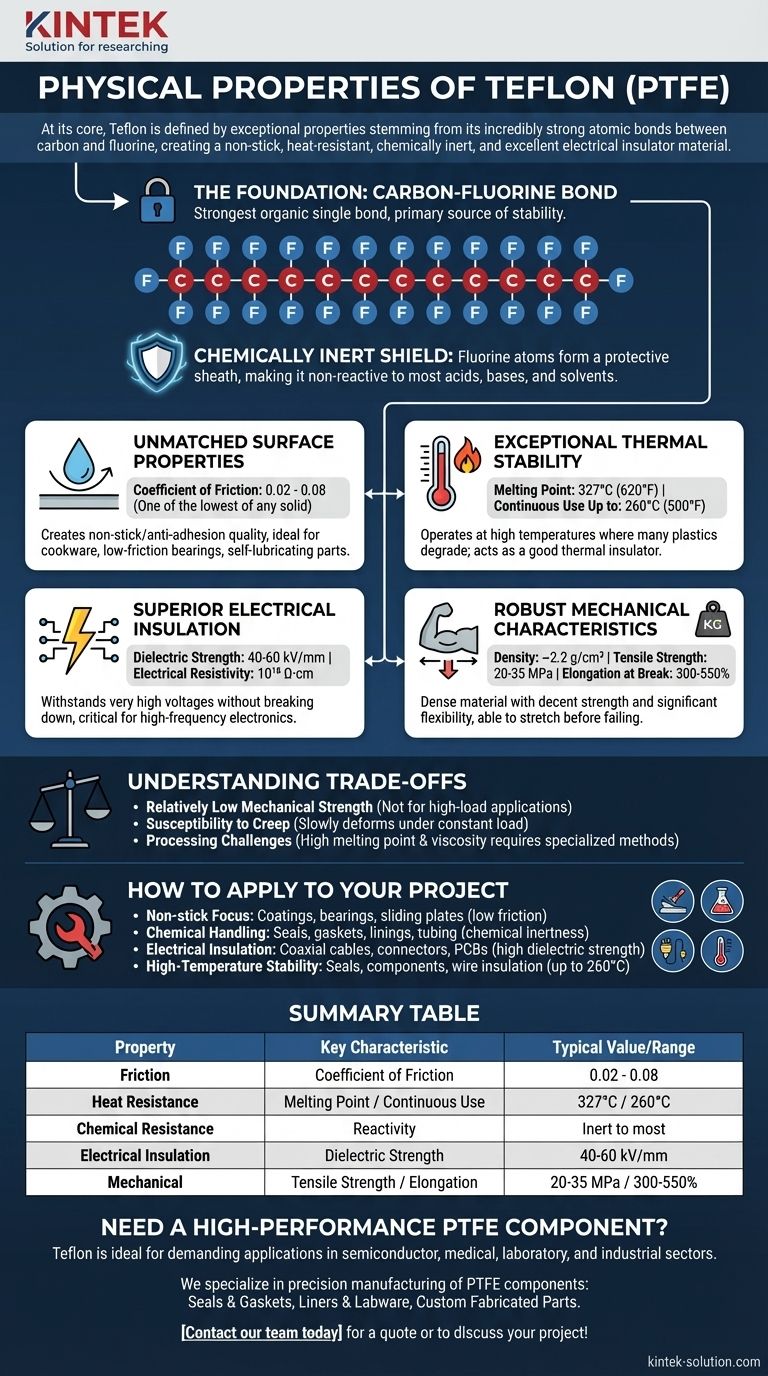
At its core, Teflon (PTFE) is defined by four exceptional physical properties: an extremely low coefficient of friction creating a non-stick surface, high heat resistance with a melting point of 327°C, near-total chemical inertness, and excellent performance as an electrical insulator. These traits all stem from the incredibly strong atomic bonds between carbon and fluorine that form its molecular structure.
The key takeaway is that Teflon's properties are not just a list of metrics; they are a direct result of its unique molecular structure. The strength of the carbon-fluorine bond makes it simultaneously non-reactive, heat-stable, and electrically insulating, creating one of the most versatile and resilient polymers available.

The Foundation: Why Teflon Behaves The Way It Does
To truly understand Teflon's physical properties, we must first look at its chemical makeup. Its remarkable characteristics are not accidental; they are a direct consequence of its molecular architecture.
