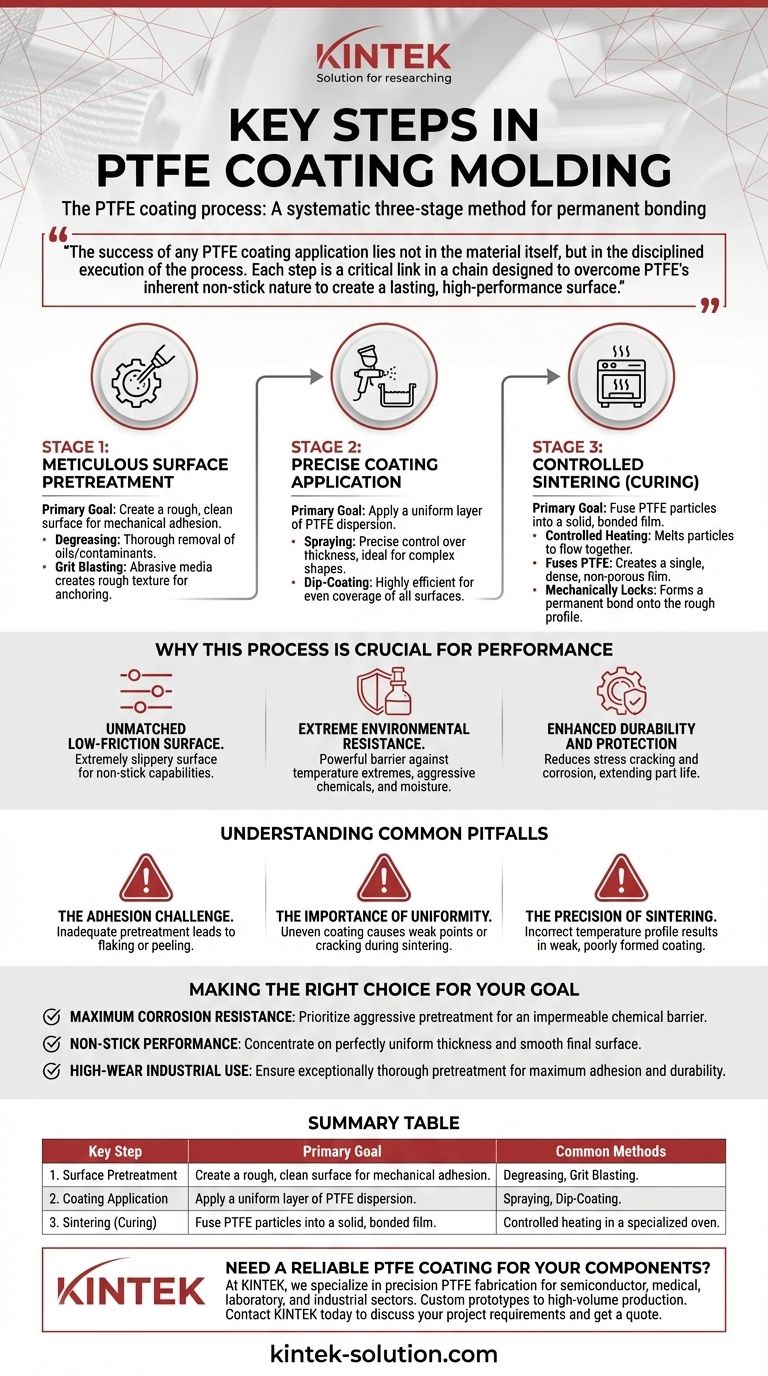
The PTFE coating process is a systematic, three-stage method designed to permanently bond one of the world's most non-reactive materials to a substrate. The essential steps are meticulous surface pretreatment to ensure adhesion, the precise application of a PTFE dispersion, and a controlled high-temperature sintering phase to fuse the coating into a durable, solid film.
The success of any PTFE coating application lies not in the material itself, but in the disciplined execution of the process. Each step is a critical link in a chain designed to overcome PTFE's inherent non-stick nature to create a lasting, high-performance surface.

The Foundational Stages of PTFE Coating
Applying PTFE is fundamentally different from applying paint. Because PTFE is engineered to not stick to anything, the substrate must be perfectly prepared and the coating must be thermally fused to it in a process that transforms it from a liquid dispersion into a solid, integrated layer.
Step 1: Meticulous Surface Pretreatment
This initial stage is the most critical factor in determining the final quality and longevity of the coating. Its sole purpose is to create a surface that the PTFE can mechanically grip.
