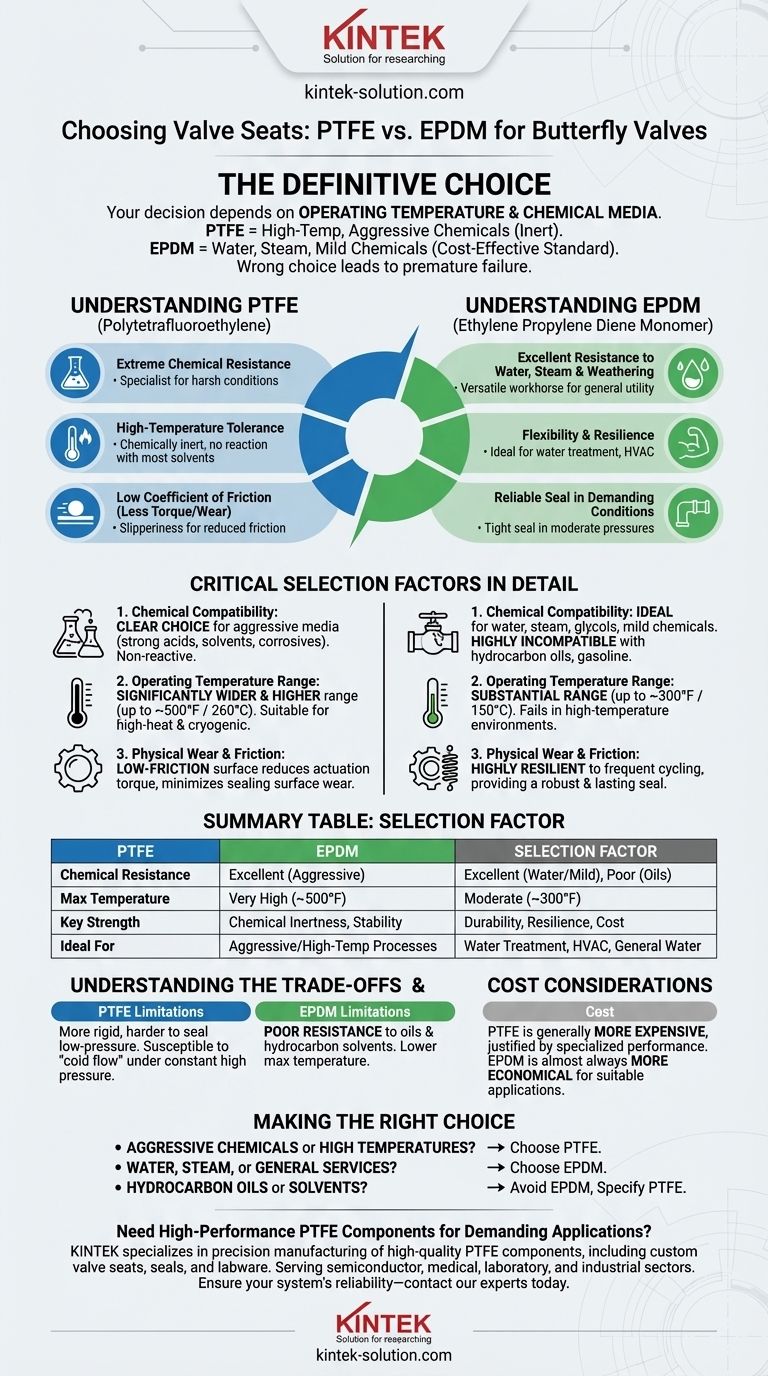
The definitive choice between a PTFE and EPDM valve seat is determined by your system's specific operating temperature and chemical media. PTFE is the superior choice for high-temperature, chemically aggressive environments due to its inertness. EPDM is the reliable, cost-effective standard for applications involving water, steam, and many mild chemicals.
Choosing the wrong valve seat material is a common cause of premature valve failure, leading to costly leaks and system downtime. The decision is not about which material is "better," but which one possesses the specific chemical and thermal properties required to ensure the long-term integrity and safety of your application.

Core Properties: PTFE vs. EPDM
To make an informed decision, you must first understand the fundamental characteristics of each material. These properties directly dictate their performance in a given environment.
Understanding PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene)
PTFE is a high-performance fluoropolymer known for its exceptional resistance properties. Think of it as the specialist for harsh conditions.
