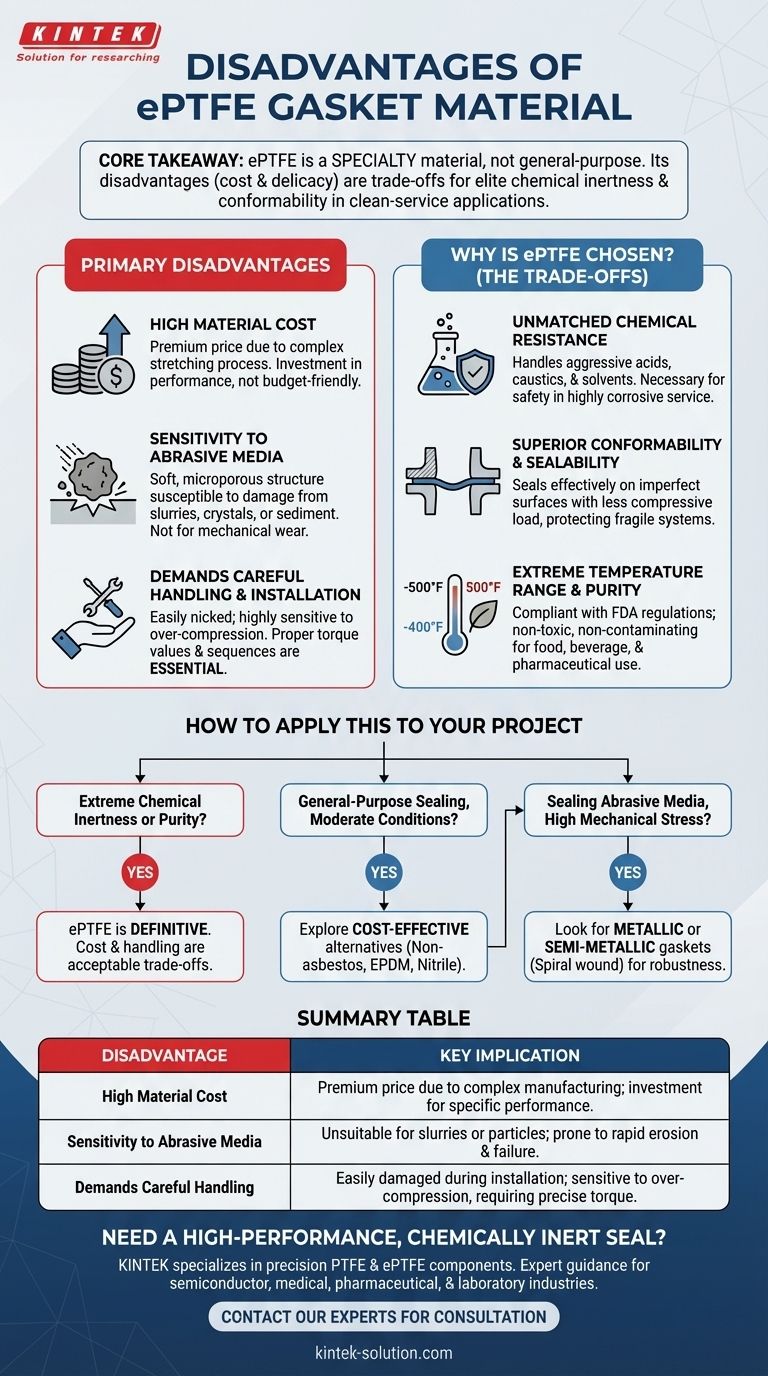
While an exceptional performer, expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) is not a universal solution for all sealing applications. Its primary disadvantages are a high material cost, an inability to handle abrasive media, and a low tolerance for improper handling or installation. These limitations stem directly from the material's unique microporous structure, which is also the source of its greatest strengths.
The core takeaway is that ePTFE is a specialty material, not a general-purpose one. Its disadvantages—cost and physical delicacy—are the direct trade-offs for its elite chemical inertness and conformability in demanding, clean-service applications.

A Deeper Look at the Primary Disadvantages
Understanding the "why" behind each limitation is critical for proper material selection and avoiding costly failures.
High Material Cost
The manufacturing process for ePTFE involves mechanically stretching standard PTFE to create a strong, microporous structure. This complex process is significantly more expensive than producing conventional elastomers or fiber-based gasket sheets.
As a result, ePTFE gaskets carry a premium price tag. They are an investment in performance, not a budget-friendly, all-purpose choice.
Sensitivity to Abrasive Media
The soft, porous nature of ePTFE that allows it to conform perfectly to flange irregularities also makes it highly susceptible to damage from hard particles.
Using an ePTFE gasket in a fluid system containing abrasives—such as slurries, crystals, or sediment—will lead to rapid erosion and premature seal failure. The material is simply not designed for mechanical wear.
Demands Careful Handling and Installation
ePTFE's softness requires a higher degree of care during installation compared to more robust materials. The gasket can be easily nicked or gouged by tools or rough flange surfaces, creating a potential leak path.
Furthermore, it is highly sensitive to over-compression. Applying excessive torque can crush the material's porous structure, destroying its ability to rebound and maintain a long-term seal. Proper torque values and sequences are not just recommended; they are essential.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Is ePTFE Still Chosen?
The disadvantages of ePTFE are often accepted because its advantages are impossible to achieve with other materials in certain critical applications.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is one of the most chemically inert substances known. It can handle a vast range of aggressive acids, caustics, and solvents that would instantly degrade rubber or other synthetic materials. For highly corrosive service, the high cost of ePTFE is a necessary investment in safety and reliability.
Superior Conformability and Sealability
The soft, pliable structure of ePTFE allows it to create an effective seal on surfaces that are not perfectly flat, including scratched, pitted, or slightly warped flanges. It requires less compressive load to seal, reducing stress on fragile piping systems like plastic or glass-lined steel.
Extreme Temperature Range and Purity
ePTFE maintains its properties across a vast temperature range, from cryogenic conditions (-400°F / -240°C) to high heat (500°F / 260°C).
Crucially, it is also compliant with FDA regulations, making it non-toxic and non-contaminating. This makes it an essential material in food, beverage, and pharmaceutical manufacturing where product purity is paramount.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Use these guidelines to determine if ePTFE is the right choice or if an alternative is more suitable.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical inertness or purity: ePTFE is the definitive choice, and its cost and handling requirements are an acceptable trade-off for its performance.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose sealing in moderate conditions: Explore more cost-effective materials like non-asbestos composites or specific elastomers (EPDM, Nitrile) that are better suited for the application.
- If your primary focus is sealing abrasive media or handling high mechanical stress: You should look toward metallic or semi-metallic gaskets (like spiral wound gaskets) designed for mechanical robustness.
Choosing the correct gasket is about matching the material's specific strengths to the unique demands of the application.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Implication |
|---|---|
| High Material Cost | Premium price due to complex manufacturing; an investment for specific performance needs. |
| Sensitivity to Abrasive Media | Unsuitable for slurries or particles; prone to rapid erosion and failure. |
| Demands Careful Handling | Easily damaged during installation; sensitive to over-compression, requiring precise torque. |
Need a High-Performance, Chemically Inert Seal?
While ePTFE has limitations, its strengths in chemical resistance, purity, and conformability are unmatched for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, pharmaceutical, and laboratory industries.
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE and ePTFE components. We provide expert guidance to help you select or custom-fabricate the perfect seal for your specific service conditions—from prototypes to high-volume production.
Let's ensure your application's safety and reliability. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components
- How does PTFE compare to other low-friction plastics like UHMW-PE and Nylon? A Guide to Material Selection
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications



















