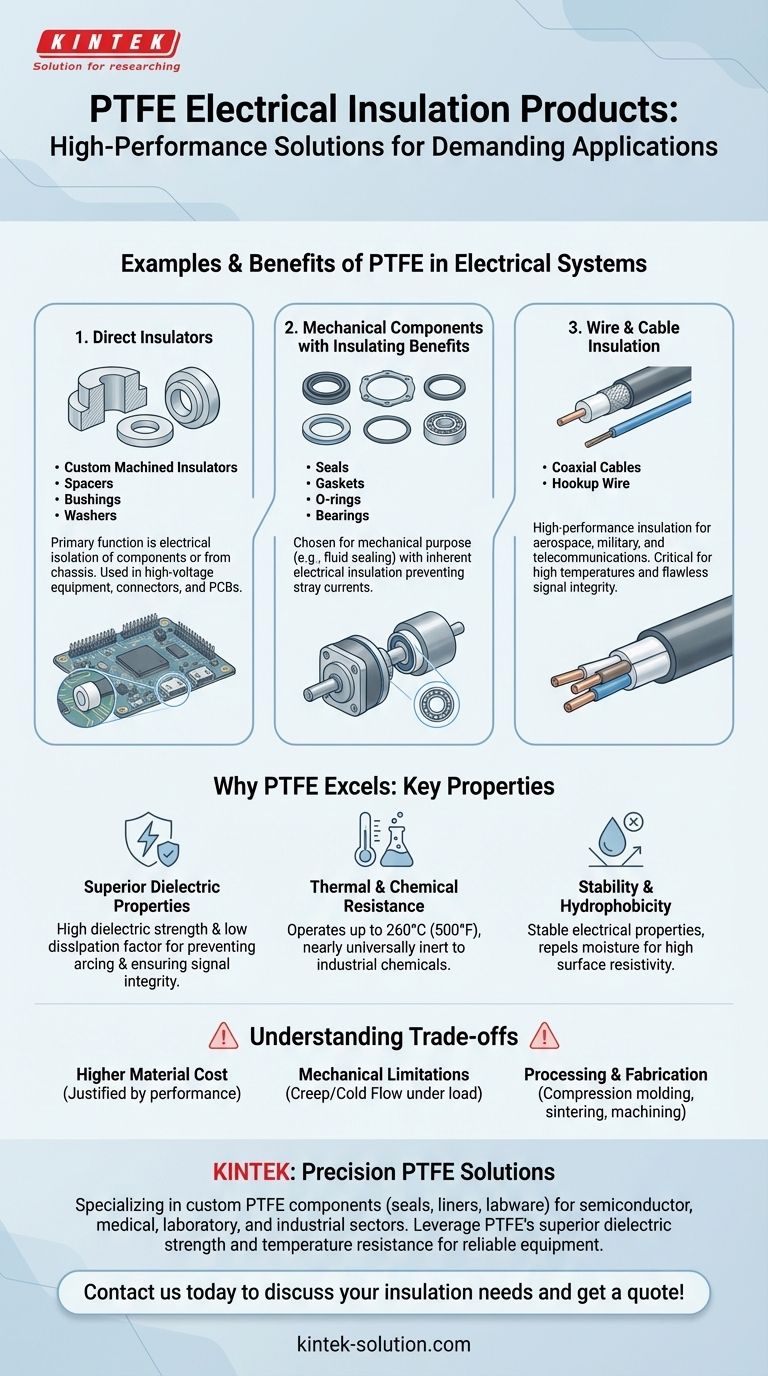
In short, common electrical insulation products made from PTFE include dedicated components like insulators, spacers, bushings, and washers. However, many other mechanical parts such as seals, gaskets, and bearings are also made from PTFE, leveraging its insulating properties as a critical secondary benefit in complex systems.
The core reason PTFE is chosen for electrical applications is not just its exceptional insulating capability, but its unique combination of high dielectric strength, extreme temperature tolerance, and chemical inertness, making it a premier material for the most demanding environments.