Its primary strengths are extreme chemical resistance and a high-temperature tolerance. Because it is chemically inert, it will not react with or degrade when exposed to the vast majority of industrial chemicals and solvents.
Furthermore, PTFE has a very low coefficient of friction. This "slipperiness" reduces the torque needed to operate the valve and minimizes wear on the seat over time, contributing to a longer service life.
Understanding EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer)
EPDM is a highly durable synthetic rubber that serves as a versatile workhorse for many industrial applications. It is the go-to material for general utility services.
EPDM’s standout feature is its excellent resistance to water, steam, and weathering (UV and ozone). It is also compatible with a wide range of mild acids, alkalis, and alcohols.
Its flexibility and resilience allow it to maintain a tight seal even in demanding conditions, making it a reliable choice for water treatment, HVAC, and general industrial water lines.
Critical Selection Factors in Detail
Your final decision will be based on a direct comparison of your application's demands against the strengths of each material.
Factor 1: Chemical Compatibility
This is the most critical factor. An incompatible material will degrade rapidly, causing seal failure.
PTFE is the clear choice for aggressive media such as strong acids, solvents, and corrosive chemicals. Its non-reactive nature ensures system integrity.
EPDM is ideal for water, steam, glycols, and many mild chemicals. However, it is highly incompatible with hydrocarbon oils, gasoline, and many solvents, which will cause it to swell and fail.
Factor 2: Operating Temperature Range
Every material has a safe operating temperature window. Exceeding this limit will cause the seat to soften or become brittle, destroying its sealing capability.
PTFE has a significantly wider and higher operating temperature range than EPDM, making it suitable for both high-heat processes and certain cryogenic applications.
EPDM offers a substantial temperature range suitable for most water and general industrial systems but will fail in the high-temperature environments where PTFE excels.
Factor 3: Physical Wear and Friction
The physical properties of the seat impact the valve's operational life and energy consumption.
PTFE's low-friction surface reduces the torque required for actuation, which can be a benefit in automated systems. This property also minimizes sealing surface wear during operation.
EPDM's flexibility and durability make it highly resilient to the rigors of frequent cycling in moderate-pressure water systems, providing a robust and lasting seal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. Acknowledging their limitations is key to preventing misapplication.
The Limitations of PTFE
While chemically robust, PTFE is a more rigid material. This can sometimes make it more challenging to achieve a perfect bubble-tight seal in very low-pressure applications. It can also be susceptible to "cold flow" or creep over time when subjected to constant high pressure.
The Limitations of EPDM
The primary limitation of EPDM is its poor resistance to oils and hydrocarbon solvents. Using an EPDM seat in a line containing these substances is a near-certain recipe for failure. Its lower maximum temperature also restricts its use in high-heat processes.
Cost Considerations
Generally, PTFE is a more expensive material than EPDM. Its cost is justified by its specialized high-performance capabilities. For applications where EPDM is a suitable choice, it will almost always be the more economical option.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Answering one or two simple questions about your system's media and conditions will guide you to the correct selection.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals or high temperatures: Choose PTFE for its unmatched chemical inertness and thermal stability.
- If your primary focus is water, steam, or general industrial services: Select EPDM for its excellent durability, sealing performance, and cost-effectiveness in these common applications.
- If your system involves any hydrocarbon oils or solvents: Avoid EPDM entirely and specify PTFE to ensure safe and reliable operation.
Ultimately, selecting the correct valve seat is a critical step in engineering a reliable and long-lasting system.
Summary Table:
| Selection Factor | PTFE | EPDM |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent for aggressive chemicals, solvents, strong acids | Excellent for water, steam, mild chemicals; poor for oils/hydrocarbons |
| Max Temperature | Very high (up to ~500°F / 260°C) | Moderate (up to ~300°F / 150°C) |
| Key Strength | Chemical inertness, high-temperature stability | Durability, resilience, cost-effectiveness for water/steam |
| Ideal For | Chemically aggressive, high-temperature processes | Water treatment, HVAC, general industrial water lines |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Demanding Applications?
Selecting the right material is critical for valve seat performance and system integrity. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-quality PTFE components, including custom valve seats, seals, liners, and labware.
We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, providing solutions from prototypes to high-volume production. Our expertise ensures your components meet exact specifications for chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and longevity.
Ensure your system's reliability—contact our experts today to discuss your custom PTFE fabrication needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE and Nitrile Diaphragm Pump Components for Demanding Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications



















