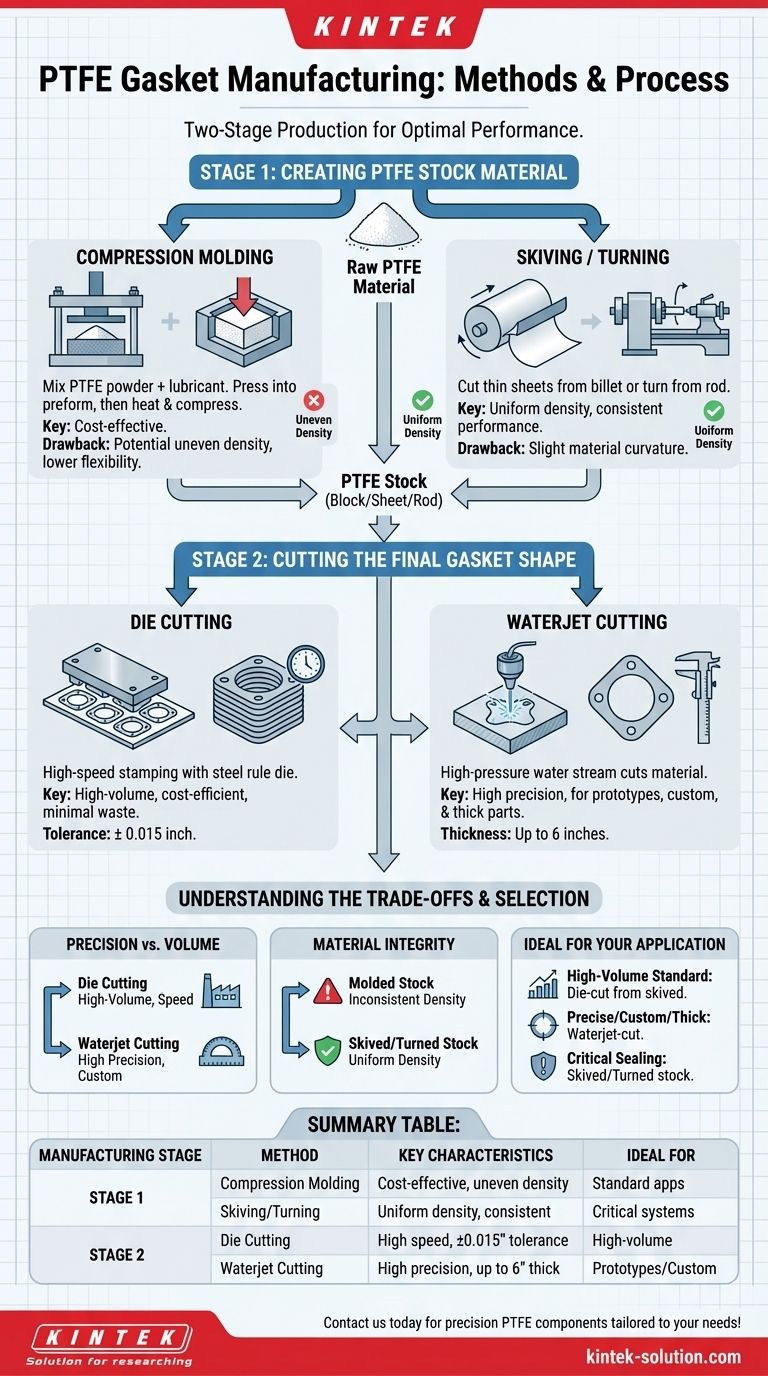
PTFE gaskets are produced through two primary pathways: first, by forming the raw material into stock shapes, and second, by cutting those shapes into the final gasket profile. The initial material is created via compression molding or skiving/turning, while the final cutting is typically accomplished with die cutting or waterjet cutting. Each step in this process influences the gasket's final quality and performance.
The manufacturing method directly impacts a PTFE gasket's final properties, such as its density, flexibility, and dimensional accuracy. While molding and skiving create the raw PTFE stock, the choice between die cutting and waterjet cutting determines the final gasket's precision for a specific application.

