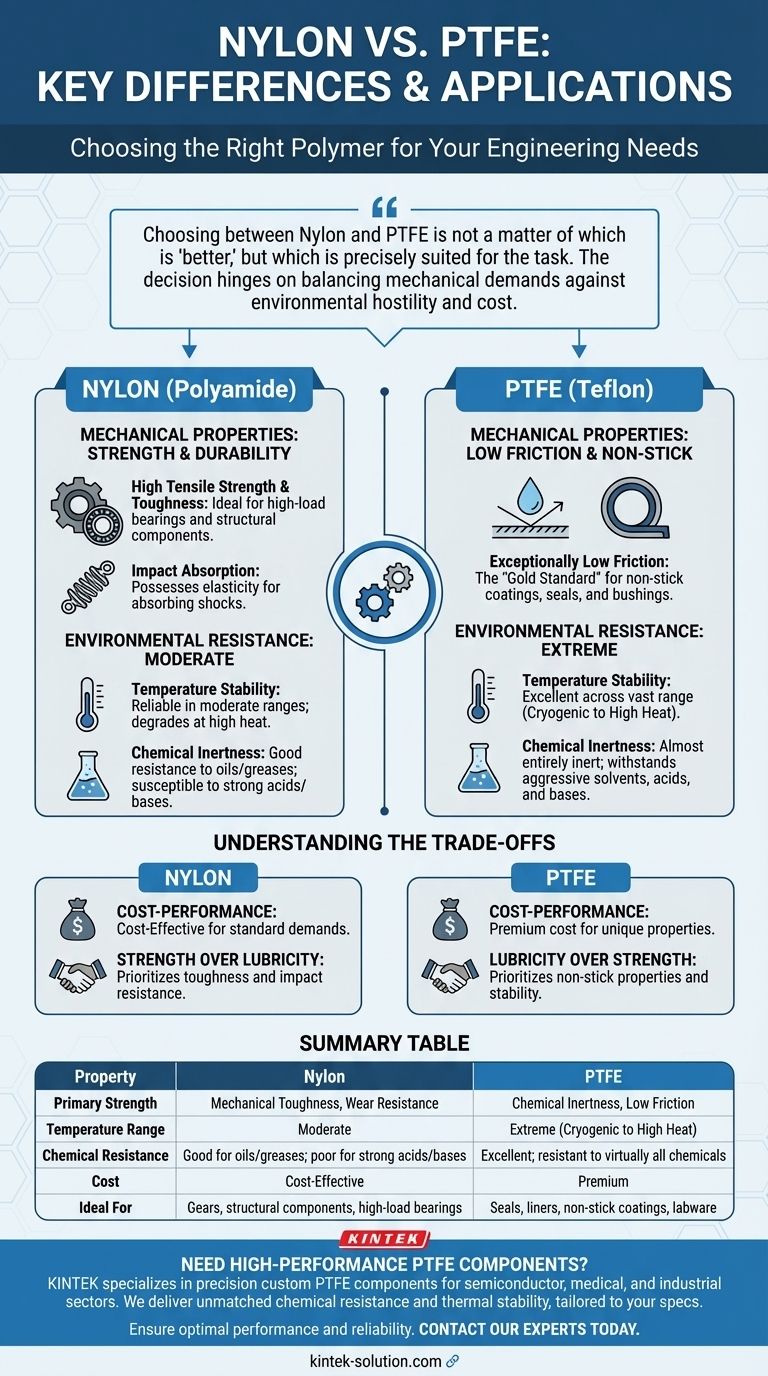
The primary difference lies in their core strengths: Nylon is chosen for its mechanical toughness and cost-effectiveness, while PTFE is selected for its extreme chemical resistance, non-stick surface, and ability to handle a wide range of temperatures. While both are versatile polymers, they solve fundamentally different engineering problems.
Choosing between Nylon and PTFE is not a matter of which is "better," but which is precisely suited for the task. The decision hinges on balancing mechanical demands against environmental hostility and cost.

Comparing Core Mechanical Properties
Your application's physical demands are the first point of evaluation. The materials offer distinct advantages in how they handle stress and friction.
