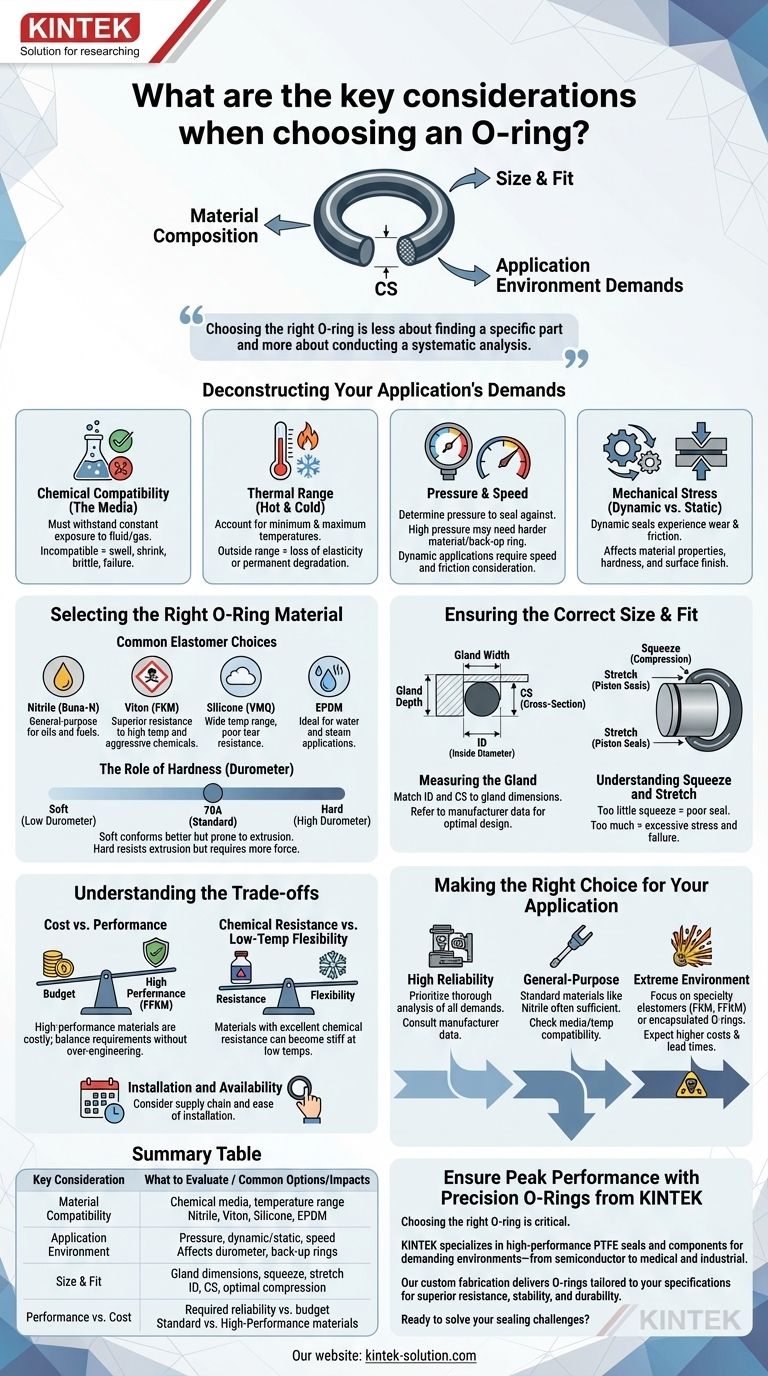
The most critical considerations when choosing an O-ring are its material composition, its size, and the specific demands of its application environment. A successful seal depends entirely on correctly matching the O-ring's properties—like chemical resistance and temperature range—to the precise conditions it will face, including pressure, media, and mechanical stress.
Choosing the right O-ring is less about finding a specific part and more about conducting a systematic analysis. You must first define the chemical, thermal, and mechanical challenges of your application, as this will dictate the correct material and size needed to ensure a reliable, long-lasting seal.
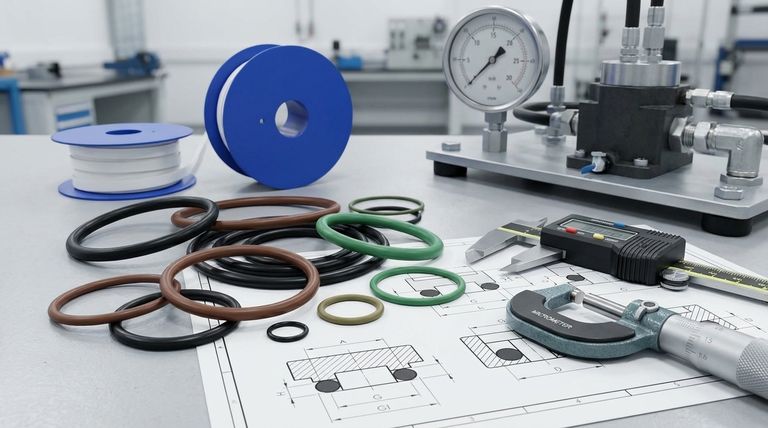

Deconstructing Your Application's Demands
Before you can select a material or size, you must have a complete picture of the environment where the O-ring will operate. Answering these questions is the most important step in the process.
Chemical Compatibility (The Media)
The first filter is chemical compatibility. The O-ring material must be able to withstand constant exposure to the fluid or gas it is sealing without degrading.
