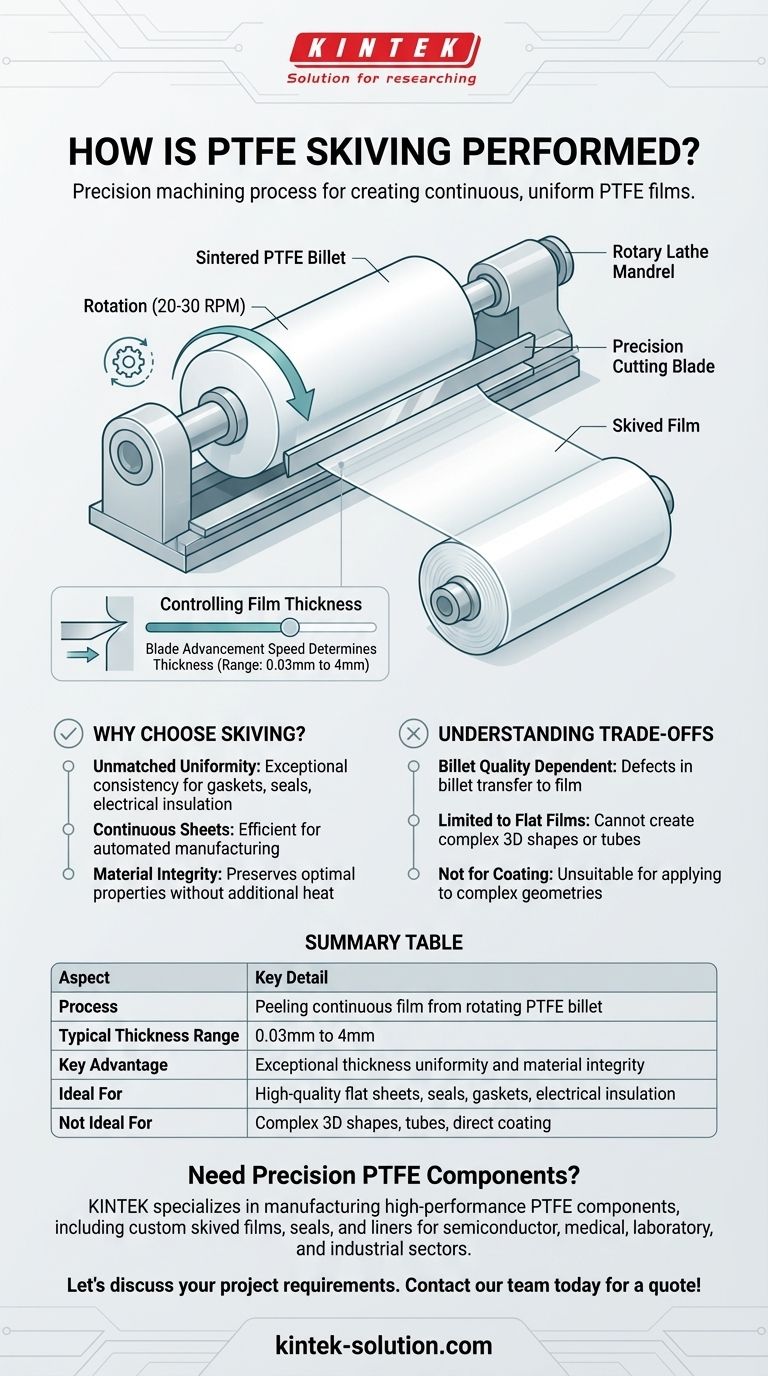
At its core, PTFE skiving is a precision machining process used to create thin, continuous films of PTFE material. It involves mounting a solid, cylindrical block of sintered PTFE, known as a billet, onto a specialized lathe and using a sharp, precisely controlled blade to peel off a layer of material in a continuous sheet, much like peeling an apple in one long strip.
The central principle of skiving is mechanical precision. By carefully controlling the rotation of the PTFE billet and the advancement speed of a cutting blade, manufacturers can produce exceptionally uniform films of a specific thickness for a wide range of industrial applications.