Why PTFE Excels as an Electrical Insulator
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance fluoropolymer with a set of properties that make it one of the best and most widely used electrical insulators available.
### Superior Dielectric Properties
PTFE has a very high dielectric strength, meaning it can withstand a strong electric field before breaking down. This is crucial for preventing electrical arcing.
It also has a very low dissipation factor, which means it absorbs very little energy from an alternating electric field. This makes it ideal for high-frequency applications where signal integrity is paramount.
### Stability Across Environments
PTFE's electrical properties remain remarkably stable across a wide range of temperatures and frequencies.
Furthermore, it is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water. This prevents moisture absorption, which is critical for maintaining high surface resistivity and ensuring insulation does not fail in humid conditions.
### Thermal and Chemical Resistance
PTFE can operate continuously at temperatures up to 260°C (500°F) without degrading its electrical or mechanical properties.
It is also nearly universally inert, resisting almost all industrial chemicals and solvents. This ensures its reliability in harsh operational environments where other insulators would fail.
Common Forms of PTFE Electrical Insulation
PTFE's versatility allows it to be formed into a wide array of components, serving both direct and indirect insulating roles.
### Direct Insulating Components
These are parts whose primary function is to electrically isolate components from each other or from a chassis.
Examples include custom machined insulators, spacers, washers, and bushings. These are often used in high-voltage equipment, connectors, and circuit board assemblies.
### Mechanical Components with Insulating Benefits
Many PTFE parts are chosen for a mechanical purpose, but their inherent electrical insulation is a vital secondary characteristic.
This includes seals, gaskets, O-rings, and bearings. In an electromechanical assembly, using a PTFE seal not only prevents fluid leaks but also stops stray electrical currents from passing through that junction.
### Wire and Cable Insulation
One of the most significant applications for PTFE is as a high-performance insulation for electrical wires and cables.
It is used extensively in aerospace, military, and telecommunications for applications like coaxial cables and hookup wire where high temperatures and flawless signal integrity are non-negotiable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE is an exceptional material, it's essential to understand its limitations to use it effectively.
### Higher Material Cost
High-performance, virgin PTFE is more expensive than many common insulating plastics. Specialized grades processed for even higher insulation needs can add to the cost, making it a choice for applications where performance justifies the investment.
### Mechanical Limitations
PTFE is a relatively soft material and is subject to creep, or "cold flow," under sustained compressive loads. This must be accounted for in mechanical designs to prevent the component from deforming over time.
### Processing and Fabrication
Unlike many thermoplastics, PTFE cannot be melt-processed or injection molded. It is typically shaped through compression molding followed by a heating process (sintering), or by machining it from stock shapes like rods and blocks. This can influence part complexity and production speed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE depends on the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency performance: Choose PTFE for components like coaxial connectors and circuit board substrates where its low, stable dielectric constant is essential.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature or chemical resistance: Use PTFE for insulators and seals in industrial sensors, chemical processing equipment, or downhole tools.
- If your primary focus is a combined mechanical and electrical role: Select PTFE for insulating bearings, gaskets, or valve seats in electromechanical devices to prevent both wear and electrical leakage.
Ultimately, PTFE is the definitive choice when an application demands reliable electrical insulation that will not compromise under thermal, chemical, or high-frequency stress.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Insulation Product Type | Common Examples | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Insulators | Insulators, Spacers, Bushings, Washers | Electrically isolate components |
| Mechanical Components | Seals, Gaskets, O-rings, Bearings | Provide mechanical function with insulating benefit |
| Wire & Cable | Coaxial cables, Hookup wire | Insulate conductors in high-temp/high-frequency environments |
Need a reliable, high-performance PTFE insulator for your project?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We leverage PTFE's superior dielectric strength and temperature resistance to create parts that ensure your equipment's reliability in the most demanding environments.
From prototyping to high-volume production, we deliver the quality and performance your application requires. Contact us today to discuss your specific electrical insulation needs and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE considered a significant discovery? A Material That Revolutionized Industry
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries



















