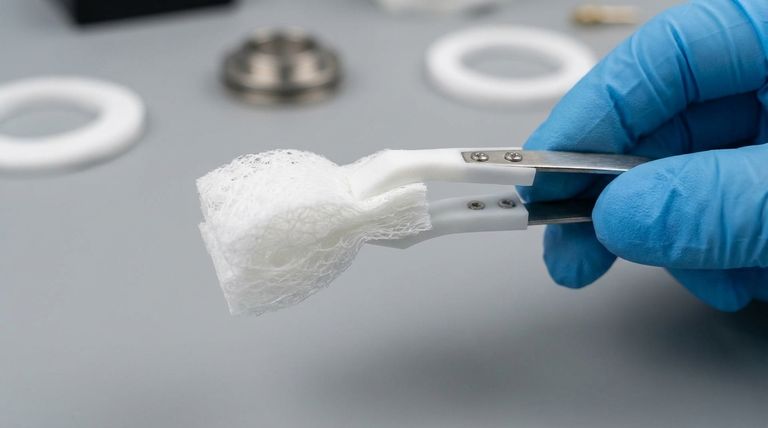
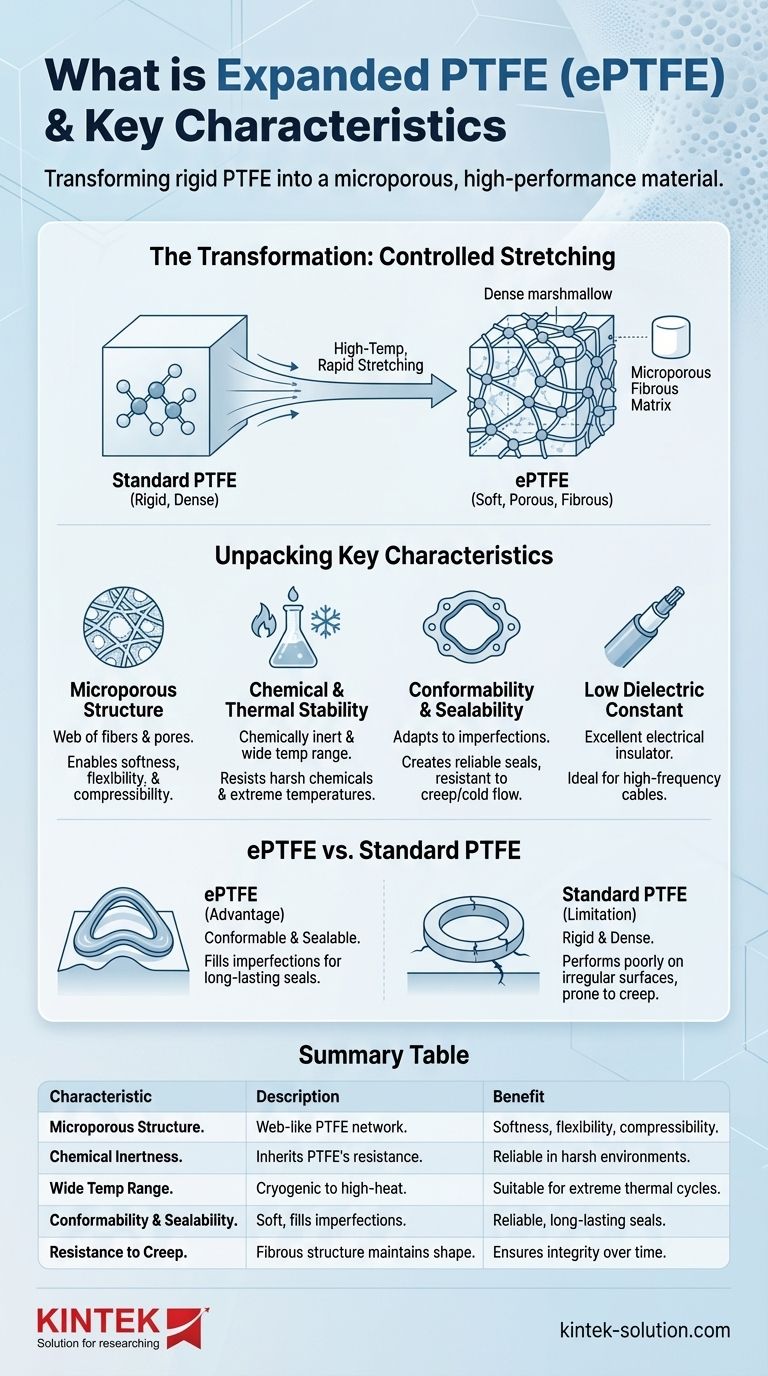
At its core, expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) is a specialized form of PTFE that has been physically modified to create a unique, porous structure. This process transforms standard, rigid PTFE into a remarkably soft, flexible, and strong material composed of microscopic fibers, all while retaining PTFE's legendary chemical resistance and ability to withstand extreme temperatures.
