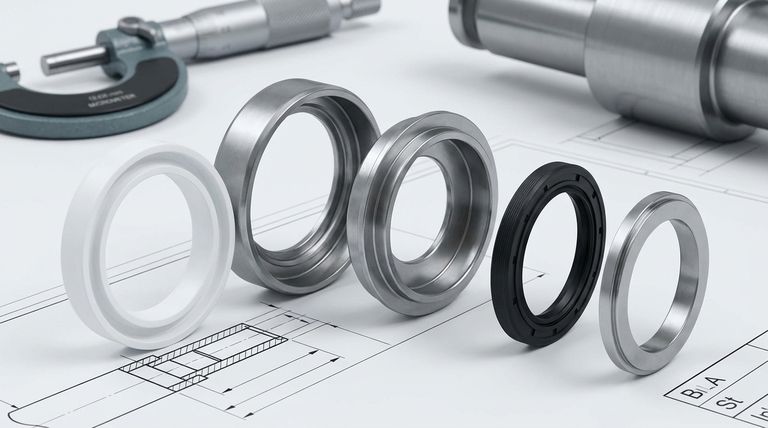
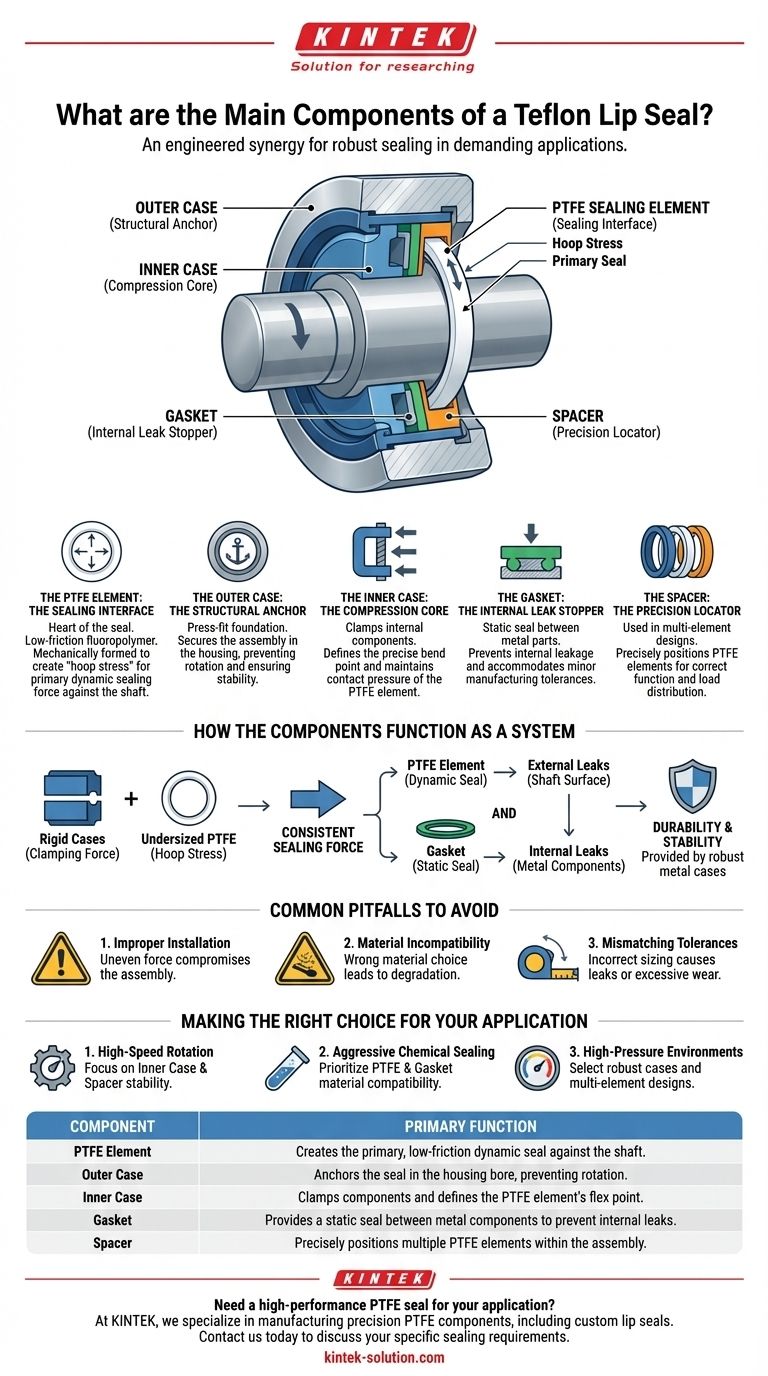
At its core, a Teflon lip seal is a multi-part assembly designed for demanding sealing applications. Its main components are the outer case, inner case, gasket, spacer, and one or more Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) sealing elements. These parts work in unison to create a robust and reliable seal against a rotating shaft.
