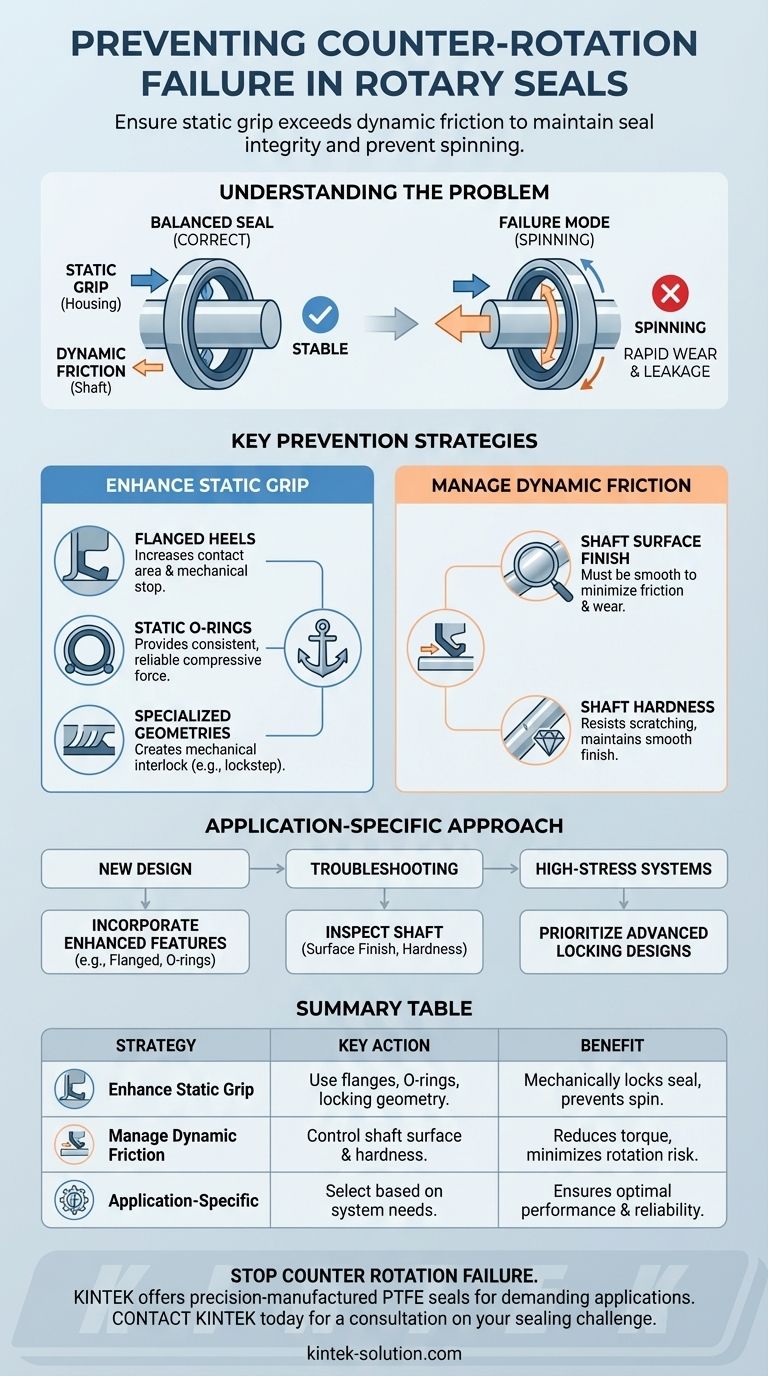
To prevent counter rotation failure, you must ensure the static part of the rotary seal maintains a stronger grip on the housing than the dynamic lip has on the rotating shaft. This is achieved through specific design features that mechanically lock the seal in place and by carefully controlling the surface properties of the shaft to manage friction.
The core principle is simple: the friction holding the seal stationary must always be greater than the friction acting on it from the moving component. When the dynamic friction on the shaft overcomes the static friction in the housing, the seal breaks loose and fails.

