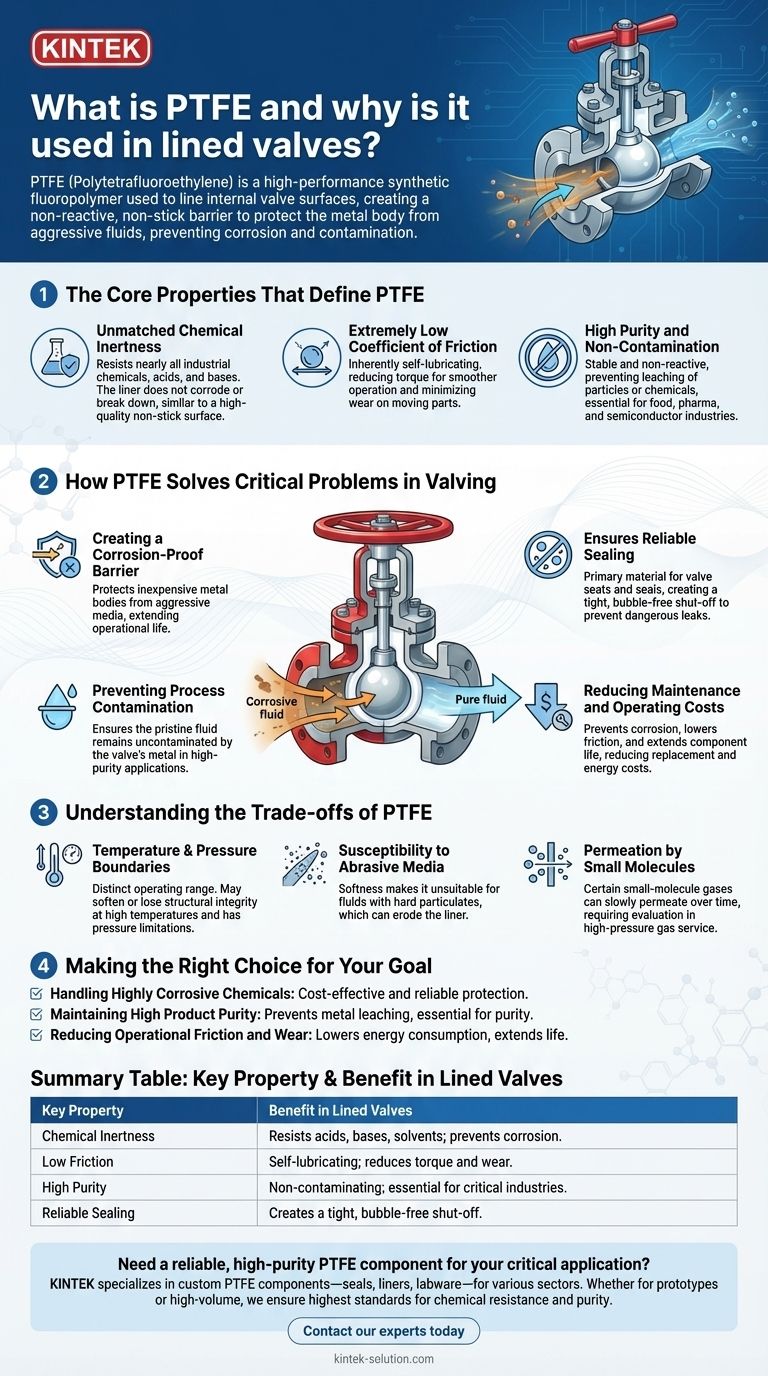
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance synthetic fluoropolymer. It is used to line the internal surfaces of valves to create a non-reactive, non-stick barrier that protects the valve's metal body from aggressive or corrosive fluids. This lining prevents corrosion, eliminates process contamination, and significantly reduces wear, extending the valve's operational life.
The core function of a PTFE liner is to isolate the valve's structural metal body from the process fluid. This allows you to use a cost-effective material like cast iron for the body while achieving the near-universal chemical resistance of a solid, high-end alloy, but at a fraction of the cost.

