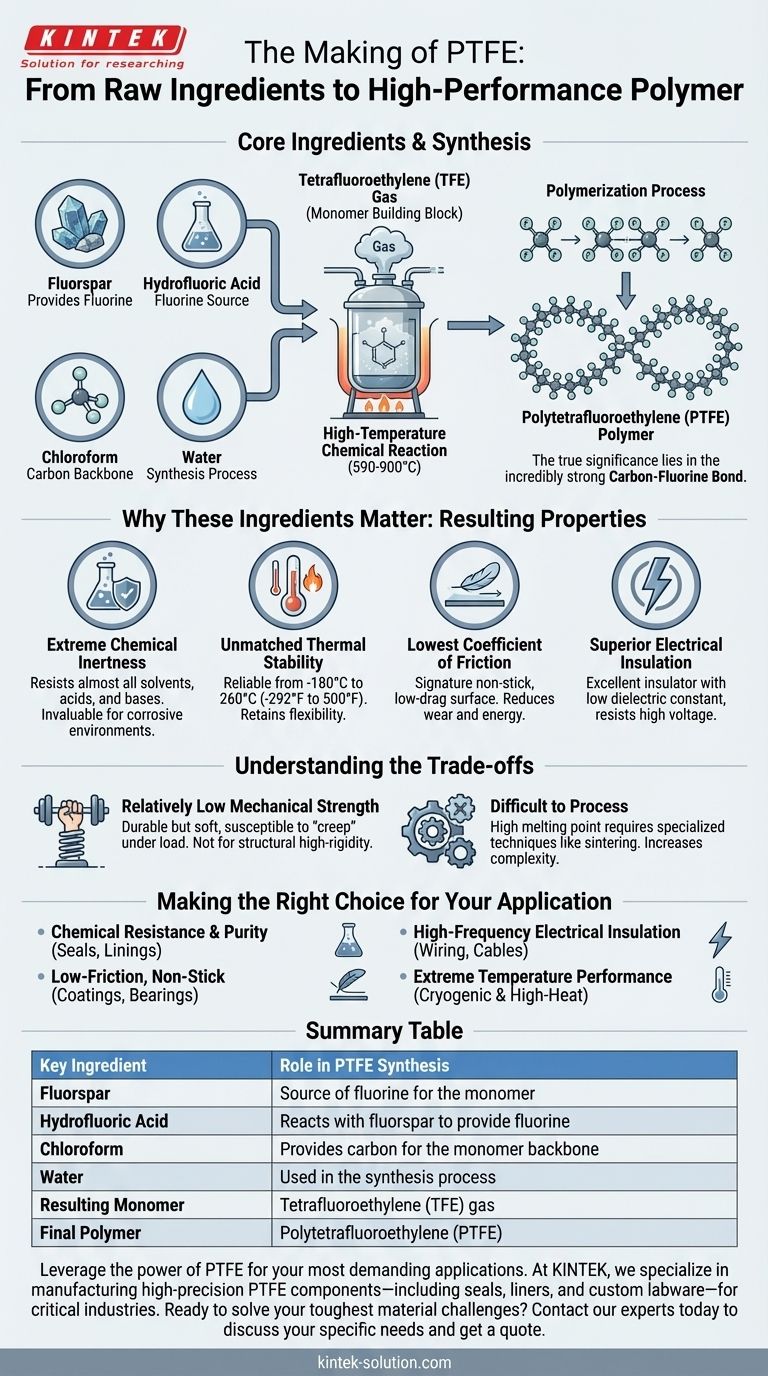
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is produced from four primary ingredients. These are fluorspar, hydrofluoric acid, chloroform, and water. These components are combined and synthesized in a high-temperature chemical reaction to first create tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) gas, the monomer building block which is then polymerized into the final PTFE material.
The true significance of PTFE lies not in the complexity of its ingredients, but in how their synthesis creates the incredibly strong carbon-fluorine bond. This single chemical feature is the source of nearly all of PTFE's remarkable and commercially valuable properties.

The Foundation: From Raw Materials to a Stable Polymer
Understanding PTFE begins with its creation. The process is not about mixing ingredients like a recipe, but about a chemical synthesis that builds a unique molecular structure from the ground up.
