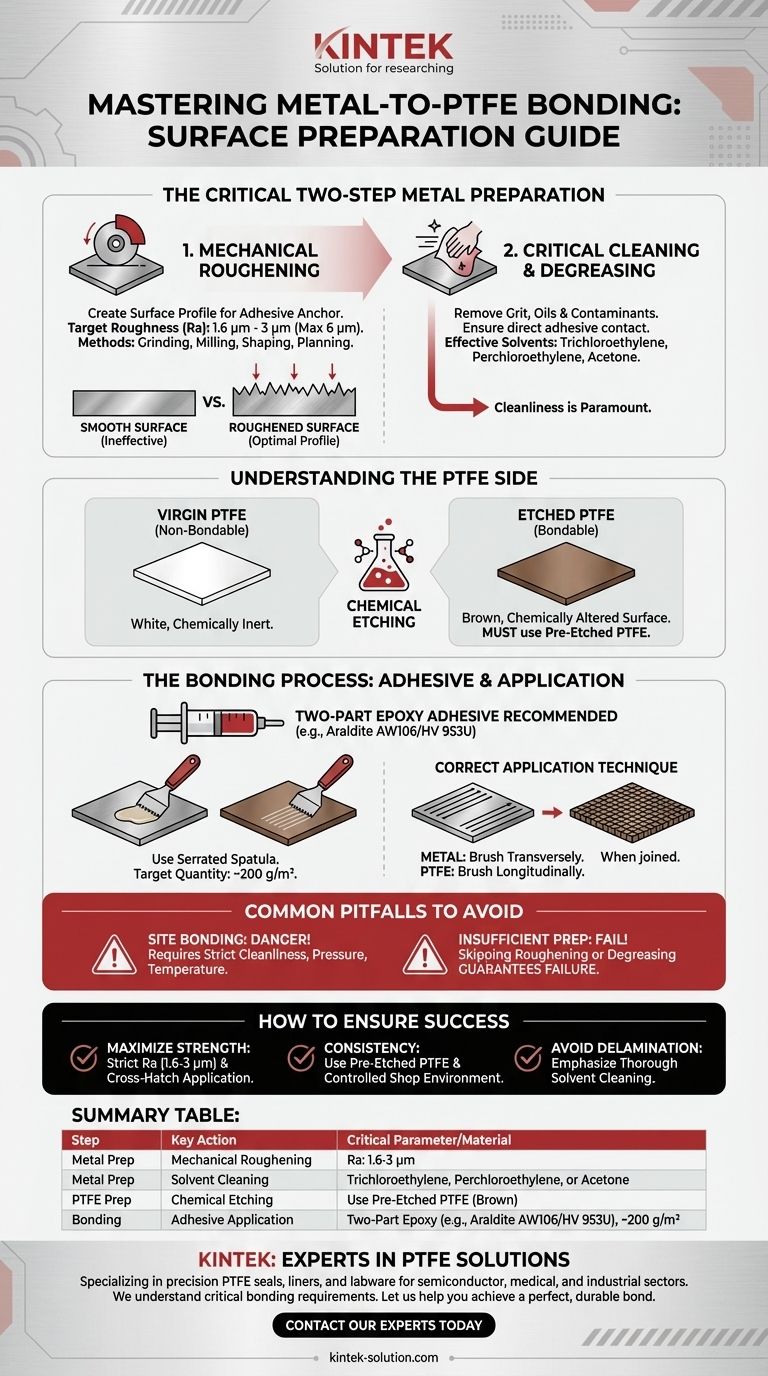
Proper metal surface preparation for bonding with PTFE is a critical two-step process. First, the metal must be mechanically roughened to create a specific surface profile that allows the adhesive to anchor itself. Second, the surface must be meticulously cleaned with solvents to remove all grit, oils, and other contaminants that would otherwise prevent a successful bond.
The key to a durable bond is recognizing that success depends equally on three factors: the mechanical preparation of the metal, the chemical preparation of the PTFE, and the correct application of the adhesive. Overlooking any one of these elements will compromise the integrity of the final bond.

The Foundational Steps for Metal Preparation
To create a strong mechanical lock for the adhesive, the metal surface cannot be smooth. It requires a specific texture that can only be achieved through controlled mechanical processes followed by absolute cleaning.
Achieving Optimal Surface Roughness
The goal of this step is to create microscopic peaks and valleys for the adhesive to grip.
This is typically accomplished using machining methods like grinding, milling, shaping, or planning.
The ideal surface roughness (Ra) is between 1.6 µm and 3 µm. While some variation is acceptable, the roughness should never exceed Ra = 6 µm, as a surface that is too coarse can also lead to a poor bond.
