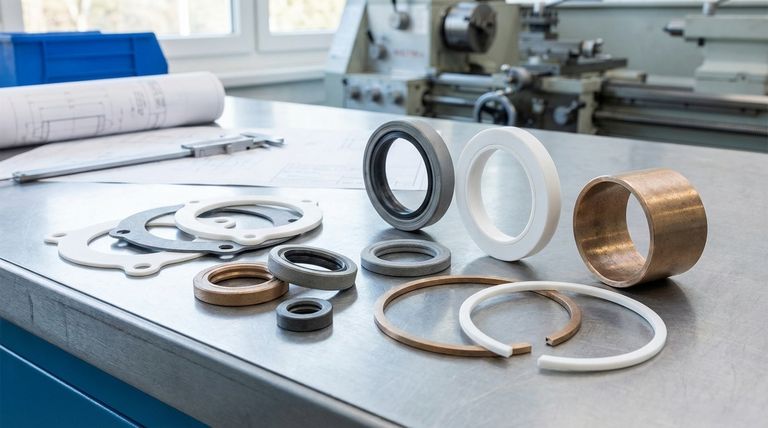
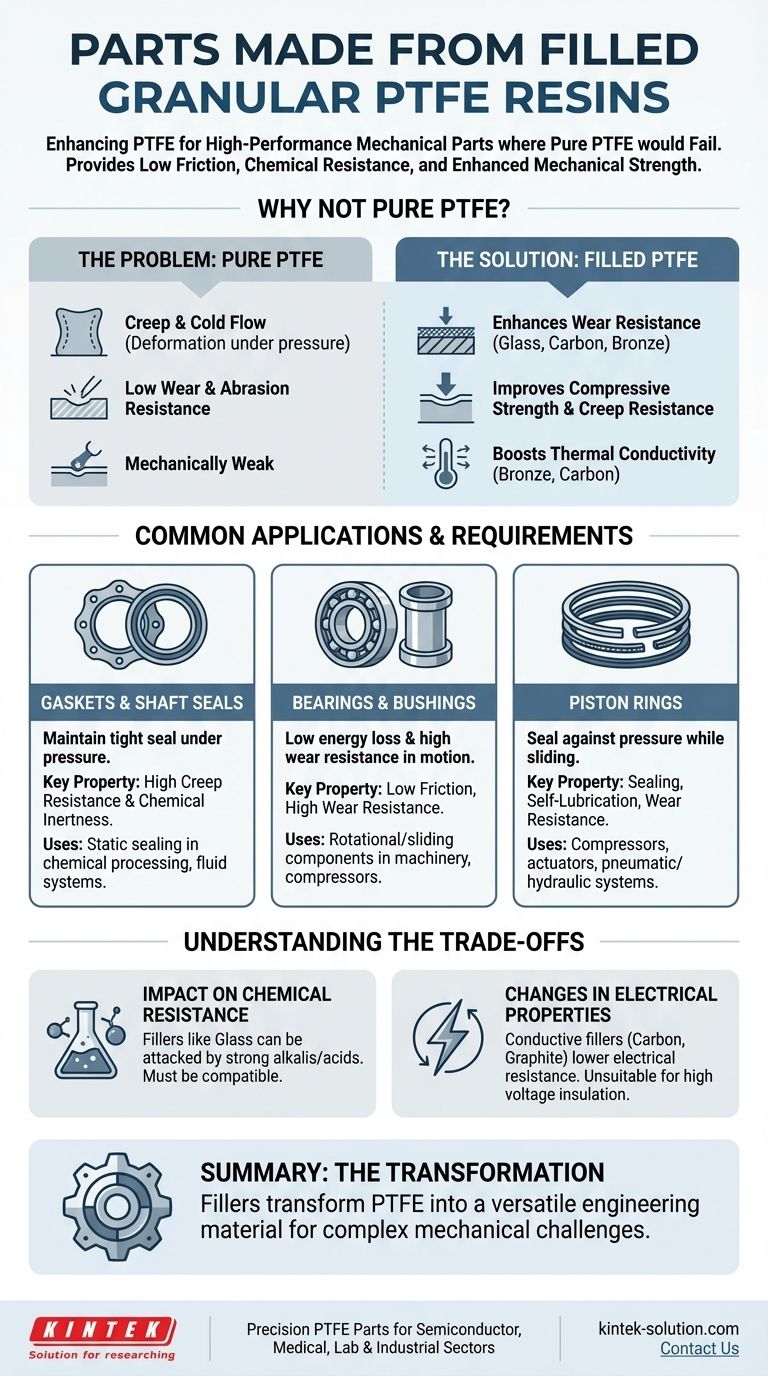
In short, filled granular PTFE resins are used to manufacture high-performance mechanical components where pure PTFE would fail, including gaskets, shaft seals, bearings, and piston rings. These parts are critical in demanding industrial environments that require a combination of low friction, chemical resistance, and enhanced mechanical strength.
The core principle is simple: while pure PTFE offers exceptional lubricity and chemical inertness, it is mechanically weak. Adding fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze fundamentally enhances properties like wear resistance and compressive strength, making PTFE suitable for dynamic, load-bearing applications.

Why Not Just Use Pure PTFE?
