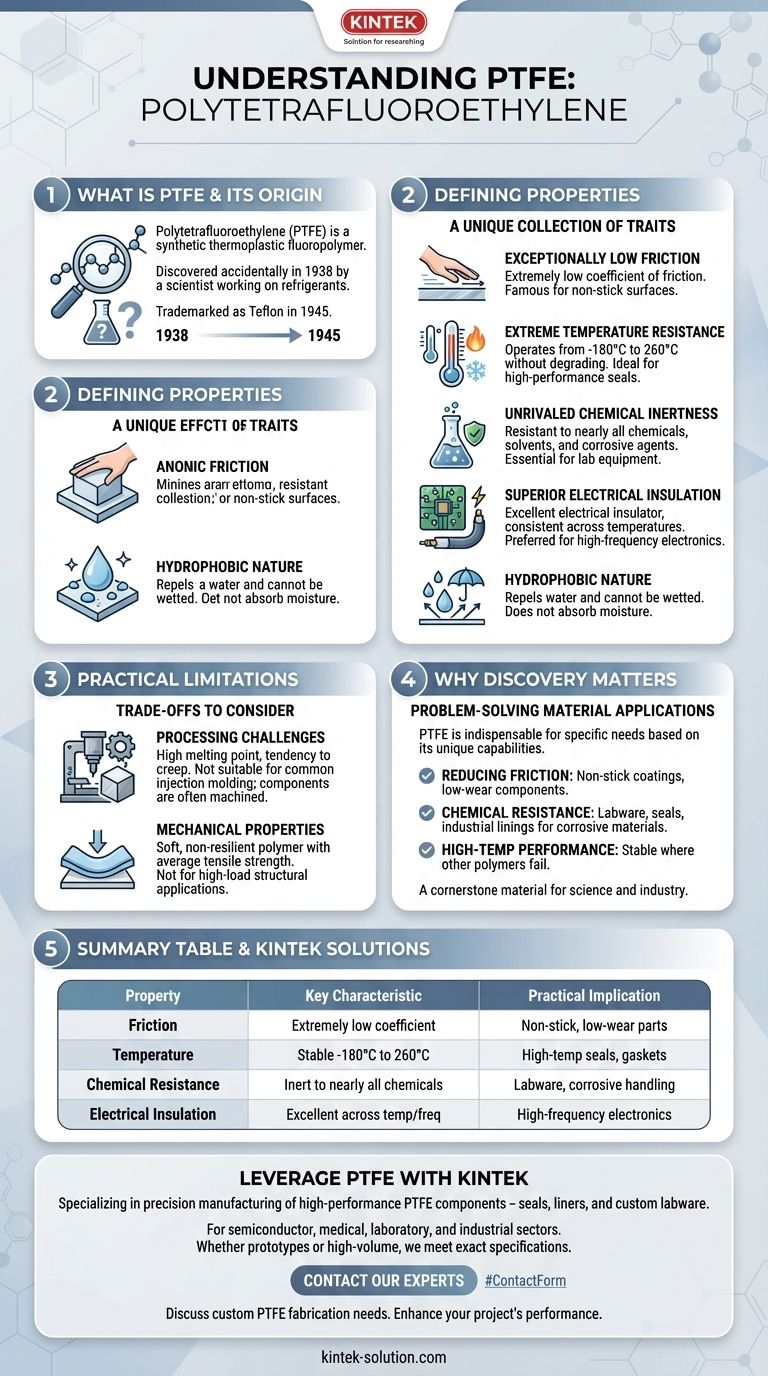
To be precise, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic thermoplastic fluoropolymer. It was discovered entirely by accident in 1938 by a scientist working on refrigerants, and its unique properties led to it being trademarked in 1945 as Teflon.
PTFE's accidental discovery revealed a material with a nearly unmatched combination of properties: extreme chemical resistance, high-temperature stability, and the lowest coefficient of friction of almost any solid. These characteristics make it one of the most versatile and valuable polymers in modern engineering.

The Defining Properties of PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene is not a single feature but a unique collection of traits. Understanding these core properties explains why it is used in everything from aerospace components to non-stick cookware.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction, meaning surfaces slide against it with very little resistance. It is often cited as having one of the lowest friction values of any known solid material.
This is the property responsible for its famous non-stick characteristics.
Extreme Temperature Resistance
The material is remarkably stable across a vast range of temperatures. It can operate continuously in environments from -180°C up to 260°C (-320°F to 500°F) without degrading.
This stability makes it invaluable for high-performance seals, gaskets, and components used in extreme heat or cold.
Unrivaled Chemical Inertness
PTFE exhibits outstanding resistance to nearly all chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. Its high chemical stability means it does not react with the substances it comes into contact with.
This makes it an essential material for laboratory equipment, chemical processing, and industrial linings where corrosive materials are handled.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator. Importantly, its insulating properties remain consistent across a wide range of temperatures and frequencies.
This reliability makes it a preferred choice for high-frequency electronics, such as in coaxial cables and circuit boards.
Hydrophobic Nature
As a hydrophobic material, PTFE repels water and cannot be wetted. It does not absorb moisture, which contributes to its stability and performance in various environments.
Understanding the Practical Limitations
Despite its remarkable advantages, PTFE is not the solution for every engineering problem. Its unique nature comes with specific trade-offs that are critical to understand.
Processing Challenges
PTFE has a very high melting temperature and a tendency to creep or "cold flow" under load. This makes it unsuitable for common high-volume manufacturing processes like injection molding or extrusion.
Instead, components are often machined from solid blocks of PTFE, which can make individual items more expensive to produce.
Mechanical Properties
While tough and flexible, PTFE is a soft, non-resilient polymer with only average tensile strength. It is not designed for high-load structural applications where rigidity and resistance to deformation are the primary requirements.
Why PTFE's Discovery Matters
The accidental discovery of PTFE provided engineers with a unique problem-solving material. Its applications are dictated directly by its fundamental properties.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction: PTFE offers one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid, making it ideal for non-stick coatings and low-wear components.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: Its chemical inertness makes it indispensable for handling corrosive materials in labware, seals, and industrial linings.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance: PTFE maintains its stability and integrity across a vast temperature range where most other polymers would fail.
Ultimately, PTFE remains a cornerstone material in science and industry precisely because no other single polymer offers its unique combination of capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Practical Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Friction | Extremely low coefficient of friction | Ideal for non-stick surfaces and low-wear parts |
| Temperature | Stable from -180°C to 260°C | Perfect for high-temperature seals and gaskets |
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to nearly all chemicals | Essential for labware and corrosive material handling |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent insulator across temperatures/frequencies | Preferred for high-frequency electronics |
Leverage PTFE's unique properties for your most demanding applications. At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures your components meet exact specifications for chemical resistance, temperature stability, and low friction.
Contact our experts today to discuss your custom PTFE fabrication needs and discover how we can enhance your project's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE considered versatile? A Material That Excels in Chemical, Thermal, and Frictional Resistance
- What are the key properties of PFA (PerFluoroAlkoxy)? A Guide to Extreme Chemical and Thermal Resistance
- What industries commonly use RPTFE and for what purposes? Enhance Durability in High-Load Applications
- What are the key properties and limitations of PTFE? Leveraging its Strengths for Your Application
- How does PTFE's flexibility affect its performance? Unlock Durability and Sealing Power
- What industries commonly use PTFE? Leverage Its Chemical Resistance, Low Friction & Electrical Insulation
- What is PTFE's resistance to chemicals? Discover the Ultimate Chemical-Resistant Polymer
- How does PTFE perform when exposed to sulfuric acid? Unmatched Chemical Resistance for Demanding Applications



