Critical Cleaning and Degreasing
After machining, the surface is contaminated with cutting fluids, oils, and metal debris. This residue must be completely removed.
A thorough solvent cleaning is essential to ensure the adhesive bonds directly to the metal, not to a layer of contaminants.
Effective solvents for this purpose include trichloroethylene, perchloroethylene, or acetone.
Understanding the PTFE Side of the Equation
Preparing the metal is only half the battle. Virgin PTFE is a non-stick material by its very nature and will not bond to anything without special surface treatment.
The Necessity of Chemical Etching
To make PTFE bondable, its surface must be chemically altered through a process called etching.
This proprietary process changes the molecular structure of the PTFE surface, making it receptive to standard industrial adhesives.
For any bonding application, you must use PTFE sheets that are specified as etched on one or both sides.
Identifying Properly Etched PTFE
You can visually confirm if your PTFE is ready for bonding.
Virgin, unbondable PTFE is white. A properly etched, bondable surface will have a uniform brown color.
The Bonding Process: Adhesives and Application
With both surfaces properly prepared, the final stage involves selecting the right adhesive and applying it correctly to ensure complete coverage and optimal strength.
Selecting the Right Adhesive
A two-part epoxy adhesive is highly recommended due to its excellent shear strength, which is crucial for this application.
A proven combination is Araldite AW106 resin used with Araldite HV 953U hardener.
Correct Application Technique
Uniform adhesive application is critical for a void-free bond line.
Use a serrated spatula to apply the mixed epoxy to both the prepared metal and the etched PTFE surface. The target quantity should be around 200 grams per square meter.
For the best dispersion, brush the adhesive longitudinally on the PTFE and transversely on the metal, creating a cross-hatch pattern when joined.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mistakes in the preparation or bonding process are the primary cause of failure. Understanding these common errors is key to preventing them.
The Dangers of Site Bonding
Attempting to bond PTFE to metal in the field (site bonding) is strongly discouraged.
This process requires strictly controlled conditions of cleanliness, pressure, and temperature that are nearly impossible to replicate outside of a dedicated workshop environment.
Insufficient Surface Preparation
The single most common cause of bond failure is inadequate preparation.
Skipping the mechanical roughening step or, more frequently, failing to completely degrease the surface will guarantee a weak bond that delaminates under stress.
How to Ensure a Successful Bond
To achieve a reliable and durable bond, your methodology should align with your project's primary requirement.
- If your primary focus is maximizing bond strength: Adhere strictly to the Ra = 1.6–3 µm surface roughness specification and use the cross-hatch adhesive application technique.
- If your primary focus is consistency and reliability: Always procure pre-etched PTFE from a reputable supplier and perform all bonding in a controlled shop environment, never on-site.
- If your primary focus is avoiding delamination: Place the greatest emphasis on the solvent cleaning step, as residual contamination is the most common and preventable cause of bond failure.
Ultimately, a successful metal-to-PTFE bond is not a matter of a single technique, but the result of a precise and disciplined multi-stage process.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Critical Parameter / Material |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Preparation | Mechanical Roughening | Surface Roughness (Ra): 1.6 - 3 µm |
| Solvent Cleaning | Trichloroethylene, Perchloroethylene, or Acetone | |
| PTFE Preparation | Chemical Etching | Use Pre-Etched PTFE (Brown Color) |
| Bonding Process | Adhesive Application | Two-Part Epoxy (e.g., Araldite AW106/HV 953U) |
| Application Quantity: ~200 g/m² |
Need reliable, high-performance PTFE components for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in material science ensures we understand the critical bonding requirements for demanding applications.
We can provide custom-fabricated components or advise on your specific bonding challenges. Let us help you achieve a perfect, durable bond every time.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What technical services are provided for PTFE product development? A Guide from Concept to Component
- What are the primary uses of Expanded PTFE? Unlock Its Unique Properties for Your Application
- What is a Teflon O-ring? A Guide to PTFE Seals for Extreme Chemical and Temperature Resistance
- What types of applications are PTFE / FEP / PFA lined pipes suitable for? Handle Extreme Corrosive Fluids Safely
- What are some examples of ePTFE applications in aerospace and automotive industries? Critical Components for Extreme Environments
- How can Teflon PTFE sheets be used in heat press applications? Protect Your Designs and Equipment
- What advantages do 40% bronze-filled PTFE bushings provide? Boost Load Capacity, Wear Resistance & Heat Dissipation
- What industries commonly use expanded PTFE gaskets? A Guide to Critical Sealing Solutions



















