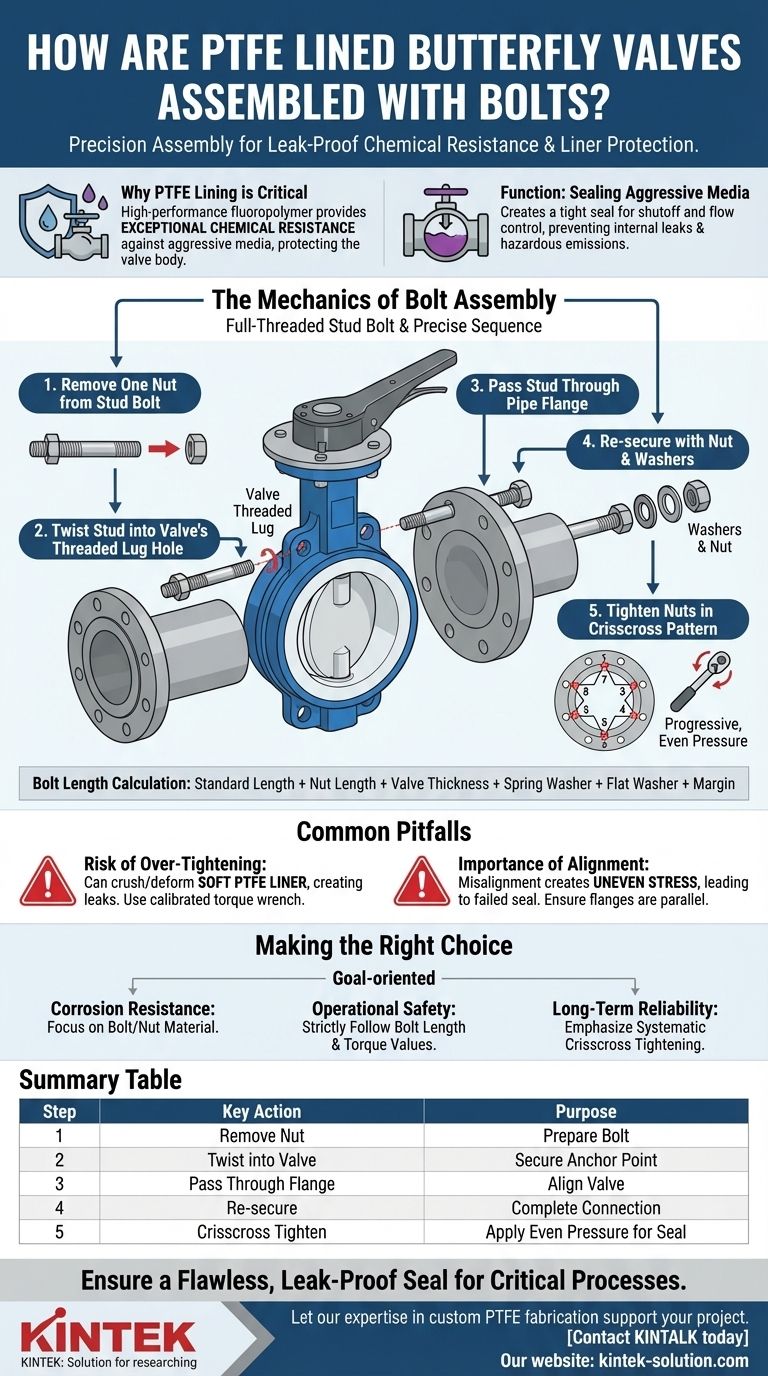
The assembly of PTFE lined butterfly valves involves a specific sequence using full-threaded stud bolts. The process requires removing one nut, twisting the stud bolt into the valve's threaded lug hole, passing it through the pipe flange, and then re-securing it with the removed nut. This method ensures a secure connection that protects the integrity of the valve's critical PTFE lining.
The core principle is not just about connecting parts; it's about applying even, controlled pressure to create a perfect seal without damaging the soft, chemically-resistant PTFE liner that is the valve's primary feature.

