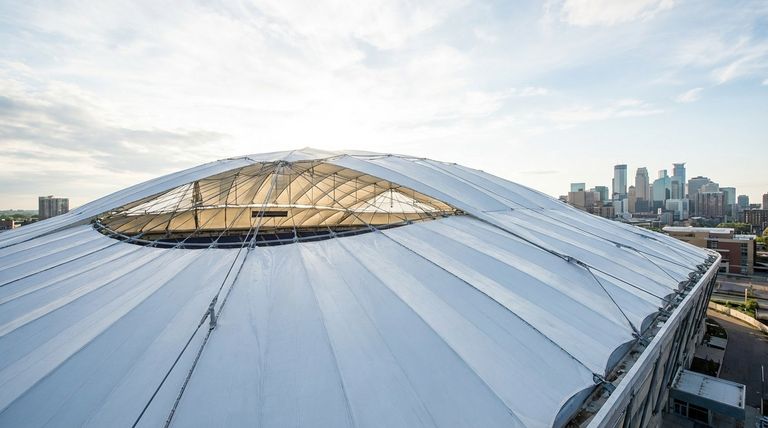
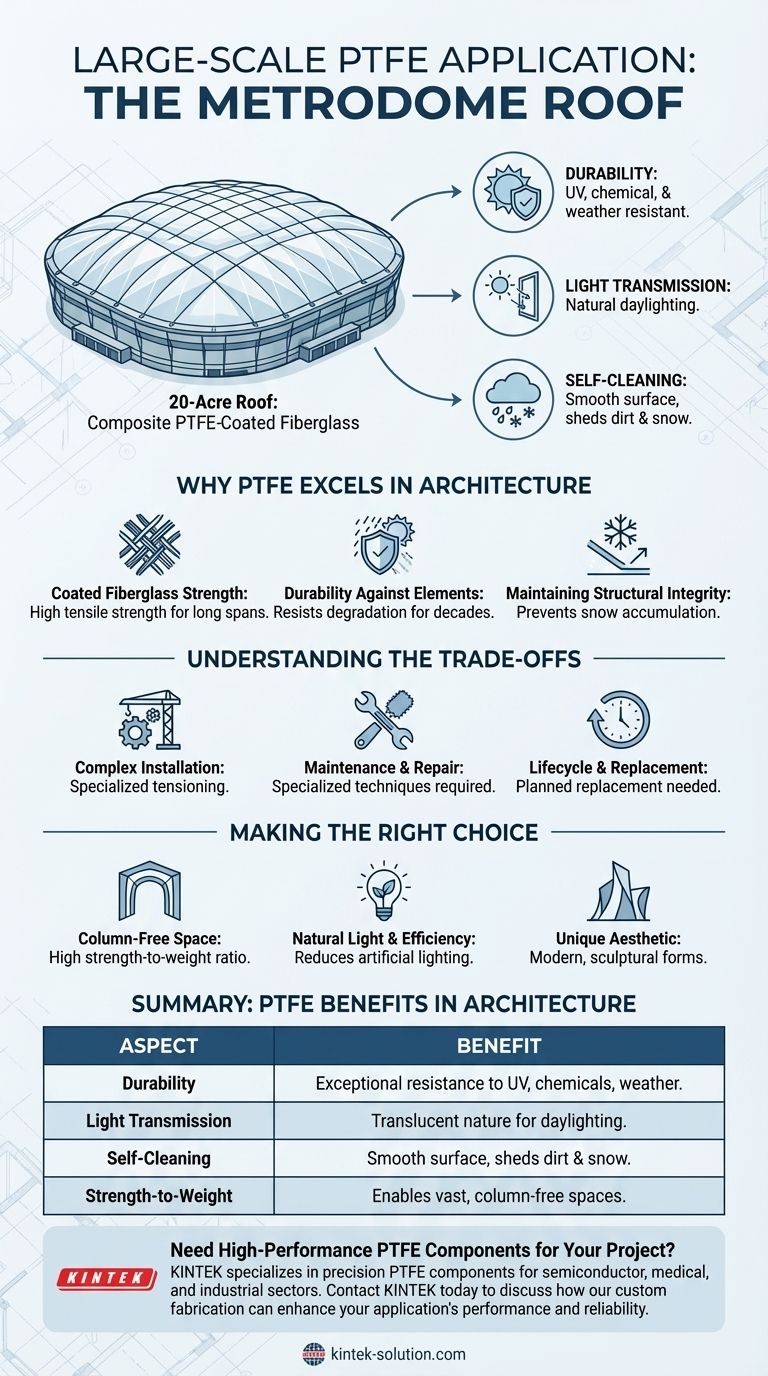
Without question, one of the most prominent large-scale applications of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) was in architectural fabric structures, exemplified by the roof of the Hubert H. Humphrey Metrodome in Minneapolis. This massive, 20-acre roof was constructed from a composite material of PTFE-coated fiberglass, showcasing the material's unique capabilities on an enormous scale.
