The most common material for lining valves is PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), widely known by its trade name, Teflon. This fluoropolymer is chosen for its exceptional chemical stability, corrosion resistance, and high-lubricity surface. It provides a robust, inert barrier that protects the valve's metal body from aggressive process media across a wide range of temperatures.
The core reason PTFE dominates as a valve liner is not a single feature, but its unique combination of near-total chemical inertness, a wide operational temperature range, and an extremely low-friction surface. This makes it the default solution for safely containing and controlling corrosive or high-purity fluids.
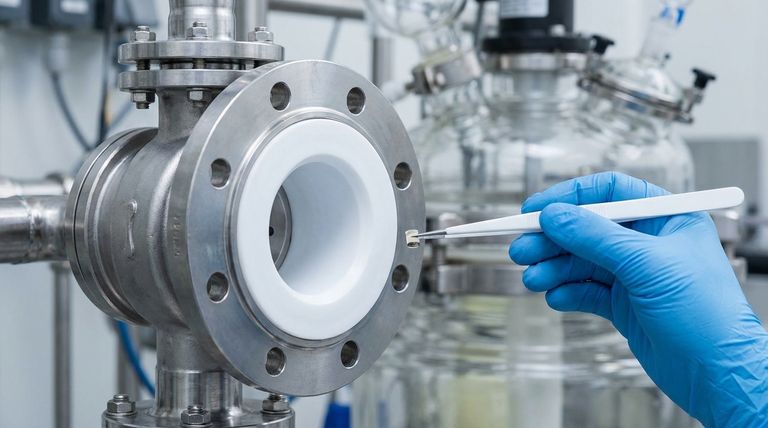

Why PTFE is the Industry Standard for Valve Linings
The properties of PTFE directly address the most common challenges faced in industrial fluid handling, from chemical processing to pharmaceuticals.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually immune to chemical attack. It can withstand highly corrosive substances, including strong acids, strong alkalis, and powerful oxidants, without degrading.
This inertness prevents the valve body from corroding, which ensures mechanical integrity and prevents catastrophic failures and leaks.
Superior Sealing and Low Friction
Valves rely on tight seals to prevent leaks. PTFE's molecular structure gives it a very slippery, "non-stick" surface with a low coefficient of friction.
This high lubricity means that valve components, like a ball or plug, can rotate against the PTFE seat with minimal force. This reduces the torque required to operate the valve and significantly extends its service life by minimizing wear on sealing surfaces.
Wide Operational Temperature Range
PTFE maintains its integrity and properties over an impressive temperature spectrum, typically from -200°C to 180°C (-328°F to 356°F).
This versatility allows it to be used in applications ranging from cryogenic services to moderately high-temperature chemical processes, making it a flexible choice for many plant designs.
Preventing Media Contamination
The non-viscous, or non-stick, nature of PTFE is critical in industries where purity is paramount, such as food production or pharmaceuticals.
Process media does not adhere to the liner, preventing buildup, reducing the risk of cross-contamination between batches, and making clean-in-place (CIP) procedures more effective.
Understanding the Trade-offs of PTFE Linings
While highly effective, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to proper application and avoiding premature failure.
The Upper Temperature Limit
While its range is wide, the 180°C (356°F) ceiling is a firm limit. In applications involving high-temperature steam or chemical processes that exceed this, PTFE will soften, deform, and lose its sealing capability.
Susceptibility to Permeation
Under certain conditions of high pressure and temperature, very small gas molecules (like chlorine or hydrogen) can slowly pass through the PTFE liner. This can lead to a buildup of corrosive gas between the liner and the valve body, potentially causing hidden corrosion.
Vulnerability to Abrasive Media
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is not suitable for services containing abrasive particles or slurries, which can easily scratch or erode the liner and compromise its protective barrier.
Potential for Thermal Expansion
PTFE expands and contracts with temperature changes at a different rate than the metal valve body. Valve designs must account for this differential expansion to maintain seal integrity across all operating temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right valve lining depends entirely on the specific demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: PTFE is almost certainly your best choice due to its near-universal chemical resistance.
- If your primary focus is ensuring product purity: PTFE's non-stick surface makes it ideal for preventing media buildup and contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-cycle or automated actuation: The low-friction properties of PTFE will reduce the required actuator torque and minimize wear over thousands of cycles.
- If your process exceeds 180°C or contains abrasive solids: You must look beyond standard PTFE to other materials, such as metal alloys or ceramic-lined valves.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE-lined valve is an investment in the long-term reliability and safety of your most critical fluid handling systems.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Valve Lining |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists virtually all corrosive chemicals, protecting the valve body. |
| Low Friction | Reduces operating torque, extends valve life, and ensures tight sealing. |
| Wide Temperature Range | Performs reliably from -200°C to 180°C. |
| Non-Stick Surface | Prevents media buildup and contamination, ideal for high-purity applications. |
Need a reliable PTFE-lined valve solution for your critical process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components, including custom valve liners, seals, and labware. Our expertise ensures your fluid handling systems in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors achieve maximum reliability, safety, and purity.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, tailored to your specific operational demands.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and receive a quote for a solution built to last.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application



