The defining characteristic of ePTFE is its microporous, fibrous structure. This structure is the source of its unique mechanical properties—like softness and conformability—which solve the rigidity limitations of standard PTFE in demanding applications.

The Transformation from PTFE to ePTFE
To understand ePTFE, you must first understand how it is made. It is not a different chemical, but a different physical form of the same base material.
The Manufacturing Process: Controlled Stretching
The process begins with 100% virgin PTFE, often in the form of a fine powder or paste, which is extruded into a specific shape. The key step follows: this material is rapidly stretched, or expanded, under carefully controlled high-temperature conditions.
The Resulting Structure: A Web of Fibers and Pores
This expansion process pulls the PTFE molecules apart, creating a web-like structure of interconnected fibers and nodes. The result is a material that is mostly empty space, or porosity, giving it a feel often compared to a dense marshmallow. This unique fibrous matrix is what gives ePTFE its distinctive set of properties.
Unpacking the Key Characteristics of ePTFE
The value of ePTFE comes from the combination of its new physical form and the inherent properties it retains from standard PTFE.
Superior Mechanical Performance
The fibrous structure makes ePTFE exceptionally soft, flexible, and conformable. It can easily adapt to irregular shapes, making it an outstanding sealing material.
Despite its softness, the material is incredibly strong and lightweight. The multi-directional network of fibers provides high tensile strength. It is also highly compressible and, crucially, resistant to the creep and cold flow that can plague standard PTFE seals over time.
Inherited Chemical and Thermal Stability
Like its parent material, ePTFE is chemically inert. It is resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents, making it suitable for the harshest environments.
It also maintains an excellent operational temperature range, performing reliably in both cryogenic conditions and high-heat applications.
The Power of Microporosity
The porous nature of ePTFE gives it a very low dielectric constant, making it an exceptional electrical insulator for high-performance wires and cables.
The pores are small enough to make the material watertight at low pressure, yet this microporosity can be engineered for specific applications requiring breathability. It is also highly resistant to UV radiation.
Understanding the Trade-offs: ePTFE vs. Standard PTFE
Choosing between standard PTFE and ePTFE requires understanding their fundamental structural differences. They are not interchangeable.
The Advantage: Conformability and Sealability
Standard PTFE is a rigid, dense plastic. While excellent for many uses, it performs poorly as a gasket on irregular, scratched, or fragile surfaces.
ePTFE solves this problem directly. Its softness allows it to compress and fill imperfections, creating a long-lasting, reliable seal where a standard PTFE gasket would fail. Its resistance to creep means the seal holds its integrity under pressure and over time.
The Limitation: Lower Density and Structural Rigidity
The porosity that makes ePTFE a great sealant also makes it less dense than solid PTFE. It is not a material you would use for a high-load structural component. Its strength is in its fibrous, flexible nature, not its bulk rigidity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision depends entirely on the mechanical requirements of your project.
- If your primary focus is sealing: Choose ePTFE for its superior conformability, compressibility, and resistance to creep, especially on uneven or delicate surfaces.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: ePTFE is the premier choice for flexible, high-frequency cable and wire wrapping due to its extremely low dielectric constant.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: Choose standard, solid PTFE for applications requiring a dense, rigid material that can withstand high compressive loads without deforming.
- If your primary focus is chemical compatibility: Both materials offer the same world-class chemical inertness, but ePTFE provides it in a more forgiving, flexible form factor.
Ultimately, ePTFE is an engineered material designed to deliver the chemical and thermal benefits of PTFE without its mechanical rigidity.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Microporous Structure | Web-like network of PTFE fibers and nodes created by a controlled stretching process. | Enables softness, flexibility, and compressibility. |
| Chemical Inertness | Inherits PTFE's resistance to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents. | Performs reliably in harsh environments. |
| Wide Temperature Range | Maintains performance from cryogenic conditions to high-heat applications. | Suitable for extreme thermal cycles. |
| Conformability & Sealability | Soft and compressible to fill surface imperfections. | Creates reliable, long-lasting seals on uneven or delicate surfaces. |
| Resistance to Creep/Cold Flow | The fibrous structure helps the material maintain its shape under constant load. | Ensures seal integrity over time, unlike standard PTFE. |
| Low Dielectric Constant | Excellent electrical insulator due to its porosity. | Ideal for high-performance wires and cable insulation. |
Need a high-performance sealing or insulating solution?
KINTEK's precision-manufactured ePTFE components are engineered to solve the rigidity limitations of standard PTFE. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our custom ePTFE fabrications—from prototypes to high-volume orders—deliver the perfect combination of legendary chemical resistance, extreme temperature stability, and superior conformability for your most demanding applications.
Let's discuss how our ePTFE expertise can enhance your product's reliability and performance.
Contact our engineering team today for a consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications



















