The comparison is a strategic engineering exercise. It serves to clearly define the operational boundaries where a conventional elastomeric seal reaches its limits and a more robust, mechanically-assisted solution like a spring-energized PTFE seal becomes necessary. This analysis helps engineers pinpoint specific failure modes—chemical attack, extreme temperatures, or high pressure—and select the component engineered to overcome them.
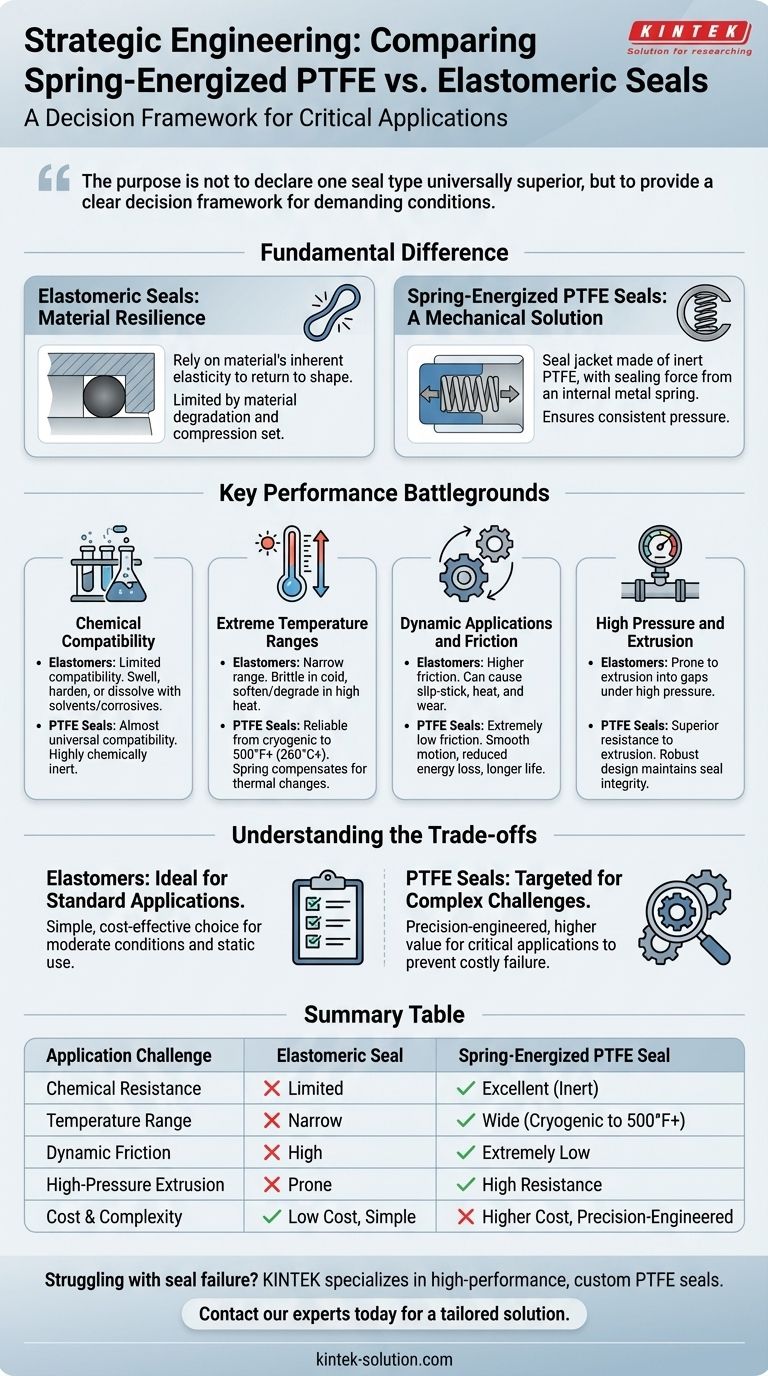
The purpose is not to declare one seal type universally superior, but to provide a clear decision framework. The comparison highlights the specific, demanding conditions where the advanced material properties and mechanical design of a spring-energized PTFE seal are required to ensure reliability and longevity.

The Fundamental Difference: Elasticity vs. Mechanics
To understand the comparison, you must first understand the core principle behind how each seal generates its sealing force. They are fundamentally different engineering approaches to the same problem.
Elastomeric Seals: Relying on Material Resilience
Elastomeric seals, like O-rings, function by being compressed into a gland. Their ability to seal depends entirely on the material's inherent elasticity—its desire to return to its original shape.
This reliance on material properties is also its primary limitation. If the material degrades from chemical exposure, becomes brittle in the cold, or permanently deforms under heat and pressure (compression set), the sealing force is lost.
Spring-Energized PTFE Seals: A Mechanical Solution
Spring-energized PTFE seals separate the sealing material from the force-generating mechanism. The seal jacket is made of low-friction, chemically inert PTFE, but the PTFE itself provides minimal sealing force.