The Role of PTFE Lined Valves
Before detailing the assembly, it's essential to understand why this specific valve type is chosen. The installation method is directly tied to its function.
Why the PTFE Lining is Critical
PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) is a high-performance fluoropolymer. Its primary benefit is providing exceptional chemical resistance against aggressive and corrosive media.
This lining protects the valve's metal body from attack, making it suitable for demanding applications in chemical processing plants where other materials would fail.
The Function: Sealing Aggressive Media
These valves are primarily used for shutoff and flow control of harsh chemicals. The disc and liner create a tight seal when the valve is closed.
A proper bolt assembly is crucial for maintaining this seal, preventing both internal system leaks and dangerous fugitive emissions into the atmosphere.
The Mechanics of Bolt Assembly
The assembly process is designed for precision and stability, ensuring the valve functions as intended without compromising the liner.
Selecting the Correct Bolt Type
The standard for these valves is the full-threaded stud bolt. This type of bolt is threaded along its entire length.
This design allows clamping force to be applied from both ends by two separate nuts, ensuring even pressure distribution across the valve body and flanges.
Calculating Proper Bolt Length
The correct bolt length is not arbitrary. It is calculated to ensure sufficient thread engagement for a secure connection.
The formula is: Bolt Length = Standard Bolt Length + Nut Length + Valve Thickness + Spring Washer Thickness + Flat Washer Thickness + Margin. This calculation ensures the stud is long enough to accommodate all components without bottoming out or having insufficient thread.
The Installation Sequence
The physical installation follows a precise order to ensure correct alignment and sealing.
- One nut is removed from the full-threaded stud bolt.
- The stud is inserted through the pipe flange and twisted into the valve's threaded bolt hole.
- The washers and the previously removed nut are placed on the other end of the stud.
- The nuts are tightened progressively and in a star or crisscross pattern to apply uniform pressure.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
A successful installation depends on avoiding common mistakes that can compromise the valve's integrity.
The Risk of Over-Tightening
The most common failure point is applying excessive or uneven torque. The PTFE liner is a relatively soft material.
Over-tightening can crush, deform, or damage the liner, creating a leak path and defeating the entire purpose of the valve. Always use a calibrated torque wrench and follow manufacturer specifications.
The Importance of Alignment
The valve's lightweight design makes it easy to install, but also easy to misalign.
Ensure the pipe flanges are perfectly parallel and aligned before inserting the valve. Any misalignment will create uneven stress on the valve body and liner, leading to a failed seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your assembly procedure should be guided by your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance: Ensure the bolt and nut material is suitable for the external environment, as a failed fastener will compromise the entire joint.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Strictly follow the calculated bolt length and specified torque values to prevent leaks and fugitive emissions of hazardous materials.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability: Emphasize a systematic, crisscross tightening pattern to guarantee even pressure on the PTFE liner, preventing stress points that lead to premature failure.
A methodical and precise assembly is the key to leveraging the full chemical resistance and longevity of your PTFE lined valve.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Remove one nut from stud bolt | Prepares the bolt for insertion into the valve. |
| 2 | Twist stud into valve's threaded lug hole | Creates a secure anchor point on the valve body. |
| 3 | Pass stud through pipe flange | Aligns the valve between the pipeline flanges. |
| 4 | Re-secure with nut and washers | Completes the connection, ready for tightening. |
| 5 | Tighten nuts in a crisscross pattern | Applies even, controlled pressure to seal without damaging the PTFE liner. |
Ensure a flawless, leak-proof seal for your critical processes.
The precise assembly of PTFE components is paramount for safety and performance in demanding semiconductor, medical, and industrial applications. At KINTEK, we don't just supply high-quality PTFE seals, liners, and labware—we understand the engineering behind their successful installation.
Let our expertise in custom PTFE fabrication support your project, from prototype to high-volume production.
Contact KINTALK today to discuss your specific requirements and achieve reliable, long-lasting chemical resistance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application



