Nylon: The Case for Strength and Durability
Nylon is a go-to material for applications requiring high tensile strength and resistance to wear and abrasion. It possesses a degree of elasticity that allows it to absorb impacts.
This makes it ideal for gears, structural components, and high-load bearings where toughness is paramount.
PTFE: The Gold Standard for Low Friction
PTFE is defined by its exceptionally low coefficient of friction, giving it its characteristic non-stick, or lubricious, surface. It is one of the most slippery solid materials known.
This property is critical for applications like non-stick coatings, chemically resistant seals, and low-friction bushings where smooth, effortless movement is the primary goal.
Evaluating Environmental Resistance
The operating environment—specifically temperature and chemical exposure—is often the deciding factor between these two materials.
Temperature Stability
Nylon performs reliably in moderate temperature environments but can degrade or lose its structural integrity at higher temperatures.
PTFE, in contrast, excels in extreme conditions. It maintains its properties across a vast temperature range, from cryogenic levels up to very high heat, without becoming brittle or melting.
Chemical Inertness
While Nylon offers decent resistance to some oils and greases, it can be susceptible to strong acids and bases.
PTFE is almost entirely chemically inert. It can withstand exposure to the most aggressive solvents, acids, and bases, making it essential for use in corrosive chemical processing and laboratory equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. Understanding the inherent limitations of both Nylon and PTFE is critical for avoiding costly design failures.
The Cost-Performance Equation
Nylon is significantly more affordable than PTFE. Its lower cost and excellent mechanical properties make it a highly efficient choice for cost-sensitive projects that do not involve extreme temperatures or harsh chemicals.
PTFE's superior performance characteristics come at a premium. Its specialized manufacturing process and raw material costs make it a more expensive option, reserved for applications where its unique properties are non-negotiable.
The Strength vs. Lubricity Compromise
Choosing Nylon means prioritizing mechanical strength and impact resistance over surface lubricity. You gain toughness at the expense of a low-friction surface.
Opting for PTFE means prioritizing its non-stick properties and environmental stability. You gain extreme resistance and low friction but sacrifice the high tensile strength and abrasion resistance found in Nylon.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection should be a direct reflection of your project's most critical requirement.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability and cost-efficiency: Choose Nylon for its proven strength, wear resistance, and affordability in standard operating conditions.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme environments: Choose PTFE for its unmatched thermal stability and resistance to virtually all chemicals.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and creating a non-stick surface: Choose PTFE for its exceptionally low coefficient of friction, which is essential for seals, coatings, and slide bearings.
Ultimately, aligning the material's inherent strengths with your application's specific demands ensures optimal performance and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Property | Nylon | PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Strength | Mechanical Toughness, Wear Resistance | Chemical Inertness, Low Friction |
| Temperature Range | Moderate | Extreme (Cryogenic to High Heat) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good for oils/greases; poor for strong acids/bases | Excellent; resistant to virtually all chemicals |
| Cost | Cost-Effective | Premium |
| Ideal For | Gears, structural components, high-load bearings | Seals, liners, non-stick coatings, labware |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
Selecting the right material is critical for your project's success. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We deliver the unmatched chemical resistance and thermal stability of PTFE, tailored to your exact specifications from prototype to high-volume production.
Ensure optimal performance and reliability. Contact our experts today for a consultation on your specific application needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some key properties of PTFE? Discover the High-Performance Polymer for Extreme Applications
- How does RPTFE differ from PTFE in terms of reactivity? A Guide to Chemical Compatibility
- How does PTFE interact with water and other liquids? Unmatched Hydrophobic & Chemical Inert Properties
- How does PTFE behave in terms of chemical inertness? Unmatched Resistance for Demanding Applications
- What are the uses of Teflon in personal care products? Enhance Makeup Longevity & Heat Protection
- How is PTFE laminated fabric manufactured? A Guide to High-Performance Material Engineering
- How is PTFE used in lubrication applications? Achieve Superior Friction Reduction
- Why is Teflon suitable for waterproof makeup products? Unlock the Secret to Smudge-Proof Wear



















