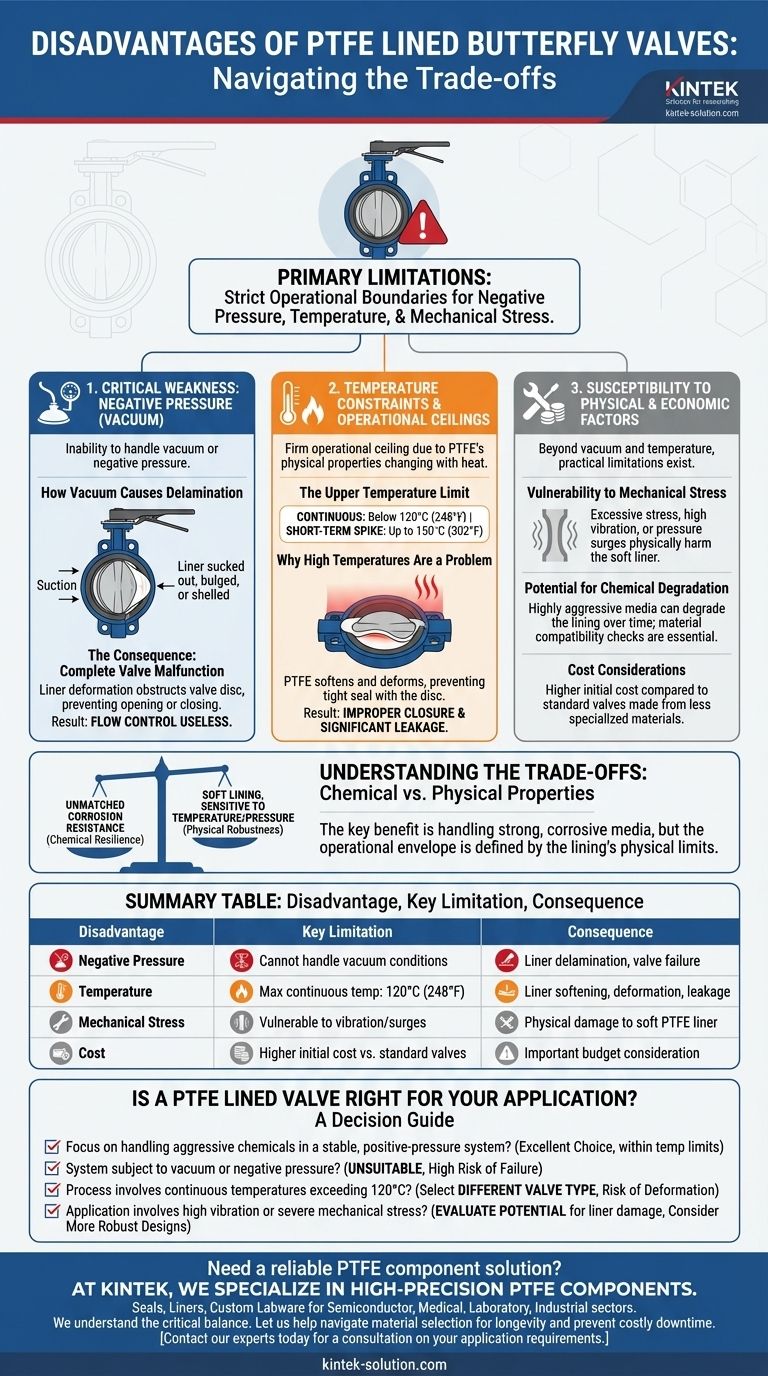
The primary disadvantages of PTFE lined butterfly valves are their strict operational limitations regarding negative pressure (vacuum), temperature, and mechanical stress. These valves offer exceptional chemical resistance, but failing to operate within their specific physical boundaries can lead to premature failure, liner damage, and leakage.
While unmatched for handling corrosive media, the effectiveness of a PTFE lined butterfly valve is entirely dependent on maintaining stable system conditions. Its key weaknesses—vulnerability to vacuum and limited temperature tolerance—are not design flaws but inherent trade-offs for its chemical inertness.

The Critical Weakness: Negative Pressure
One of the most significant limitations of PTFE lined valves is their inability to handle vacuum or negative pressure conditions within a pipeline.
How Vacuum Causes Delamination
Negative pressure creates a suction effect inside the valve body. This force can pull the soft PTFE liner away from the rigid inner wall of the valve, causing it to be sucked out, bulged, or shelled.
