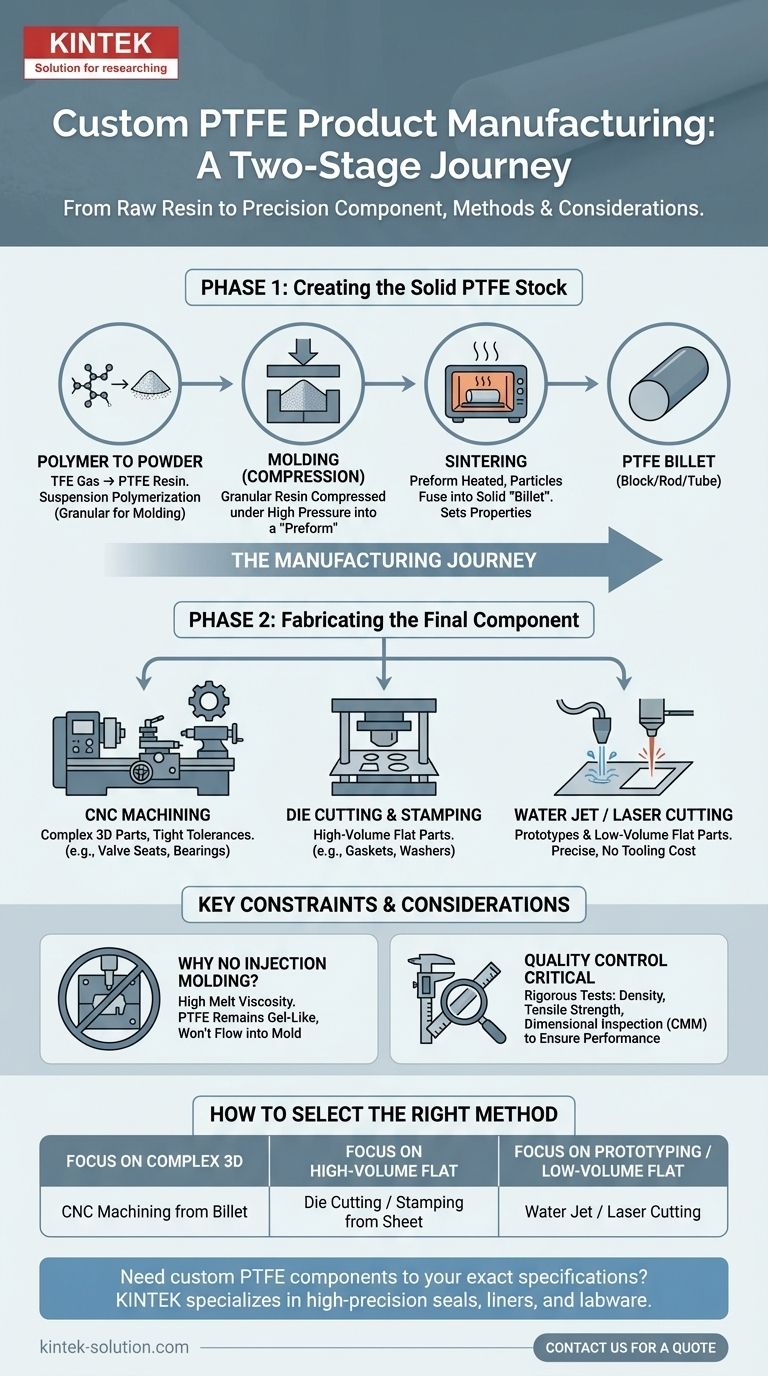
At its core, custom PTFE products are fabricated from solid stock material using methods like machining, die cutting, stamping, and water or laser cutting. However, this is the final step in a multi-stage process that begins with molding raw PTFE resin into a basic shape, as the material's unique properties prevent it from being processed like common plastics.
The critical takeaway is that creating a custom PTFE part is a two-step process: first, raw PTFE powder is molded and sintered into a solid block or rod (a "billet"), and second, that billet is precisely machined or cut into the final desired shape. Unlike many plastics, it cannot be injection molded.