The effectiveness of a Teflon lip seal doesn't come from a single part, but from the engineered synergy between its components. A rigid housing provides structural integrity, while the flexible PTFE element uses its inherent properties to create a tight, low-friction seal.

The Anatomy of a Teflon Lip Seal
To understand how the seal functions, we must first examine the specific role of each component within the assembly.
The PTFE Element: The Sealing Interface
The PTFE element is the heart of the seal. PTFE, commonly known by the brand name Teflon, is a high-performance fluoropolymer consisting of carbon and fluorine.
This element is mechanically formed to a diameter slightly smaller than the shaft it will seal against. This size difference creates a natural tension, known as hoop stress, which provides the primary sealing force against the shaft's surface.
The Outer Case: The Structural Anchor
The outer case is the seal's foundation. It is designed to be press-fit into the equipment's housing or bore.
Its primary function is to secure the entire seal assembly in place, preventing it from rotating along with the shaft. This provides the necessary stability for the other components to function correctly.
The Inner Case: The Compression Core
The inner case works in tandem with the outer case to clamp and compress all the internal components.
Crucially, it also helps define the precise bend point, or flex point, of the PTFE sealing element, ensuring it maintains correct contact and pressure on the shaft.
The Gasket: The Internal Leak Stopper
While the PTFE element prevents fluid from leaking along the shaft, the gasket prevents leakage through the seal body itself.
It is compressed between the other components, sealing any potential internal leak paths and taking up minor manufacturing tolerances to ensure a tight fit.
The Spacer: The Precision Locator
In designs with multiple sealing elements or complex geometries, a spacer is used.
Its role is to properly position the PTFE elements relative to each other and the inner case. This ensures each sealing lip is correctly located and functions as intended.
How the Components Function as a System
No single component works in isolation. The seal's performance relies on the precise interaction between the rigid and flexible parts.
Creating the Sealing Force
The outer and inner cases act as a rigid clamp, holding the softer gasket and PTFE element under constant pressure. This mechanical clamping, combined with the hoop stress of the undersized PTFE element, creates a consistent and durable seal.
Preventing Internal vs. External Leaks
The design cleverly addresses two distinct leak paths. The PTFE element manages the dynamic seal at the rotating shaft surface, preventing external leaks. Simultaneously, the static gasket manages the internal seal between the metal components, preventing fluid from bypassing the PTFE element entirely.
Ensuring Durability and Stability
The robust metal cases protect the relatively soft PTFE element from damage during installation and operation. By anchoring the seal in the bore, the outer case guarantees that only the shaft rotates, allowing the sealing lip to maintain its optimal position.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding the design also highlights potential failure points if not handled correctly.
Improper Installation
The seal's reliance on a precise press-fit means that improper installation can be catastrophic. Applying uneven force or damaging the outer case can compromise the entire assembly, leading to immediate leaks or premature failure.
Material Incompatibility
While PTFE offers excellent chemical resistance, it is not universally compatible. The gasket material and even the case metal must be selected based on the specific fluids, temperatures, and pressures of the application to prevent degradation.
Mismatching Seal and Shaft Tolerances
The principle of hoop stress relies on a specific size difference between the PTFE element and the shaft. Using a seal on a shaft that is out of its specified tolerance range will result in either an ineffective seal (if the shaft is too small) or excessive friction and wear (if the shaft is too large).
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right seal requires understanding which components are most critical for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is high-speed rotation: The design of the inner case and spacer is crucial, as they control the stability and contact point of the PTFE element.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical sealing: The material grades of the PTFE element and the internal gasket are the most important factors for ensuring long-term compatibility.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure environments: Look for designs with robust cases and potentially multiple PTFE elements, which distribute the sealing load more effectively.
Understanding how each part contributes to the whole empowers you to select and install a seal that will perform reliably in its intended application.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| PTFE Element | Creates the primary, low-friction dynamic seal against the shaft. |
| Outer Case | Anchors the seal in the housing bore, preventing rotation. |
| Inner Case | Clamps components and defines the PTFE element's flex point. |
| Gasket | Provides a static seal between metal components to prevent internal leaks. |
| Spacer | Precisely positions multiple PTFE elements within the assembly. |
Need a high-performance PTFE seal for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom lip seals, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your seals deliver reliable performance, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact us today to discuss your specific sealing requirements and let our experts provide a solution tailored to your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