The Consequence: Complete Valve Malfunction
Once the liner has delaminated or deformed, it obstructs the movement of the valve disc. This prevents the valve from opening or closing properly, leading to a complete functional failure and rendering the flow control useless.
Understanding the Temperature Constraints
PTFE's physical properties change significantly with temperature, creating a firm operational ceiling that cannot be ignored.
The Upper Temperature Limit
For long-term, continuous operation, the media temperature should be kept below 120°C (248°F). While the valve can tolerate brief, short-term spikes up to 150°C (302°F), sustained exposure at this level is damaging.
Why High Temperatures Are a Problem
At elevated temperatures, the PTFE material begins to soften and deform. This plastic deformation prevents the liner from creating a tight seal with the disc, resulting in improper closure and significant leakage.
Susceptibility to Physical and Economic Factors
Beyond vacuum and temperature, these valves have other practical limitations that influence their suitability for a given application.
Vulnerability to Mechanical Stress
The PTFE liner can be damaged by excessive mechanical stress. This includes high-vibration environments or sudden, excessive pressure surges that can physically harm the soft lining material.
Potential for Chemical Degradation
Although PTFE has excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, certain highly aggressive or corrosive media can still degrade the lining over time. This makes material compatibility checks essential for specialized applications.
Cost Considerations
Compared to standard valves made from less specialized materials, PTFE lined butterfly valves can be more expensive. This initial cost must be weighed against their performance benefits in corrosive environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Chemical vs. Physical Properties
The decision to use a PTFE lined valve is a classic engineering trade-off between chemical resilience and physical robustness.
The Primary Benefit: Unmatched Corrosion Resistance
Engineers choose PTFE lined valves for one main reason: their outstanding ability to handle strong, corrosive media. For many applications in chemical plants, this chemical inertness is non-negotiable for ensuring safety and system longevity.
The Inherent Limitation: A Soft Lining
The very properties that make PTFE chemically inert also make it physically soft and sensitive to temperature and pressure changes. Unlike a solid metal valve, a lined valve has an operational envelope defined by the physical limits of its lining, not its structural body. Respecting these limits is paramount.
Is a PTFE Lined Valve Right for Your Application?
Your final decision should be based on a clear understanding of your system's operating conditions.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals in a stable, positive-pressure system: This valve is an excellent choice, provided you operate strictly within its temperature limits.
- If your system is subject to vacuum conditions or negative pressure: This valve is unsuitable and presents a high risk of failure through liner delamination.
- If your process involves continuous temperatures exceeding 120°C (248°F): You must select a different valve type to avoid liner deformation and guaranteed leakage.
- If your application involves high vibration or severe mechanical stress: Carefully evaluate the potential for liner damage and consider more robust valve designs.
Understanding these operational boundaries is the key to successfully leveraging the powerful chemical resistance of PTFE lined valves.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Limitation | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Negative Pressure | Cannot handle vacuum conditions | Liner delamination, valve failure |
| Temperature | Max continuous temp: 120°C (248°F) | Liner softening, deformation, leakage |
| Mechanical Stress | Vulnerable to vibration/surges | Physical damage to the soft PTFE liner |
| Cost | Higher initial cost vs. standard valves | Important budget consideration |
Need a reliable PTFE component solution that fits your specific operating conditions?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the critical balance between chemical resistance and physical performance.
Let us help you navigate material selection and deliver a custom-fabricated part, from prototype to high-volume production, that ensures longevity and prevents costly downtime.
Contact our experts today for a consultation on your application requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Can PTFE bushings operate without lubrication? Achieve maintenance-free performance in harsh environments.
- What is the recommended method for bonding PTFE to its support? Achieve a Permanent, High-Strength Bond
- What is the PH range and temperature tolerance of pure PTFE gaskets? Master Extreme Chemical and Thermal Sealing
- In which industries are PTFE tri clamp gaskets commonly used? Essential for Purity & Chemical Resistance
- Why are PTFE-coated O-rings particularly suitable for food processing applications? Ensure Ultimate Hygiene & Safety
- What are the key characteristics of PTFE oil seals? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- How do PTFE Lip Seals contribute to efficiency in industrial machinery? Boost Speed, Cut Costs & Reduce Downtime
- Why are glass-filled PTFE rods used in aerospace? Achieve Superior Strength & Wear Resistance



