The Power of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
Teflon, or Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is a polymer consisting of a long chain of carbon atoms, where each carbon is completely surrounded by fluorine atoms.
The bond between carbon and fluorine is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry. This immense bond strength is the primary source of Teflon's stability.
A Chemically Inert Shield
The fluorine atoms form a tight, protective sheath around the carbon backbone. This sheath effectively shields the carbon chain from reacting with outside chemicals.
As a result, Teflon is chemically inert and non-reactive to the vast majority of corrosive acids, bases, and solvents. Only a few highly reactive substances, like molten alkali metals, can affect it.
A Breakdown of Key Physical Properties
Each of Teflon's famous properties can be traced back to its stable molecular structure. This makes it uniquely suited for applications where other materials would quickly fail.
Unmatched Surface Properties (Low Friction)
Teflon has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid, typically between 0.02 and 0.08.
This extremely low friction is what creates its signature non-stick or anti-adhesion quality, making it ideal for cookware, low-friction bearings, and self-lubricating parts.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
With a melting point around 327°C (620°F), Teflon can operate at high temperatures where many other plastics would degrade. It is stable for continuous use up to 260°C (500°F).
Furthermore, it has a low thermal conductivity of about 0.25 W/(m·K), meaning it does not transfer heat well and acts as a good thermal insulator. It also maintains its properties at extremely low temperatures.
Superior Electrical Insulation
Teflon is an exceptional electrical insulator. It possesses a very high dielectric strength (around 40-60 kV/mm) and extremely high electrical resistivity (10¹⁸ Ω·cm).
This means it can withstand very high voltages without breaking down, making it a critical material for high-frequency cables, circuit boards, and other demanding electronic components.
Robust Mechanical Characteristics
Teflon is a dense material, with a density of approximately 2.2 g/cm³. It combines decent strength with significant flexibility.
It has a moderate tensile strength (20-35 MPa) but a very high elongation at break (300-550%), meaning it can stretch significantly before failing. Its hardness is relatively soft for a polymer, typically 55-60 on the Shore D scale.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect, and Teflon's unique strengths come with inherent limitations. Understanding these is critical for proper material selection in any engineering context.
Relatively Low Mechanical Strength
While durable, Teflon is not a high-strength structural plastic. Its tensile and compressive strengths are significantly lower than materials like nylon, PEEK, or metals. It should not be used for high-load-bearing applications.
Susceptibility to Creep
Like many soft polymers, Teflon is susceptible to creep, which is the tendency to slowly deform over time when under a constant load. This is a key consideration for designing seals and gaskets that must maintain pressure.
Processing Challenges
Teflon's high melting point and high melt viscosity make it more difficult to process using conventional methods like injection molding. It often requires specialized techniques like compression molding and sintering.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of material depends entirely on the primary challenge you need to solve. Teflon's properties make it the ideal solution for several distinct problems.
- If your primary focus is non-stick surfaces or low-friction movement: Leverage its uniquely low coefficient of friction for coatings, bearings, or sliding plates.
- If your primary focus is handling corrosive chemicals: Use its chemical inertness for seals, gaskets, linings, and tubing in harsh chemical environments.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: Rely on its high dielectric strength and low signal loss for coaxial cables, connectors, and printed circuit boards.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability: Choose it for seals, components, and wire insulation that must perform reliably in environments up to 260°C (500°F).
Ultimately, Teflon's value lies in its ability to perform reliably where other materials simply cannot survive.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Typical Value/Range |
|---|---|---|
| Friction | Coefficient of Friction | 0.02 - 0.08 |
| Heat Resistance | Melting Point / Continuous Use | 327°C (620°F) / Up to 260°C (500°F) |
| Chemical Resistance | Reactivity | Inert to most acids, bases, and solvents |
| Electrical Insulation | Dielectric Strength | 40-60 kV/mm |
| Mechanical | Tensile Strength / Elongation at Break | 20-35 MPa / 300-550% |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Component for Your Application?
Teflon's unique properties make it the ideal material for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require non-stick surfaces, chemical resistance, or high-temperature stability, KINTEK can help.
We specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including:
- Seals & Gaskets for corrosive or high-temperature environments
- Liners & Labware for chemical processing and research
- Custom Fabricated Parts from prototypes to high-volume production runs
Leverage our expertise to get durable, reliable components tailored to your exact specifications. Contact our team today for a quote or to discuss your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