To understand the value of filled PTFE, we must first recognize the limitations of the raw material. Pure, or "virgin," PTFE is an exceptional polymer, but it has two key weaknesses in mechanical applications.
The Problem of "Creep" or Cold Flow
Pure PTFE is mechanically soft and susceptible to creep, also known as cold flow. Under sustained pressure, especially at elevated temperatures, the material will slowly deform and lose its original shape.
This makes it unsuitable for components like gaskets or seals that must maintain a constant, tight fit under compression to prevent leaks.
Low Wear Resistance
While PTFE has an incredibly low coefficient of friction, it has poor wear and abrasion resistance. In dynamic applications with moving surfaces, such as a bearing or piston ring, pure PTFE would wear away very quickly, leading to premature component failure.
How Fillers Transform PTFE's Performance
Introducing a filler material into the PTFE matrix directly counteracts its inherent weaknesses. The specific filler is chosen to target a desired improvement, creating a composite material tailored for a specific job.
Enhancing Wear Resistance
Fillers like glass fiber, carbon, and bronze act as a reinforcing structure within the PTFE. They create a harder, more durable surface that can withstand friction and abrasion far better than virgin PTFE.
This is the single most important enhancement for dynamic parts like bearings and piston rings, dramatically extending their service life.
Improving Compressive Strength and Creep Resistance
The solid particles of the filler material provide structural support, making the composite much more resistant to deformation under load. This reduces creep significantly.
This property is essential for static seals and gaskets, ensuring they maintain their sealing pressure over long periods without needing to be re-tightened.
Boosting Thermal Conductivity
Pure PTFE is an excellent thermal insulator. However, in high-speed moving parts, friction generates heat that needs to be dissipated.
Fillers like bronze and carbon are thermally conductive, allowing them to draw heat away from the wearing surface. This prevents overheating and material degradation, which is critical for high-performance seals and bearings.
Common Applications and Their Requirements
Each of the primary parts made from filled PTFE leverages a specific set of these enhanced properties.
Gaskets and Shaft Seals
For gaskets and seals, the primary requirement is maintaining a tight seal under constant pressure. The improved creep resistance of filled PTFE is paramount here, preventing leaks over time. Its chemical inertness also ensures it won't degrade when exposed to aggressive fluids.
Bearings and Bushings
Bearings require a material with an extremely low coefficient of friction to reduce energy loss and high wear resistance to survive constant rotational or sliding motion. Filled PTFE provides a self-lubricating surface that is also tough enough for significant mechanical loads.
Piston Rings
Piston rings in compressors and actuators perform a dual role: they must seal against pressure while enduring constant sliding motion. Filled PTFE is ideal due to its combination of sealing capability, self-lubrication, and excellent wear resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Adding fillers is not without compromises. It is crucial to understand that enhancing one property may alter another.
Impact on Chemical Resistance
While PTFE itself is nearly universally inert, some fillers are not. For example, glass fiber-filled PTFE can be attacked by strong alkalis or hydrofluoric acid. The choice of filler must be compatible with the application's chemical environment.
Changes in Electrical Properties
Virgin PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator. However, adding conductive fillers like carbon or graphite will drastically lower its electrical resistance. This can be a benefit for anti-static applications but makes it unsuitable for high-voltage insulation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct material grade depends entirely on the primary demand of your application.
- If your primary focus is dynamic wear resistance: Opt for PTFE grades filled with glass, carbon, or bronze, which are ideal for bearings, bushings, and piston rings.
- If your primary focus is static sealing under high pressure: Choose a grade with fillers that offer the best creep resistance to ensure long-term gasket and seal integrity.
- If your primary focus is chemical compatibility in an aggressive environment: Carefully select a filler (or use virgin PTFE if mechanical loads are low) that will not react with the process media.
Ultimately, understanding the role of fillers transforms PTFE from a specialized polymer into a versatile engineering material capable of solving complex mechanical challenges.
Summary Table:
| Part Type | Key Enhanced Properties | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Gaskets & Seals | Creep resistance, chemical inertness | Static sealing in chemical processing, fluid systems |
| Bearings & Bushings | Wear resistance, low friction | Rotational/sliding components in machinery, compressors |
| Piston Rings | Wear resistance, self-lubrication, sealing | Compressors, actuators, pneumatic/hydraulic systems |
Need a custom PTFE component that stands up to your toughest challenges? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE parts—including seals, liners, labware, and more—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, we deliver materials engineered for superior performance. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE and Nitrile Diaphragm Pump Components for Demanding Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How does the non-stick surface of Teflon sheets benefit heat transfer projects? Achieve Flawless, Professional Results
- What special considerations are needed when machining PTFE? Master High-Precision Fabrication
- What is PTFE and what makes it suitable for gaskets? The Ultimate Guide to High-Performance Sealing
- What does the leakage rate indicate about PTFE gaskets? Understanding the Sealing Performance Trade-off
- What construction industry uses are there for ePTFE sheets? High-Performance Solutions for Durability
- What are the recommended tools for CNC machining Teflon? Achieve Clean, Precise Cuts
- Describe the PTFE injection molding process and its optimization strategies. Master Complex PTFE Part Production
- Which type of PTFE gasket is better for high-pressure and high-temperature applications? Discover the Best Solution for Demanding Seals



