An incompatible material can swell, shrink, or become brittle, leading to seal failure, equipment damage, and costly downtime.
Thermal Range (Hot and Cold)
Every O-ring material has a specific functional temperature range. You must account for both the minimum and maximum operating temperatures of your system.
A material used outside its intended range can lose elasticity at low temperatures or degrade permanently at high temperatures, compromising its ability to maintain a seal.
Pressure and Speed
You must determine the pressure the O-ring needs to seal against. High-pressure applications may require a harder material (higher durometer) or the use of a back-up ring to prevent extrusion.
For dynamic applications where parts are moving, you must also consider the speed of movement, which generates friction and heat, influencing material choice.
Mechanical Stress (Dynamic vs. Static)
Is the seal static (between two non-moving parts) or dynamic (between moving parts)? Dynamic seals experience wear and friction that static seals do not.
This distinction is critical, as it affects the required material properties, hardness, and even the surface finish of the hardware.
Selecting the Right O-Ring Material
Once you understand the application's demands, you can select an appropriate material. The material is the primary factor driving the O-ring's performance.
Common Elastomer Choices
Different elastomers are engineered for specific conditions. For example, Nitrile (Buna-N) is a good general-purpose choice for oils and fuels, while Viton (FKM) offers superior resistance to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals.
Silicone (VMQ) is excellent for a wide temperature range but has poor tear resistance, whereas EPDM is ideal for water and steam applications.
The Role of Hardness (Durometer)
Hardness, measured in durometer, indicates the material's resistance to indentation. A standard durometer is 70A.
Softer materials (lower durometer) conform better to surface imperfections but are more prone to extrusion under pressure. Harder materials (higher durometer) resist extrusion but require more force to create a seal.
Ensuring the Correct Size and Fit
An O-ring seals by being compressed within a groove, known as a gland. Incorrect sizing is a leading cause of leaks.
Measuring the Gland
The O-ring's dimensions—its inside diameter (ID) and cross-section (CS)—must be correctly matched to the gland's dimensions.
Always refer to manufacturer data sheets or industry guidelines for proper gland design and sizing calculations to ensure optimal performance.
Understanding Squeeze and Stretch
Proper sealing requires a specific amount of "squeeze" (compression of the cross-section) and, for piston-style seals, a slight "stretch" of the inside diameter.
Too little squeeze results in a poor seal, while too much can cause excessive stress on the material, leading to premature failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
There is no single "best" O-ring for every situation. Every choice involves balancing competing factors.
Cost vs. Performance
High-performance materials like Perfluoroelastomers (FFKM) offer exceptional chemical and thermal resistance but come at a significant cost premium.
It is crucial to select a material that meets the application's requirements without over-engineering and incurring unnecessary expense.
Chemical Resistance vs. Low-Temp Flexibility
There is often a trade-off between a material's properties. For instance, many elastomers with excellent resistance to aggressive chemicals become stiff and brittle at low temperatures.
You must prioritize the most critical performance characteristic for your specific application.
Installation and Availability
The perfect O-ring is useless if it is not readily available or is difficult to install without damage.
Consider the practical realities of your supply chain and maintenance procedures when making your final selection.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your application's primary goal to guide your final decision.
- If your primary focus is high reliability in a critical system: Prioritize material selection based on a thorough analysis of chemical, thermal, and pressure demands, and always consult manufacturer data.
- If your primary focus is a general-purpose, low-cost application: Standard materials like Nitrile (Buna-N) are often sufficient, but always perform a basic check for media and temperature compatibility.
- If your primary focus is performance in an extreme environment: Focus on specialty elastomers (like FKM, FFKM) or encapsulated O-rings, and be prepared for higher costs and potentially longer lead times.
Ultimately, a methodical approach that prioritizes understanding your system's needs is the key to ensuring sealing integrity.
Summary Table:
| Key Consideration | What to Evaluate | Common Options/Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Material Compatibility | Chemical media, temperature range | Nitrile (Buna-N), Viton (FKM), Silicone (VMQ), EPDM |
| Application Environment | Pressure, dynamic/static use, speed | Affects durometer, need for back-up rings, wear resistance |
| Size & Fit | Gland dimensions, squeeze, stretch | Inside Diameter (ID), Cross-Section (CS), optimal compression |
| Performance vs. Cost | Required reliability vs. budget | Standard (Nitrile) vs. High-Performance (FFKM) materials |
Ensure Peak Performance with Precision O-Rings from KINTEK
Choosing the right O-ring is critical for the reliability and longevity of your equipment. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE seals and components tailored to withstand the most demanding environments—from semiconductor manufacturing and medical devices to laboratory and industrial applications.
Our expertise in custom fabrication means we can deliver O-rings that meet your exact specifications, whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders. We prioritize precision and material integrity to ensure every seal offers superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and durability.
Ready to solve your sealing challenges? Contact our experts today to discuss your application requirements and discover how KINTEK’s tailored solutions can enhance your system’s performance and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for sealing applications? | High-Performance Seals for Extreme Conditions
- What makes PTFE stand out among materials used in sealing technology? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the primary characteristics of PTFE seals? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Conditions
- How do FEP and PTFE encapsulated O-rings contribute to equipment longevity? Prevent Costly Downtime with Superior Seals
- Why are PTFE seals preferred over traditional rubber seals? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions



