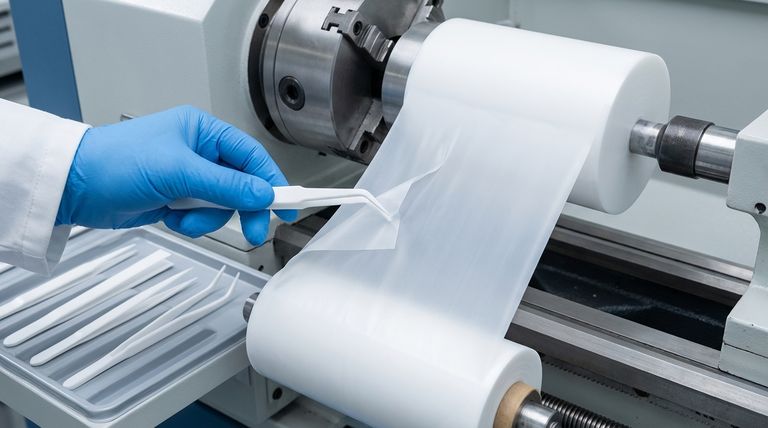

The Mechanics of the Skiving Process
Understanding the skiving process is best done by breaking it down into its core mechanical steps. Each stage is critical for achieving the final film's required specifications.
Step 1: Preparing the PTFE Billet
The process begins with a high-quality, cylindrical PTFE billet. This billet is created by sintering PTFE powder under heat and pressure to form a solid, void-free block. The quality of this initial billet is paramount, as any imperfections will be transferred to the final skived film.
Step 2: Mounting and Rotation
The billet is securely mounted onto the mandrel of a rotary lathe. The lathe then begins to rotate the billet at a slow and highly consistent speed, typically between 20 and 30 RPM. This steady rotation is crucial for ensuring a uniform cut.
Step 3: The Precision Cutting Blade
A long, extremely sharp blade is positioned parallel to the axis of the billet. This blade is the cutting instrument that will peel away the film. Its angle, sharpness, and stability are critical factors that influence the surface finish and quality of the PTFE sheet.
Step 4: Controlling Film Thickness
The final thickness of the film is determined by the advancement speed of the blade relative to the rotating billet. As the billet spins, the blade is slowly and precisely advanced into it. A faster advance creates a thicker film, while a slower advance produces a thinner one. This method allows for the production of films with thicknesses ranging from 0.03mm to 4mm.
Why Choose Skiving for PTFE Films?
Skiving is not the only way to form PTFE, but it is the preferred method for producing high-quality, thin films and sheets for specific reasons.
Unmatched Uniformity
The skiving process excels at producing films with exceptional thickness consistency across their entire length and width. This level of uniformity is difficult to achieve with other methods like extrusion or coating, making it ideal for applications in gaskets, seals, and electrical insulation.
Production of Continuous Sheets
Because the film is peeled from a large billet, skiving can produce very long, continuous rolls of PTFE. This is highly efficient for automated manufacturing processes where long, uninterrupted lengths of material are required.
Material Integrity
Skiving is a purely mechanical process that does not subject the PTFE to additional heat cycles after the initial sintering of the billet. This preserves the material's optimal molecular structure and superior properties, such as its chemical inertness and low coefficient of friction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the skiving process has specific requirements and is not the ideal solution for every application.
The Billet is the Bottleneck
The final film quality is entirely dependent on the quality of the initial billet. Any internal stresses, voids, or contaminants within the billet will result in defects in the final product. This necessitates a highly controlled and often expensive billet manufacturing process.
Limited to Flat Films
By its very nature, skiving can only produce flat films and sheets. It cannot be used to create complex three-dimensional shapes, tubes, or profiles. For those applications, methods like extrusion or molding are required.
Comparison to Other Methods
For applications like creating a non-stick layer inside a pipe, processes like spray coating or inserting an extruded liner are more practical. Skiving is specialized for producing the raw film stock itself, not for applying it to complex geometries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct PTFE manufacturing process depends entirely on the final form and function you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is creating a large, continuous, and highly uniform flat film or sheet: Skiving is the superior and most common manufacturing method.
- If your primary focus is producing tubing, rods, or simple, continuous profiles: PTFE extrusion is the standard and most efficient process.
- If your primary focus is coating the interior of a complex part or container: Methods like spray coating or rotational lining are far more suitable than using a skived film.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental mechanics of skiving empowers you to specify the right material form for your project's success.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | Peeling a continuous film from a rotating PTFE billet with a precision blade. |
| Typical Thickness Range | 0.03mm to 4mm |
| Key Advantage | Exceptional thickness uniformity and material integrity. |
| Ideal For | High-quality flat sheets for seals, gaskets, and electrical insulation. |
| Not Ideal For | Complex 3D shapes, tubes, or direct coating of parts. |
Need Precision PTFE Components?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom skived films, seals, liners, and labware. Our expertise in precision production ensures the material integrity and uniformity your application demands.
We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors with custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our team today for a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