The Core Components
The synthesis of PTFE starts with creating its monomer, tetrafluoroethylene (TFE). The key raw materials—fluorspar, hydrofluoric acid, and chloroform—are reacted under intense heat, often between 590-900°C (1094-1652°F).
This reaction produces the TFE gas, a simple molecule consisting of two carbon atoms and four fluorine atoms.
The Polymerization Process
The TFE gas is the fundamental building block. Through a process called polymerization, countless individual TFE molecules (monomers) are linked together into extremely long, stable chains.
This final chain is the polymer known as Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). The strength and stability of this chain are what give the material its famous characteristics.
Why These Ingredients Matter: The Resulting Properties
The simple ingredients of PTFE give rise to a material with an extraordinary combination of useful traits. The high concentration of fluorine is the key to its performance.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
The carbon-fluorine bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry. This makes PTFE almost universally inert, resisting attack from nearly all common solvents, acids, and bases.
This property makes it invaluable for seals, linings, and lab equipment used in highly corrosive chemical environments.
Unmatched Thermal Stability
PTFE performs reliably across an exceptionally broad temperature range, from as low as -180°C (-292°F) to a high continuous service temperature of 260°C (500°F).
Unlike most plastics, it retains its flexibility at cryogenic temperatures and remains stable at temperatures that would degrade other polymers.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material. This gives it the signature non-stick, low-drag surface recognized in everything from cookware to industrial bearings.
This property reduces wear and energy consumption in mechanical applications.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with a very low dielectric constant and high dielectric strength. It resists high voltages and does not absorb water, which can affect electrical performance.
This makes it a critical material for high-frequency applications, such as in coaxial cables and insulating wiring in aerospace and computing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every application. To use PTFE effectively, it's critical to understand its limitations, which also stem from its unique chemical structure.
Relatively Low Mechanical Strength
While durable and flexible, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It has average tensile strength and can be susceptible to "creep"—a slow deformation under sustained load.
It is not suitable for structural applications where high rigidity or load-bearing capacity is required.
Difficult to Process
The same chemical stability and high melting point that make PTFE so durable also make it difficult to process using conventional polymer methods like injection molding.
It typically requires specialized techniques like sintering or machining from stock shapes, which can increase manufacturing complexity and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE is a decision driven by the need for performance under extreme conditions where other materials would fail.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance and purity: PTFE is an ideal choice for seals, gaskets, and vessel linings in the chemical processing and pharmaceutical industries.
- If your primary focus is a low-friction, non-stick surface: It is the go-to material for coatings on cookware, self-lubricating bearings, and surfaces that require easy release.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: PTFE's electrical properties are essential for high-performance wiring and cable insulation, especially in aerospace and telecommunications.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature performance: It is one of the few materials that can function reliably in both cryogenic and high-heat environments.
Ultimately, the simple chemical foundation of PTFE gives rise to its exceptional performance in the world's most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Ingredient | Role in PTFE Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Fluorspar | Source of fluorine for the monomer. |
| Hydrofluoric Acid | Reacts with fluorspar to provide fluorine. |
| Chloroform | Provides carbon for the monomer backbone. |
| Water | Used in the synthesis process. |
| Resulting Monomer | Tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) gas. |
| Final Polymer | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). |
Leverage the power of PTFE for your most demanding applications.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for industries where performance under extreme conditions is critical. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our expertise in custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders ensures you get a component that delivers unmatched chemical inertness, thermal stability, and reliability.
Ready to solve your toughest material challenges? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What PTFE formulations are recommended for automotive and aerospace applications and why? Optimize with Bronze-Filled PTFE
- What is PTFE and what are its main properties? Discover the Ultimate High-Performance Polymer
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- What are the key properties of PTFE? Unlock Superior Performance in Harsh Environments
- What is PTFE and what are its primary characteristics? The Ultimate High-Performance Polymer
- What are some common applications of PTFE? Harnessing the Power of a Versatile Polymer
- Why is PTFE considered non-reactive? The Power of an Unbreakable Molecular Bond
- What is the chemical composition of PTFE? Unlocking the Power of Carbon-Fluorine Bonds



