The Two-Stage Manufacturing Process
Understanding PTFE gasket production is best broken down into two distinct stages. The first stage involves creating the bulk material, and the second involves fabricating the final part from that material.
Stage 1: Creating the PTFE Stock Material
Before a gasket can be cut, a solid block, sheet, or rod of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) must be produced. The two common methods for this have different implications for the material's internal structure.
The Compression Molding Method
Compression molding begins by mixing PTFE powder with a lubricant. This mixture is then pressed into a preliminary shape, called a preform, before being heated and compressed into its final stock form.
However, molding can sometimes result in uneven density and poor flexibility in the final material.
The Skiving or Turning Method
This method involves cutting or "skiving" thin sheets from a larger billet or turning gaskets from a solid rod of PTFE. This process generally produces a more uniform and consistent material density.
The main drawback is that gaskets produced this way may have a slight curvature due to the processing technology, which can sometimes complicate installation.
Stage 2: Cutting the Final Gasket Shape
Once the PTFE stock material is ready, it must be cut into the precise dimensions of the final gasket. This is where precision and speed become critical factors.
Die Cutting
Die cutting is a high-speed process that uses a specialized steel rule die to stamp out gaskets, much like a cookie-cutter. It is highly efficient for producing exact and complex shapes with minimal material waste.
This method is known for its high cutting speeds and can achieve tight tolerances of approximately ± 0.015 inch.
Waterjet Cutting
Waterjet cutting uses a high-pressure stream of water to cut the PTFE material. This method offers exceptional precision, positioning, and repeatability.
It is particularly effective for thicker materials, capable of cutting PTFE up to 6 inches thick, with tolerances that vary based on the material's size and thickness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of manufacturing method is not arbitrary; it involves a balance of cost, precision, and material integrity that directly affects the gasket's performance in its intended environment.
Precision vs. Volume
Die cutting is ideal for high-volume production runs where speed and cost-efficiency are paramount. It consistently produces large quantities of identical parts.
Waterjet cutting is the superior choice for prototypes, custom designs, or applications requiring the highest level of precision, especially for very thick or complex gaskets.
Material Integrity and Performance
A gasket made from molded stock may have inconsistent density, which could potentially compromise its ability to create a perfect seal under pressure.
A gasket made from skived or turned stock will have more uniform density, leading to more predictable sealing performance, though installers may need to account for slight material curvature.
Why It Matters for Your Application
While all virgin PTFE gaskets share core properties like outstanding chemical resistance and a wide temperature range (from -200°C to 260°C), the manufacturing process refines their mechanical suitability. An improperly manufactured gasket can fail to seal effectively, even if the base material is correct.
Selecting the Right Gasket for Your Application
Your final choice should align with your project's specific needs for precision, volume, and performance.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of standard gaskets: A die-cut gasket from skived PTFE sheets offers a cost-effective balance of speed and material consistency.
- If your primary focus is a precise, custom, or thick gasket: A waterjet-cut gasket is the superior choice, providing the best dimensional accuracy for critical sealing applications.
- If your primary focus is reliable sealing in a critical system: Specify a gasket made from skived/turned stock for its uniform density and predictable performance.
Understanding how a PTFE gasket is made is the first step to ensuring it delivers the reliable, long-lasting seal your system requires.
Summary Table:
| Manufacturing Stage | Method | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1: Creating PTFE Stock | Compression Molding | Cost-effective; potential for uneven density | Standard applications |
| Skiving/Turning | Uniform density; consistent performance | Critical sealing systems | |
| Stage 2: Cutting Gasket Shape | Die Cutting | High speed (± 0.015" tolerance); minimal waste | High-volume production |
| Waterjet Cutting | High precision; handles thick materials (up to 6") | Prototypes, custom, or thick gaskets |
Need a PTFE Gasket That Perfectly Matches Your Application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require a high-volume run of die-cut gaskets or a custom, waterjet-cut solution for a critical seal, our precision production and custom fabrication services (from prototypes to high-volume orders) ensure you get a gasket with the right density, flexibility, and dimensional accuracy for reliable performance.
Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss your project and get a quote tailored to your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability



