The critical sealing force comes from a metal spring inside the jacket. This spring exerts a constant, consistent outward pressure on the seal lips, ensuring they remain in contact with the mating surfaces regardless of temperature fluctuations, material creep, or pressure spikes.
Key Performance Battlegrounds
The choice between these seals becomes clear when analyzing applications that push materials to their limits.
Chemical Compatibility
Elastomeric seals require careful compatibility checks, as many solvents, acids, and corrosive fluids can cause them to swell, harden, or dissolve, leading to catastrophic failure.
Spring-energized PTFE seals are almost universally compatible. PTFE is one of the most chemically inert polymers, making it the default choice for sealing aggressive media where elastomers would quickly degrade.
Extreme Temperature Ranges
Elastomers have a relatively narrow effective temperature range. In cryogenic conditions, they become brittle and crack. At high temperatures, they can soften, degrade, and suffer from an accelerated compression set.
The PTFE jacket and metal spring allow these seals to function reliably from cryogenic temperatures up to over 500°F (260°C). The spring compensates for any dimensional changes in the PTFE jacket, maintaining a consistent sealing force across this vast temperature spectrum.
Dynamic Applications and Friction
In rotating or reciprocating applications, the higher friction of elastomers can lead to problems like slip-stick (jerky motion), heat generation, and accelerated wear. They can also adhere to surfaces after periods of inactivity.
PTFE's extremely low coefficient of friction ensures smooth, continuous motion, reduces energy loss, and significantly extends the seal's service life, often without the need for lubrication.
High Pressure and Extrusion
Under high pressure, elastomeric seals can be physically forced, or extruded, into the clearance gap between components, causing permanent damage and immediate leakage.
The robust design of a spring-energized seal, combined with the strength of the PTFE material, provides superior resistance to extrusion. The spring ensures the sealing lip stays engaged, even under immense pressure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Objectivity requires acknowledging that a spring-energized PTFE seal is not a universal replacement for an elastomeric seal. It is a targeted solution for problems elastomers cannot solve.
The Role of Elastomers
For a vast majority of standard sealing applications with moderate temperatures, common fluids, and static conditions, elastomeric seals are the ideal choice. They are simple, highly effective, and extremely cost-efficient.
The Complexity and Cost Factor
Spring-energized PTFE seals are multi-component, precision-engineered parts. Their design and manufacturing complexity naturally result in a higher unit cost. They represent a value-driven decision, where the higher initial cost prevents costly downtime, equipment damage, or safety failures in a critical application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific demands should dictate your choice. Use this comparison as a diagnostic tool.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness in a standard environment: An elastomeric seal is almost always the correct, reliable, and economical choice.
- If your application involves aggressive chemicals or solvents: A spring-energized PTFE seal is necessary to prevent material degradation and ensure seal integrity.
- If you operate at extreme temperatures (cryogenic or high heat): A PTFE seal provides performance reliability where an elastomer would physically fail.
- If you have a high-pressure or high-speed dynamic application: The low friction and mechanical force of a PTFE seal will prevent premature wear and ensure consistent performance.
Understanding this distinction empowers you to select a seal based on precise engineering requirements, not just material familiarity.
Summary Table:
| Application Challenge | Elastomeric Seal | Spring-Energized PTFE Seal |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Limited; degrades with solvents/corrosives | Excellent; PTFE is highly chemically inert |
| Temperature Range | Narrow; fails at cryogenic/high heat | Wide; reliable from cryogenic to 500°F+ (260°C+) |
| Dynamic Friction | High; can cause slip-stick and wear | Extremely low; enables smooth motion, long life |
| High-Pressure Extrusion | Prone to extrusion into gaps | High resistance; robust design maintains seal |
| Cost & Complexity | Low cost, simple design | Higher cost, precision-engineered for critical use |
Struggling with seal failure in extreme conditions? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components—including spring-energized seals—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision engineering ensures reliability where standard seals fail. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and get a solution tailored for longevity and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What general maintenance practices can extend the lifespan of PTFE gaskets? Optimize Selection, Installation, and Monitoring
- How do PTFE expansion bellows compare to rubber bellows in terms of chemical resistance? PTFE Offers Near-Universal Chemical Resistance
- How are Teflon sheets used in Direct-to-Garment (DTG) printing? Achieve a Professional, Durable Finish
- How do PTFE bearing pads contribute to structural safety and efficiency? Enhance Structural Integrity with Low-Friction Support
- What is the shelf life of PTFE O-rings? Unlock the Secret to Indefinite Storage Stability
- What materials are used in the core of PTFE Envelope Gaskets? Select the Right Core for Chemical Resistance & Strength
- What are the industrial applications of ePTFE? Solve Critical Sealing, Filtration & Medical Challenges
- What issue is associated with the leakage rate of PTFE ring gaskets? Overcoming Inherent Sealing Challenges



















