach should be dictated by the specific requirements of your component.
- If your primary focus is extreme precision (±0.02 mm or less): Your process must include post-machining annealing, meticulous heat control with coolant, and non-contact inspection methods.
- If your primary focus is general functional parts: Standard practices with sharp tools, optimized speeds, and gentle clamping will suffice, but always design to account for thermal changes.
- If you are prototyping a new design: Start with generous tolerances to lower cost and complexity, and only tighten them on features where it is absolutely critical for function.
By respecting the material's unique properties and implementing a controlled process, you can reliably produce accurate and stable PTFE components.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Expansion | High coefficient causes part size fluctuation | Use coolant, optimize speeds/feeds, manage heat input |
| Stress Relaxation & Creep | Material deforms under clamping pressure | Implement gentle workholding, custom fixtures, minimize clamping force |
| Material Softness | Tools push/deform material rather than cutting cleanly | Use exceptionally sharp HSS/carbide tools with polished edges |
| Dimensional Verification | Contact measurement can deform soft surfaces | Employ non-contact tools (laser micrometers, optical comparators) |
| Long-term Stability | Internal stresses affect dimensional accuracy over time | Apply post-machining annealing to relieve stresses |
Need precision PTFE components that meet your exact specifications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware, and more) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in managing PTFE's unique properties ensures your parts achieve tight tolerances with exceptional dimensional stability.
We combine sharp tooling strategies, optimized cutting parameters, and post-machining stabilization techniques to deliver components that perform reliably in your most demanding applications. From prototypes to high-volume production, we prioritize precision at every step.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your PTFE machining requirements and let our experts deliver the precision components your project demands.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