The substrate is first thoroughly degreased to remove any oils or contaminants. It then typically undergoes a process like grit blasting, which uses abrasive media to create a rough, high-surface-area texture for the coating to anchor into.
Step 2: Precise Coating Application
Once the surface is prepared, a liquid dispersion containing fine PTFE particles is applied. The goal here is uniformity.
The two most common industrial methods are spraying and dip-coating. Spraying offers precise control over thickness, which is ideal for complex shapes, while dip-coating is highly efficient for covering all surfaces of an object evenly.
Step 3: Controlled Sintering (Curing)
Sintering is the transformative step. The coated part is heated in a specialized oven to temperatures that cause the individual PTFE particles to melt and flow together.
This thermal process achieves two goals simultaneously. It fuses the PTFE into a single, dense, and non-porous film, and it mechanically locks that film onto the rough profile created during pretreatment. This is what forms the permanent bond.
Why This Process is Crucial for Performance
The multi-stage process is necessary to impart PTFE's exceptional properties onto a substrate. Without proper execution, these benefits are lost.
Unmatched Low-Friction Surface
Proper sintering results in an extremely slippery surface, which is why PTFE is renowned for its non-stick capabilities in applications from cookware to industrial molds.
Extreme Environmental Resistance
The dense, non-porous film created during curing provides a powerful barrier. This gives the underlying component high resistance to temperature extremes, aggressive chemicals, and moisture.
Enhanced Durability and Protection
A well-applied PTFE coating significantly reduces the risk of stress cracking and corrosion on the base material, extending the functional life of the part.
Understanding the Common Pitfalls
While highly effective, the PTFE coating process is unforgiving of error. Understanding the potential points of failure is key to achieving a successful outcome.
The Adhesion Challenge
The single most common cause of coating failure is inadequate surface pretreatment. Any remaining oil, debris, or an improperly roughened surface will prevent the coating from forming a strong mechanical bond, leading to flaking or peeling.
The Importance of Uniformity
An uneven coating application can create significant problems. Areas that are too thin will be weak points for wear and corrosion, while areas that are too thick can crack or blister during the sintering phase due to thermal stresses.
The Precision of Sintering
Sintering is more than just heating. It requires a precise temperature profile—heating at the right rate, holding at the right temperature, and cooling correctly. Rushing this process or using incorrect temperatures will result in a weak, poorly formed coating that fails prematurely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The emphasis of the process can be adjusted depending on the final application's primary requirement.
- If your primary focus is maximum corrosion resistance: Prioritize an aggressive surface pretreatment and ensure a flawless, pinhole-free coating to create an impermeable chemical barrier.
- If your primary focus is non-stick performance: Concentrate on achieving a perfectly uniform coating thickness and a smooth final surface from a well-controlled sintering cycle.
- If your primary focus is high-wear industrial use: Ensure the pretreatment is exceptionally thorough to maximize adhesion, as this is the foundation of the coating's physical durability.
By mastering these fundamental stages, you can reliably transform a standard component into a high-performance part ready to withstand the most demanding conditions.
Summary Table:
| Key Step | Primary Goal | Common Methods |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Surface Pretreatment | Create a rough, clean surface for mechanical adhesion. | Degreasing, Grit Blasting. |
| 2. Coating Application | Apply a uniform layer of PTFE dispersion. | Spraying, Dip-Coating. |
| 3. Sintering (Curing) | Fuse PTFE particles into a solid, bonded film. | Controlled heating in a specialized oven. |
Need a reliable PTFE coating for your components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision PTFE fabrication for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your parts benefit from superior non-stick properties, extreme chemical resistance, and enhanced durability.
We handle everything from custom prototypes to high-volume production, guaranteeing a flawless coating process and a high-performance result.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE and its basic chemical structure? The Key to Its Legendary Performance
- What are the advantages of using Teflon coating in cooking utensils? Discover Effortless Cooking & Cleaning
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its key properties? Unlock the Power of Teflon™
- What is the chemical composition and structure of PTFE? Unlocking the Secrets of Teflon's Power
- Is PTFE toxic to humans? The Critical Role of Temperature in PTFE Safety
- Is Teflon hard or soft compared to other engineering plastics? A Guide to Its Unique Properties
- What are the primary applications of PTFE? Unlocking High-Performance Solutions
- How does PTFE demonstrate strong chemical resistance? Unmatched Inertness for Harsh Chemical Environments



















