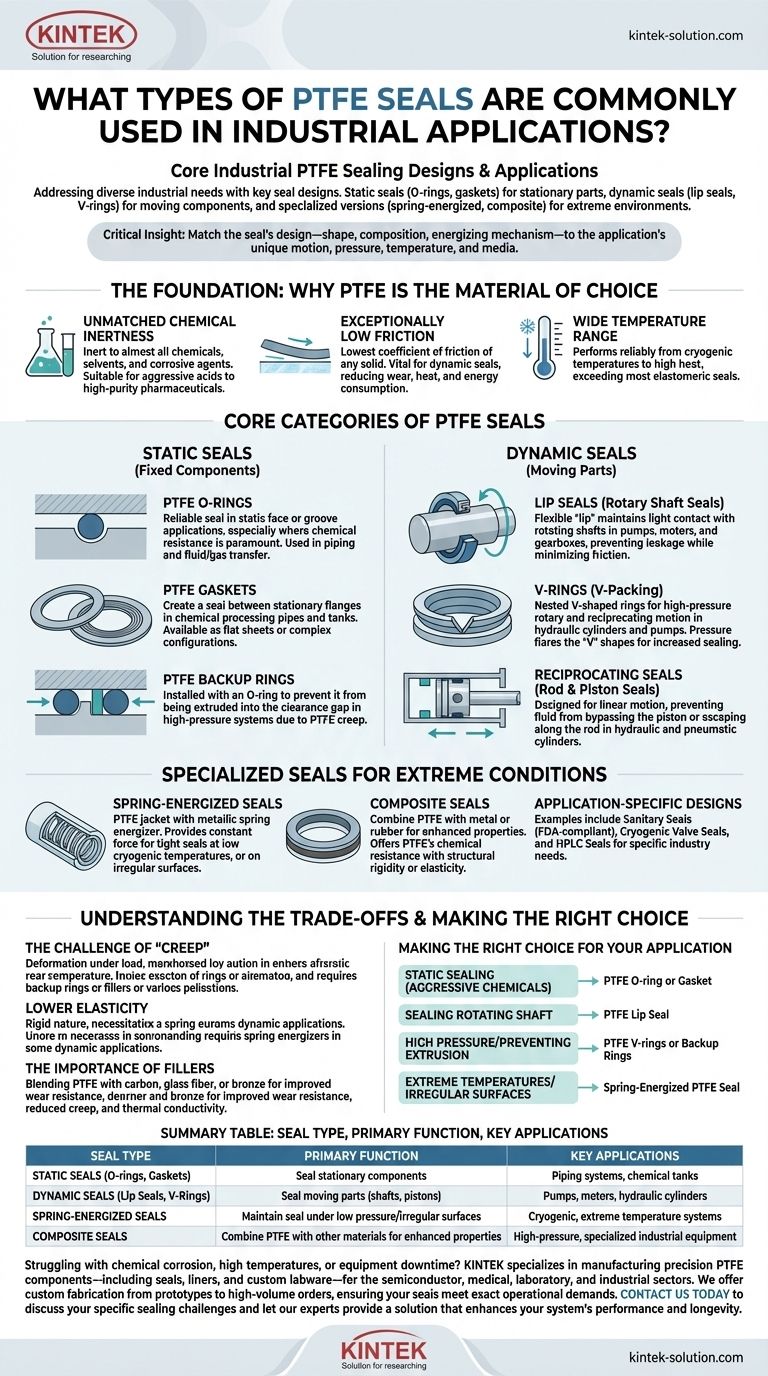
At its core, industrial PTFE sealing is addressed by a few key designs. The most common types are static seals like O-rings and gaskets for stationary parts, and dynamic seals like lip seals and V-rings for moving components like shafts. For more demanding environments, specialized versions like spring-energized or composite seals are employed to handle extreme pressures, temperatures, or chemical exposures.
The critical insight is not simply knowing the names of different seals, but understanding that the choice is dictated by the specific operational challenge. You must match the seal's design—its shape, composition, and energizing mechanism—to the application's unique combination of motion, pressure, temperature, and media.
The Foundation: Why PTFE Is the Material of Choice
Before examining specific seal types, it’s crucial to understand why Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is so prevalent in demanding industrial applications. Its unique combination of properties makes it a superior choice where other materials would fail.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. This allows it to be used in systems handling everything from aggressive acids to high-purity pharmaceuticals without degrading.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This property is vital for dynamic seals in rotating or reciprocating equipment, as it reduces wear, heat generation, and energy consumption.
Wide Temperature Range
PTFE seals can perform reliably across an exceptionally broad temperature spectrum. They are used in cryogenic applications at extremely low temperatures and can withstand high temperatures far beyond the tolerance of most elastomeric (rubber) seals.