The Manufacturing Journey of a Custom PTFE Part
Understanding the full manufacturing workflow is essential for specifying a part that meets your application's needs. The process can be broken down into two distinct phases: forming the raw stock and then fabricating the final component.
Phase 1: Creating the Solid PTFE Stock
Before any cutting or shaping can occur, the raw PTFE polymer must be consolidated into a solid, workable form.
From Polymer to Powder
The process begins with polymerization, where tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) gas is converted into PTFE resin. The two primary methods are suspension polymerization, which creates granular PTFE grains ideal for molding, and dispersion polymerization, which produces a fine powder often used for coatings. For custom components, the granular resin from suspension polymerization is the typical starting point.
Molding and Sintering
This granular PTFE resin does not flow when melted, so it cannot be processed with conventional techniques like injection molding. Instead, it is formed through compression molding. The powder is compressed into a mold under high pressure to create a "preform."
This preform is then moved to a carefully controlled oven for sintering. During this heating and cooling cycle, the PTFE particles fuse together into a solid, homogenous block, rod, or tube known as a billet. The physical and mechanical properties of the final part are largely set during this critical stage.
Phase 2: Fabricating the Final Component
Once a solid billet of PTFE is produced, it serves as the raw material for secondary fabrication processes that create the final custom part.
CNC Machining
For complex, three-dimensional components with tight tolerances, CNC machining is the most common method. The PTFE billet is shaped using lathes, mills, and routers to produce parts like valve seats, insulators, and bearings.
Die Cutting and Stamping
For high-volume production of flat, two-dimensional parts like gaskets, washers, and seals, die cutting or stamping is highly efficient. A sharp, custom-made steel die is used to punch the desired shape from a sheet of PTFE.
Water Jet and Laser Cutting
Water jet cutting uses a high-pressure stream of water to cut intricate shapes from PTFE sheets. Laser cutting achieves a similar result using a focused beam of light. Both methods are excellent for creating precise, flat parts without the tooling costs associated with die cutting, making them ideal for prototypes or low-volume runs.
Key Constraints and Considerations
Successfully manufacturing with PTFE requires an understanding of its unique limitations and the quality control measures needed to ensure performance.
Why PTFE Cannot Be Injection Molded
A common point of confusion is the inability to injection mold PTFE. Unlike thermoplastics that become liquid when heated, PTFE has an extremely high melt viscosity. Even when it reaches its melting point, it remains a gel-like solid and will not flow into a mold cavity, making molding and subsequent machining the necessary approach.
The Critical Role of Quality Control
Because manufacturing is a multi-stage process, rigorous quality control is essential. Key inspection methods ensure the final product meets specifications for density, mechanical strength, and dimensional accuracy. These tests can include density analysis, tensile testing, and precise dimensional inspection using coordinate measuring machines (CMM).
How to Select the Right Method
Choosing the best manufacturing process depends entirely on the geometry, volume, and precision requirements of your component.
- If your primary focus is complex 3D components: Specify parts to be produced via CNC machining from a compression-molded PTFE billet.
- If your primary focus is high-volume flat parts: Die cutting or stamping from PTFE sheet stock is the most cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or low-volume flat parts: Water jet or laser cutting provides exceptional precision without the expense of custom tooling.
By understanding this complete manufacturing pathway, you can better specify and source custom PTFE components that deliver the exact performance your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Manufacturing Phase | Key Processes | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Creating Stock | Compression Molding, Sintering | Forming solid PTFE billets (blocks, rods) |
| Phase 2: Final Fabrication | CNC Machining, Die Cutting, Water Jet/Laser Cutting | Creating complex 3D parts, high-volume flat parts, or prototypes |
Need a custom PTFE component manufactured to your exact specifications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in producing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in the complete manufacturing pathway, from molding raw resin to precision machining, ensures your parts meet stringent quality and performance standards.
Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, we deliver custom fabrication with a focus on accuracy and durability. Contact us today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation



