Understanding Counter Rotation Failure
A rotary seal is designed to function with a precise balance of forces. Counter rotation occurs when this balance is lost, causing the entire seal to spin with the shaft, leading to rapid wear and leakage.
The Intended Function of a Seal
A standard lip seal has two primary contact points. The static lip (or heel) is designed to press firmly against the stationary housing, creating a fixed anchor point. The dynamic lip is designed to ride on a thin film of lubricant on the rotating shaft.
How the Failure Occurs
Counter rotation failure happens when the friction between the dynamic lip and the rotating shaft becomes excessively high. This high friction creates a rotational torque that overcomes the holding force of the static lip against the housing, causing the entire seal to spin.
The Consequences of Spinning
Once a seal begins to counter-rotate, it wears rapidly against the housing, which is not designed for dynamic contact. This generates excessive heat, degrades the seal material, and ultimately leads to a complete loss of sealing capability.
Key Prevention Strategies
Preventing this failure mode involves a two-pronged approach: maximizing the seal's grip on the housing while minimizing the frictional forces from the shaft.
1. Enhancing Static Grip with Design Features
The most robust solutions involve designing the seal itself to mechanically resist rotation.
Flanged Heels
A flanged heel adds a "foot" to the outer diameter of the seal. This feature increases the contact area and provides a mechanical stop against the housing bore, significantly increasing its resistance to rotational forces.
Static O-Rings
Some seal designs incorporate a separate O-ring into the static heel. The O-ring provides a highly reliable and consistent compressive force against the housing, ensuring a very strong static grip that is less sensitive to variations in the housing's surface.
Specialized Geometries (e.g., Lockstep)
Proprietary designs often feature unique geometries on the seal's outer diameter. These features, like ridges or steps, are designed to create a mechanical interlock with the housing bore, providing the highest level of security against rotation.
2. Managing Dynamic Friction at the Shaft
Controlling the interface between the seal and the shaft is equally critical. The goal is to ensure the dynamic lip can move freely without sticking or generating excessive drag.
Shaft Surface Finish
The surface of the shaft must be smooth enough to minimize friction and wear on the dynamic lip. A rough surface will act like sandpaper, increasing drag and the likelihood of the seal sticking and rotating. Adhering to specified surface finish recommendations is non-negotiable.
Shaft Hardness
A sufficiently hard shaft surface is essential to maintain its smooth finish over the seal's service life. A soft shaft can be easily scratched or worn, creating a rougher surface that dramatically increases dynamic friction and invites counter rotation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your strategy depends on whether you are designing a new system or troubleshooting an existing one.
- If your primary focus is designing new equipment: Incorporate seals with enhanced design features like flanged heels or static O-rings from the start for maximum reliability.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting an existing failure: Begin by inspecting the shaft's surface finish and hardness, as deviations from the specification are a common and correctable cause.
- If you are dealing with high-speed or high-pressure systems: Prioritize advanced designs with mechanical locking features to provide the highest security against the extreme forces present in these applications.
Ultimately, ensuring reliable seal performance comes down to intentionally designing for the correct balance of static and dynamic forces.
Summary Table:
| Prevention Strategy | Key Action | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Enhance Static Grip | Use seals with flanged heels, static O-rings, or locking geometries. | Mechanically locks the seal in the housing, preventing spin. |
| Manage Dynamic Friction | Control shaft surface finish (smooth) and hardness (sufficient). | Reduces torque on the seal lip, minimizing risk of rotation. |
| Application-Specific Design | Select seals based on speed, pressure, and whether designing new or troubleshooting. | Ensures optimal performance and reliability for your specific system. |
Stop counter rotation failure before it stops your operation.
At KINTEK, we understand that unreliable seals lead to unplanned downtime, costly repairs, and production losses. Our precision-manufactured PTFE seals and components are engineered for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We prioritize designs that enhance static grip and compatibility, helping you maintain the critical force balance that prevents failure.
Whether you need a custom prototype or a high-volume order, our expertise ensures you get a sealing solution built for reliability.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation on your specific sealing challenge.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications



