The true value of PTFE in large-scale applications isn't just its non-stick quality, but its remarkable combination of weather resistance, durability, and light transmission, which makes ambitious architectural designs both possible and practical.

Why PTFE Excels in Architecture
The choice of PTFE for massive structures like the Metrodome roof was not accidental. It stems from a specific set of properties that solve critical challenges in modern construction, particularly for creating vast, enclosed spaces.
The Power of Coated Fiberglass
The material used wasn't pure PTFE but rather a composite. The core strength came from a woven fiberglass fabric, which provided the necessary tensile strength to cover a large span without buckling under its own weight or environmental loads.
Durability Against the Elements
PTFE's primary role was as a protective coating. Its inherent chemical inertness makes it exceptionally resistant to UV radiation, acid rain, pollution, and temperature extremes. This allowed the roof to withstand harsh Minnesota winters and direct sun exposure over many years without significant degradation.
Maintaining Structural Integrity
The PTFE coating created a smooth, low-friction surface. This "self-cleaning" property meant that rain would easily wash away dirt, and snow would slide off more readily, preventing dangerous accumulations that could compromise the structure's integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE-coated fabrics offer significant advantages, it's important to understand the associated challenges and considerations in these large-scale projects.
The Complexity of Installation
Creating a seamless, tensioned fabric roof over a 20-acre span is a highly specialized engineering feat. The panels must be precisely cut, seamed together, and anchored under tension to create the final, stable shape. This complexity adds to the initial project cost and timeline.
Maintenance and Repair
Although durable, the fabric is not indestructible. Punctures or tears from severe weather or impacts require specialized repair techniques. Unlike a traditional solid roof, inspecting and accessing damage on a vast fabric structure presents its own logistical challenges.
Lifecycle and Replacement
While the material has a long lifespan, it is not indefinite. Over decades, even PTFE will eventually show signs of wear. The eventual replacement of such a massive and integral component of a building is a major undertaking that must be planned for.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of PTFE-coated fabric is a strategic decision driven by specific architectural and functional goals.
- If your primary focus is creating a vast, column-free interior space: PTFE's high strength-to-weight ratio allows for long-span structures that would be impractical or prohibitively expensive with traditional materials.
- If your primary focus is natural light and energy efficiency: The translucent nature of the fabric allows significant natural light to pass through, reducing the need for artificial lighting during the day.
- If your primary focus is creating a unique architectural aesthetic: PTFE-coated fabrics offer a distinct, modern look and allow for dramatic, sculptural forms that are difficult to achieve with conventional building materials.
Ultimately, PTFE's role in projects like the Metrodome roof demonstrates its power to transform architectural possibilities when durability and environmental resistance are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Benefit of PTFE in Architecture |
|---|---|
| Durability | Exceptional resistance to UV rays, chemicals, and extreme weather. |
| Light Transmission | Translucent nature provides significant natural daylighting. |
| Self-Cleaning | Smooth surface allows rain to wash away dirt and snow to slide off. |
| Strength-to-Weight | Enables vast, column-free interior spaces with a lightweight material. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Your Project?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures durable, chemically inert solutions tailored to your specific needs.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our custom PTFE fabrication can enhance your application's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key properties of PTFE seals and rings? Unlock Superior Performance in Harsh Environments
- What long-term business benefits can PTFE diaphragm valves provide to pharmaceutical companies? Boost Yield & Cut Costs
- What are some common uses of PTFE in industries? Solve Challenges with a Versatile High-Performance Polymer
- What are the uses of expanded PTFE gasketing tapes? The Ultimate Solution for Flange Sealing Problems
- What causes wear and tear in PTFE butterfly valves? Avoid Premature Failure and Extend Valve Life
- What are the key properties of PTFE Bellows? Achieve Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resilience
- What advantages do PTFE gasket materials offer? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the key advantages of using PTFE packing? Superior Sealing for Demanding Applications



