The Core Properties That Define PTFE
To understand why PTFE is so dominant in these applications, you must first understand its three fundamental properties. These characteristics work together to solve critical challenges in fluid handling.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most non-reactive substances known. It resists degradation from nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, and bases.
This inertness means the liner itself does not corrode or break down. Think of it as the industrial equivalent of a high-quality non-stick pan; nothing sticks to it, and it doesn't react with what it's touching.
Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE is inherently self-lubricating, possessing one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material.
This "slipperiness" is critical inside a valve. It reduces the torque required to open or close the valve, minimizing wear on moving parts like the ball or plug. This leads to smoother operation and less demand on actuators.
High Purity and Non-Contamination
Because PTFE is so stable and non-reactive, it does not leach particles or chemicals into the fluid passing through it.
This property is essential for industries like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and semiconductor manufacturing, where even trace amounts of contamination from a metal valve body could ruin a batch of product.
How PTFE Solves Critical Problems in Valving
Engineers specify PTFE-lined valves not just for their material properties, but for the specific operational problems they solve. It's a strategic choice to enhance system reliability and safety.
Creating a Corrosion-Proof Barrier
The most common use is to protect an inexpensive valve body (like ductile iron) from highly corrosive media such as sulfuric acid or chlorine. The PTFE liner handles the chemical attack, while the metal body provides the required pressure-containing strength.
Preventing Process Contamination
In high-purity water systems or food processing, the goal is reversed. The liner's purpose is not to protect the valve, but to protect the pristine fluid from the valve's metal. The PTFE ensures the final product remains uncontaminated by metallic ions.
Ensuring Reliable Sealing
Beyond lining the body, PTFE is also a primary material for valve seats and seals. Its flexibility allows it to conform to the ball or disc, creating a tight, bubble-free shut-off. This prevents dangerous leaks, especially in gas or volatile chemical service.
Reducing Maintenance and Operating Costs
By preventing corrosion, PTFE-lined valves last significantly longer than unlined metal valves in the same service, drastically reducing replacement costs and downtime. The low friction also means smaller, less expensive actuators can be used, saving on both capital and energy costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs of PTFE
While incredibly useful, PTFE is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires understanding its limitations.
Temperature and Pressure Boundaries
PTFE has a distinct operating temperature range. At very high temperatures, it can soften, degrade, and lose its structural integrity. It is also a softer material than metal, giving it clear pressure limitations that must be respected in system design.
Susceptibility to Abrasive Media
PTFE's softness makes it unsuitable for fluids containing hard, sharp particulates (abrasive slurries). These particles can quickly erode or scour the liner, leading to premature failure.
Permeation by Small Molecules
While it is a liquid-proof barrier, certain small-molecule gases like hydrogen or chlorine can slowly pass through the PTFE material over time in a process called permeation. In high-pressure gas service, this must be evaluated to prevent gas from becoming trapped between the liner and the valve body.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision to use a PTFE-lined valve should be based on your primary engineering challenge.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive chemicals: PTFE-lined valves offer the most cost-effective and reliable protection for standard metal valve bodies.
- If your primary focus is maintaining high product purity (e.g., food, pharma, semiconductors): A PTFE liner is essential to prevent metal leaching and ensure a completely non-reactive fluid path.
- If your primary focus is reducing operational friction and wear: The self-lubricating nature of PTFE lowers energy consumption and extends the life of internal valve components.
By understanding PTFE's unique properties and trade-offs, you can confidently specify lined valves that ensure both system integrity and long-term reliability.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit in Lined Valves |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all acids, bases, and solvents; prevents corrosion. |
| Low Friction | Self-lubricating; reduces operating torque and wear on components. |
| High Purity | Non-contaminating; essential for food, pharma, and semiconductor industries. |
| Reliable Sealing | Creates a tight, bubble-free shut-off for safe operation. |
Need a reliable, high-purity PTFE component for your critical application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures your components meet the highest standards for chemical resistance and purity.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications



