Core Categories of PTFE Seals
While countless custom variations exist, most industrial PTFE seals can be grouped into logical categories based on their function and the type of motion they accommodate.
Static Seals: For Fixed Components
These seals are designed for applications where there is no movement between the sealing surfaces.
- PTFE O-Rings: Used in piping systems and fluid or gas transfer equipment, they provide a reliable seal in static face or groove applications, especially where chemical resistance is paramount.
- PTFE Gaskets: Available as flat sheets or in complex spiral-wound configurations, gaskets are used to create a seal between two stationary flanges, such as in chemical processing pipes and tanks.
- PTFE Backup Rings: These are not seals themselves but are critical components. Due to PTFE's tendency to deform under pressure, a backup ring is installed with an O-ring to prevent it from being extruded into the clearance gap in high-pressure systems.
Dynamic Seals: For Moving Parts
These seals are engineered to maintain integrity while accommodating constant motion between machine components.
- Lip Seals (Rotary Shaft Seals): The most common choice for sealing rotating shafts in pumps, motors, and gearboxes. The flexible "lip" maintains light contact with the shaft, preventing leakage while minimizing friction and wear.
- V-Rings (V-Packing): Comprised of a set of nested V-shaped rings, these are used for both rotary and reciprocating (back-and-forth) motion in high-pressure environments like hydraulic cylinders and pumps. As pressure increases, it forces the "V" shapes to flare out, increasing the sealing force.
- Reciprocating Seals (Rod & Piston Seals): Specifically designed for linear motion, these seals prevent fluid from bypassing the piston or escaping along the rod in hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders.
Specialized Seals for Extreme Conditions
When standard designs are insufficient, advanced PTFE seals are used to meet the challenges of extreme operating environments.
Spring-Energized Seals
These seals feature a PTFE jacket with a metallic spring energizer inside. The spring provides a constant, uniform force against the sealing surfaces, ensuring a tight seal even at very low pressures, in cryogenic temperatures where the material stiffens, or on slightly irregular surfaces.
Composite Seals
To gain the benefits of multiple materials, composite seals combine PTFE with components made of metal or rubber. This allows for designs that have the chemical resistance of PTFE but with the structural rigidity of metal or the enhanced elasticity of a rubber energizer.
Application-Specific Designs
Many industries require highly customized seals. Examples include sanitary seals made from FDA-compliant PTFE for food and pharmaceutical processing, cryogenic valve seals for handling liquefied gases, and HPLC seals for high-performance liquid chromatography equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, PTFE is not without its limitations. Acknowledging these is key to proper seal design and selection.
The Challenge of "Creep"
PTFE has a tendency to exhibit "creep," or cold flow, meaning it can slowly deform over time when under a constant load. This is why backup rings are essential in high-pressure static applications and why material fillers are often used to improve resistance to deformation.
Lower Elasticity
Compared to rubber elastomers, PTFE is a relatively rigid material. It does not have the same "bounce-back" memory, which is why spring energizers are necessary in certain dynamic applications to maintain constant seal contact.
The Importance of Fillers
To enhance its mechanical properties, virgin PTFE is often blended with fillers like carbon, glass fiber, or bronze. These fillers significantly improve wear resistance, reduce creep, and increase thermal conductivity, making the seal more robust for demanding dynamic use.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final selection should be guided by the primary demand of your system.
- If your primary focus is static sealing against aggressive chemicals: A PTFE O-ring or gasket is your standard solution.
- If your primary focus is sealing a rotating shaft: Begin with a PTFE lip seal designed for the specific speed and pressure.
- If your primary focus is handling high pressure or preventing extrusion: Use PTFE V-rings or add backup rings to your O-ring setup.
- If your primary focus is sealing in extreme temperatures or on irregular surfaces: A spring-energized PTFE seal is the most reliable choice.
By understanding the fundamental design of each seal type, you can confidently select the component that ensures the integrity and longevity of your system.
Summary Table:
| Seal Type | Primary Function | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Static Seals (O-rings, Gaskets) | Seal stationary components | Piping systems, chemical tanks |
| Dynamic Seals (Lip Seals, V-Rings) | Seal moving parts (shafts, pistons) | Pumps, motors, hydraulic cylinders |
| Spring-Energized Seals | Maintain seal under low pressure/irregular surfaces | Cryogenic, extreme temperature systems |
| Composite Seals | Combine PTFE with other materials for enhanced properties | High-pressure, specialized industrial equipment |
Struggling with chemical corrosion, high temperatures, or equipment downtime? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your seals meet exact operational demands.
Contact us today to discuss your specific sealing challenges and let our experts provide a solution that enhances your system's performance and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















